|
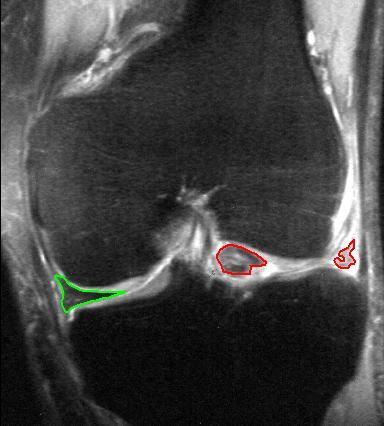
Meniscus Tear
A tear of a meniscus is a rupturing of one or more of the fibrocartilage strips in the knee called menisci. When doctors and patients refer to "torn cartilage" in the knee, they actually may be referring to an injury to a meniscus at the top of one of the tibiae. Menisci can be torn during innocuous activities such as walking or squatting. They can also be torn by traumatic force encountered in sports or other forms of physical exertion. The traumatic action is most often a twisting movement at the knee while the leg is bent. In older adults, the meniscus can be damaged following prolonged 'wear and tear'. Especially acute injuries (typically in younger, more active patients) can lead to displaced tears which can cause mechanical symptoms such as clicking, catching, or locking during motion of the joint. The joint will be in pain when in use, but when there is no load, the pain goes away. A tear of the medial meniscus can occur as part of the unhappy triad, together with a tear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct", "straight") and παιδίον ''paidion'' ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varus Deformity
Varus may refer to: * Var River or Varus, a river in France * Stura di Lanzo or Varus, a river in Italy * Varus deformity, a medical term for the inward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint ** Coxa vara, affecting the hip ** Genu varum, affecting the knee ** Hallux varus, affecting the big toe ** Cubitus varus, affecting the elbow ** Club foot (talipes equinovarus), affecting the heel People with the name * Publius Attius Varus (died 45 BC), Roman governor of Africa * Publius Quinctilius Varus (46 BC–AD 9), politician and general of the Roman Empire * Publius Quinctilius Varus the Younger (c. AD 1–27), son of Publius Quinctilius Varus * Marcus Plancius Varus (1st century AD), politician of the Roman Empire * Gaius Plancius Varus (1st–2nd century AD), son of Marcus Plancius Varus and politician of the Roman Empire * Titus Clodius Vibius Varus, Roman consul, 160 AD * Titus Vibius Varus, Roman consul, 134 AD * Titus Vibius Varus, Roman suffect consul, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extension (kinesiology)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurray Test
The McMurray test, also known as the McMurray circumduction test is used to evaluate individuals for tears in the meniscus of the knee. A tear in the meniscus may cause a pedunculated tag of the meniscus which may become jammed between the joint surfaces. To perform the test, the knee is held by one hand, which is placed along the joint line, and flexed to complete flexion while the foot is held by the sole (of the foot) with the other hand. The examiner then rotates the leg internally while extending the knee to 90 degrees of flexion. If a "thud" or "click" is felt along with pain, this constitutes a "positive McMurray test" for a tear in the posterior portion of the lateral meniscus. Likewise, external rotation of the leg can be applied to test the posterior portion of the medial meniscus. The McMurray test is named after Thomas Porter McMurray, a British orthopedic surgeon Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases and their treatment—the ''science'' of medicine—and also a decent competence in its applied practice—the art or ''craft'' of medicine. Both the role of the physician and the meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Collateral Ligament
The lateral collateral ligament (LCL, long external lateral ligament or fibular collateral ligament) is a ligament located on the lateral (outer) side of the knee, and thus belongs to the extrinsic knee ligaments and posterolateral corner of the knee. Structure Rounded, more narrow and less broad than the medial collateral ligament, the lateral collateral ligament stretches obliquely downward and backward from the lateral epicondyle of the femur above, to the head of the fibula below. In contrast to the medial collateral ligament, it is fused with neither the capsular ligament nor the lateral meniscus. Because of this, the lateral collateral ligament is more flexible than its medial counterpart, and is therefore less susceptible to injury. Both collateral ligaments are taut when the knee joint is in extension. With the knee in flexion, the radius of curvatures of the condyles is decreased and the origin and insertions of the ligaments are brought closer together which make th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Condyle
The lower extremity of femur (or distal extremity) is the lower end of the femur (thigh bone) in human and other animals, closer to the knee. It is larger than the upper extremity of femur, is somewhat cuboid in form, but its transverse diameter is greater than its antero-posterior; it consists of two oblong eminences known as the lateral condyle and medial condyle. Condyles Anteriorly, the condyles are slightly prominent and are separated by a smooth shallow articular depression called the patella surface. Posteriorly, they project considerably and a deep notch, the intercondylar fossa of femur, is present between them. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is the broader both in its antero-posterior and transverse diameters, the medial condyle is the longer and, when the femur is held with its body perpendicular, projects to a lower level. When, however, the femur is in its natural oblique position the lower surfaces of the two condyles lie practically in the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibial Plateau
{{Disambig ...
Tibial may refer to: * Tibia bone * Tibial nerve * Anterior tibial artery * Posterior tibial artery * Anterior tibial vein * Posterior tibial vein The posterior tibial veins are veins of the leg in humans. They drain the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar surface of the foot to the popliteal vein. Structure The posterior tibial veins receive blood from the medial and lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are over 100 types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs with age and affects the fingers, knees, and hips. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types include gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and septic arthritis. They are all types of rheumatic disease. Treatment may include resting the joint and alternating between applying ice and heat. Weight loss and exercise may also be useful. Recommended medications may depend on the form of arthritis. These may include pain medications such as ibuprofe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |