|
Mambo (music)
Mambo is a genre of Cuban dance music pioneered by the charanga Arcaño y sus Maravillas in the late 1930s and later popularized in the big band style by Pérez Prado. It originated as a syncopated form of the danzón, known as danzón-mambo, with a final, improvised section, which incorporated the '' guajeos'' typical of son cubano (also known as '' montunos''). These ''guajeos'' became the essence of the genre when it was played by big bands, which did not perform the traditional sections of the danzón and instead leaned towards swing and jazz. By the late 1940s and early 1950s, mambo had become a "dance craze" in the United States as its associated dance took over the East Coast thanks to Pérez Prado, Tito Puente, Tito Rodríguez and others. In the mid-1950s, a slower ballroom style, also derived from the danzón, cha-cha-cha, replaced mambo as the most popular dance genre in North America. Nonetheless, mambo continued to enjoy some degree of popularity into the 1960s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danzón
Danzón is the official musical genre and dance of Cuba.Urfé, Odilio 1965. ''El danzón''. La Habana. It is also an active musical form in Mexico and Puerto Rico. Written in time, the danzón is a slow, formal partner dance, requiring set footwork around syncopated beats, and incorporating elegant pauses while the couples stand listening to virtuoso instrumental passages, as characteristically played by a charanga or típica ensemble. The danzón evolved from the Cuban contradanza, or habanera ('Havana-dance'). The contradanza, which had English and French roots in the country dance and contredanse, was probably introduced to Cuba by the Spanish, who ruled the island for almost four centuries (1511–1898), contributing many thousands of immigrants. It may also have been partially seeded during the short-lived British occupation of Havana in 1762, and Haitian refugees fleeing the island's revolution of 1791–1804 brought the French-Haitian kontradans, contributing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
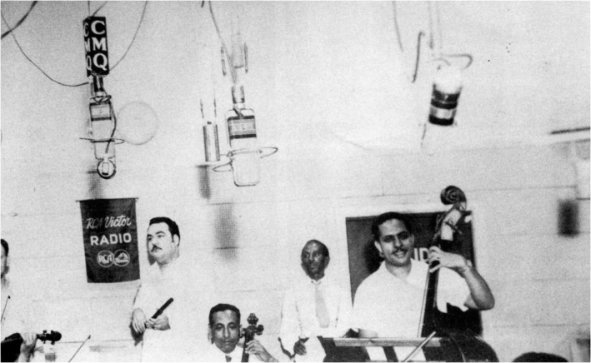
Arcaño Y Sus Maravillas
Arcaño y sus Maravillas was a Cuban charanga founded in 1937 by flautist Antonio Arcaño. Until its dissolution in 1958, it was one of the most popular and prolific danzón orchestras in Cuba, particularly due to the development of the danzón-mambo by its two main composers and musicians: Orestes López (piano, cello, bass) and his brother Israel López "Cachao" (bass). Such upbeat version of the danzón served as a precursor of the mambo popularized by Pérez Prado, as well as the chachachá created by Enrique Jorrín, a violinist who started his career in the Maravillas. Other important musicians in the Maravillas were pianist Jesús López (unrelated to Orestes and Israel), timbalero Ulpiano Díaz, violinist Félix Reina and flautist Eulogio Ortiz. Antonio Arcaño, former member of singer Fernando Collazo's La Maravilla del Siglo, founded his orchestra in November 1937 under the name La Maravilla de Arcaño, featuring many of the members of Collazo's group. Collazo hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cha-cha-cha (music)
Cha cha cha may refer to: * ''Cha-cha-chá'' (music), a style of Cuban dance music * Cha-cha-cha (dance), a Latin American dance accompanying the music Film and television * ''Cha Cha Cha'' (film), a 2013 Italian crime film * ''Cha Cha Cha'' (1964 film), a 1964 Indian film * ''Cha Cha Cha'' (TV series), a TV show from Argentina * Cha Cha Cha Films, a film production company Music * ''Cha Cha Cha'' (album), a 1995 album by EMF * ''Cha Cha Cha'', 1955 album by Monchito and the Mambo Royals * ''Cha Cha Cha'', 1982 album by Anne Linnet Band * ''Cha Cha Cha'', 1977 album by Irwin Goodman * ''Cha Cha Cha'', 2014 album by Abelardo Barroso * "Cha Cha Cha" (song), a 1989 song by hip hop artist MC Lyte * "The Bear Cha Cha Cha", a song from Bear in the Big Blue House * "The Cha-Cha-Cha", a 1962 song by Bobby Rydell * "Cha Cha Cha", by The Little Ones, 2006 * "Cha Cha Cha", a 1985 song by Finzy Kontini Other * Cha Cha Cha Township, a shopping centre in rural Zimbabwe * ChaChaCha, a te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tito Rodríguez
Pablo Rodríguez Lozada (January 4, 1923 – February 28, 1973), better known as Tito Rodríguez, was a Puerto Rican singer and bandleader. He started his career singing under the tutelage of his brother, Johnny Rodríguez. In the 1940s, both moved to New York, where Tito worked as a percussionist in several popular rhumba ensembles, before directing his own group to great success during the 1950s. His most prolific years coincided with the peak of the mambo and cha-cha-cha dance craze. He also recorded boleros, sones, guarachas and pachangas. Rodríguez is known by many fans as "El Inolvidable" (The Unforgettable One), a moniker based on his most popular song, a bolero written by Cuban composer Julio Gutiérrez. Early years Rodríguez was born in Barrio Obrero, Santurce, Puerto Rico, to José Rodríguez Fuentes from San Sebastián, Puerto Rico, and Severina Lozada from Holguín, Cuba. During his childhood he aspired to be a jockey and tried out racing horses at Hipódro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tito Puente
Ernest Anthony Puente Jr. (April 20, 1923 – June 1, 2000), commonly known as Tito Puente, was an American musician, songwriter, bandleader, and record producer of Puerto Rican descent. He is best known for dance-oriented mambo and Latin jazz compositions from his 50-year career. His most famous song is "Oye Como Va". Puente and his music have appeared in films including '' The Mambo Kings'' and Fernando Trueba's ''Calle 54''. He guest-starred on television shows, including ''Sesame Street'' and ''The Simpsons'' two-part episode " Who Shot Mr. Burns?". Early life Tito Puente was born on April 20, 1923, at Harlem Hospital Center in the New York borough of Manhattan, the son of Ernest and Felicia Puente, Puerto Ricans living in New York City's Spanish Harlem. His family moved frequently, but he spent the majority of his childhood in Spanish Harlem. Puente's father was the foreman at a razorblade factory. As a child, he was described as hyperactive, and after neighbors compla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mambo (dance)
Mambo is a Latin dance of Cuba which was developed in the 1940s when the music genre of the same name became popular throughout Latin America. The original ballroom dance which emerged in Cuba and Mexico was related to the danzón, albeit faster and less rigid. In the United States, it replaced rhumba as the most fashionable Latin dance. Later on, with the advent of salsa and its more sophisticated dance, a new type of mambo dance including breaking steps was popularized in New York. This form received the name of "salsa on 2", "mambo on 2" or "modern mambo". History The origins In the mid-1940s, bandleaders devised a dance for a new form of music known as mambo (music), taking its name from the 1938 song Mambo, a charanga composed by Orestes Lopez which had popularized a new form of danzon which later was known as danzon mambo. This style was a syncopated, less rigid form of the danzón which allowed the dancers to more freely express themselves during the last section, know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major form of musical expression in traditional and popular music. Jazz is characterized by swing and blue notes, complex chords, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and improvisation. Jazz has roots in European harmony and African rhythmic rituals. As jazz spread around the world, it drew on national, regional, and local musical cultures, which gave rise to different styles. New Orleans jazz began in the early 1910s, combining earlier brass band marches, French quadrilles, biguine, ragtime and blues with collective polyphonic improvisation. But jazz did not begin as a single musical tradition in New Orleans or elsewhere. In the 1930s, arranged dance-oriented swing big bands, Kansas City jazz (a hard-swinging, bluesy, impro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montuno
Montuno has several meanings pertaining to Cuban music and its derivatives. Literally, ''montuno'' means 'comes from the mountain', and so ''son montuno'' may refer to the older type of son played in the mountainous rural areas of Oriente. Another possibility is that the word ''montuno'' comes from the word ''montura'', the Spanish word for "saddle", because the rhythm in son music is like riding a horse. Or it may mean the final section of a song-based composition; in this sense it is simply part of a piece of music. Here it is usually a faster, brasher, semi-improvised instrumental section, sometimes with a repetitive vocal refrain. Finally, the term ''montuno'' is also used for a piano ''guajeo'', the ostinato figure accompanying the montuno section, when it describes a repeated syncopated piano vamp, often with chromatic root movement.Orovio, Helio 2004. ''Cuban music from A to Z''. Tumi, Bath. p141 References See also *Son montuno *Call and response (music) *Coro-preg� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Son Cubano
Son cubano is a genre of music and dance that originated in the highlands of eastern Cuba during the late 19th century. It is a syncretic genre that blends elements of Spanish and African origin. Among its fundamental Hispanic components are the vocal style, lyrical metre and the primacy of the tres, derived from the Spanish guitar. On the other hand, its characteristic clave rhythm, call and response structure and percussion section ( bongo, maracas, etc.) are all rooted in traditions of Bantu origin. Around 1909 the son reached Havana, where the first recordings were made in 1917. This marked the start of its expansion throughout the island, becoming Cuba's most popular and influential genre. While early groups had between three and five members, during the 1920s the ''sexteto'' ( sextet) became the genre's primary format. By the 1930s, many bands had incorporated a trumpet, becoming ''septetos'', and in the 1940s a larger type of ensemble featuring congas and piano became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guajeo
A guajeo (Anglicized pronunciation: ''wa-hey-yo'') is a typical Cuban ostinato melody, most often consisting of arpeggiated chords in syncopated patterns. Some musicians only use the term ''guajeo'' for ostinato patterns played specifically by a tres, piano, an instrument of the violin family, or saxophones. Piano guajeos are one of the most recognizable elements of modern-day salsa. Piano guajeos are also known as ''montunos'' in North America, or ''tumbaos'' in the contemporary Cuban dance music timba. History The guajeo shares rhythmic, melodic and harmonic similarities with the short ostinato figures played on marimbas, lamellophones, and string instruments in sub-Saharan Africa. The guajeo is a seamless blend of African and European musical sensibilities, and was first played as accompaniment on the tres in the Afro-Cuban son and related music. The tres is a Cuban guitar-like instrument, consisting of three sets of double strings. Changüí The guajeo emerged in Cuba du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danzón-mambo
The danzón-mambo (also known as ''danzón de nuevo ritmo'') is a subgenre of Cuban dance music that marked the transition from the classical danzόn to the mambo and the cha-cha-chá. It was also in the context of the danzón-mambo that the Cuban dance band format called charanga reached its present form. Origins The danzón-mambo was created by the musicians and arrangers of Antonio Arcaño's charanga, Arcaño y sus Maravillas, which was founded in 1937 (Orovio 1981:324). According to Santos (1982), The main forces behind Arcano's mambo were the Lopez brothers, Orestes ... and Israel (the great " Cachao") ..., who did most of the composing and arranging for the group, and played the 'cello and the string bass, respectively. Characteristics Generally speaking, the ''danzón-mambo'' represents a further and stronger incorporation of elements of the ''son'' into the '' danzón''. The first sections, or ''danzones'', did not depart significantly from the traditional '' d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |