|
Mycolactone
Mycolactone is a polyketide-derived macrolide produced and secreted by a group of very closely related pathogenic mycobacteria species including '' M. ulcerans'', '' M. liflandii'' (an unofficial designation), '' M. pseudoshottsii'', and some strains of ''M. marinum''. These mycobacteria are collectively referred to as mycolactone-producing mycobacteria or MPM. In humans, mycolactone is the toxin responsible for Buruli ulcers, doing so by damaging tissues and inhibiting the immune response. __TOC__ Variants Five distinct, naturally occurring mycolactone structural variants have been described so far: * Mycolactone A/B (''M. ulcerans'' from Africa, Malaysia, Japan * Mycolactone C (''M. ulcerans'' from Australia) * Mycolactone D (''M. ulcerans'' from China) * Mycolactone E (''M. liflandii'' from Sub-Saharan Africa) * Mycolactone F (''M. pseudoshottsii'' and ''M. marinum'' from around the world) Biosynthesis Mycolactone consists of a 12-membered macrolide core with an ester-linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buruli Ulcer
Buruli ulcer () is an infectious disease characterized by the development of painless open wounds. The disease is limited to certain areas of the world, with most cases occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa and Australia. The first sign of infection is a small painless nodule (medicine), nodule or area of swelling, typically on the arms or legs. The nodule grows larger over days to weeks, eventually forming an open Ulcer (dermatology), ulcer. Deep ulcers can cause scarring of muscles and tendons, resulting in permanent disability. Buruli ulcer is caused by skin infection with bacteria called ''Mycobacterium ulcerans''. The mechanism by which ''M. ulcerans'' is transmitted from the environment to humans is not known but may involve the bite of an aquatic insect or the infection of open wounds. Once in the skin, ''M. ulcerans'' grows and releases the toxin mycolactone, which blocks the normal function of cells, resulting in necrosis, tissue death and immune suppression at the site o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Ulcerans
''Mycobacterium ulcerans'' is a species of bacteria found in various aquatic environments. The bacteria can infect humans and some other animals, causing persistent open wounds called Buruli ulcer. ''M. ulcerans'' is closely related to ''Mycobacterium marinum'', from which it evolved around one million years ago, and more distantly to the mycobacteria which cause tuberculosis and leprosy. Description ''Mycobacterium ulcerans'' are rod-shaped bacteria. They appear purple ("Gram positive") under Gram stain and bright red ("acid fast") under Ziehl–Neelsen stain. On laboratory media, ''M. ulcerans'' grow slowly, forming small transparent colonies after four weeks. As colonies age, they develop irregular outlines and a rough, yellow surface. The bacteria was discovered by Australian scientists Jean Tolhurst and Glen Buckle in the late 1940s. Taxonomy and evolution ''Mycobacterium ulcerans'' is a species of mycobacteria within the phylum Actinomycetota. Within the genus ''Mycobact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolides
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocycle, macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but has since been used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential Life extension, longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are a diverse group with many members of very different properties: * Macrolides with 14-, 15-, or 16-membered rings and two attached sugar molecules are antibiotics that bind to bacterial ribosomes, the key representative being erythromycin. The term "macrolide antibiotics" tend to refer to just this class. * Some macrolides with very large (20+ membered) rings are immunosuppresants, the prototypical one being rapamycin. * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Marinum
''Mycobacterium marinum'' is a slow growing fresh and saltwater mycobacterium (SGM) belonging to the genus ''Mycobacterium'' and the phylum Actinobacteria. It was formerly known as ''Mycobacterium balnei''. The strain marinum was first identified by Joseph D. Aronson in 1926 and it is observed as a pathogenic mycobacterium causing tuberculosis-like infections in fish (mycobacteriosis) and skin lesions in humans. The bacteria grows optimal at a temperature around 30 °C. Human infection :''See aquarium granuloma'' ''Mycobacterium marinum'' is an acid-fast, aerobic bacterium which can infect humans. Infection is usually associated either with swimming, preparing sea food, or with keeping or working with aquarium fish. Infections of humans are rare due to the chlorination of water. The bacteria penetrate the skin through trauma, usually from bites, injuries from fins, and penetration from foreign objects. The infection is not transmittable from person to person. The bacteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolide
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but has since been used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are a diverse group with many members of very different properties: * Macrolides with 14-, 15-, or 16-membered rings and two attached sugar molecules are antibiotics that bind to bacterial ribosomes, the key representative being erythromycin. The term "macrolide antibiotics" tend to refer to just this class. * Some macrolides with very large (20+ membered) rings are immunosuppresants, the prototypical one being rapamycin. * Some 23-membered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmalonyl-CoA
Methylmalonyl-CoA is the thioester consisting of coenzyme A linked to methylmalonic acid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of succinyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (aka the Citric Acid Cycle, or Krebs Cycle). Biosynthesis and metabolism Methylmalonyl-CoA results from the metabolism of fatty acid with an odd number of carbons, of amino acids valine, isoleucine, methionine, threonine or of cholesterol side-chains, forming Propionyl-CoA. The latter is also formed from propionic acid, which bacteria produce in the intestine. Propionyl-CoA and bicarbonate are converted to Methylmalonyl-CoA by the enzyme propionyl-CoA Carboxylase. It then is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). This reaction is a reversible isomerization. In this way, the compound enters the Citric Acid Cycle. The following diagram demonstrates the aforementioned reaction: Propionyl CoA + Bicarbonate → Methylmalonyl CoA → Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyketide Antibiotics
In organic chemistry, polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (, or its reduced forms) and methylene () groups: . First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity. History Naturally produced polyketides by various plants and organisms have been used by humans since before studies on them began in the 19th and 20th century. In 1893, J. Norman Collie synthesized detectable amounts of orcinol by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
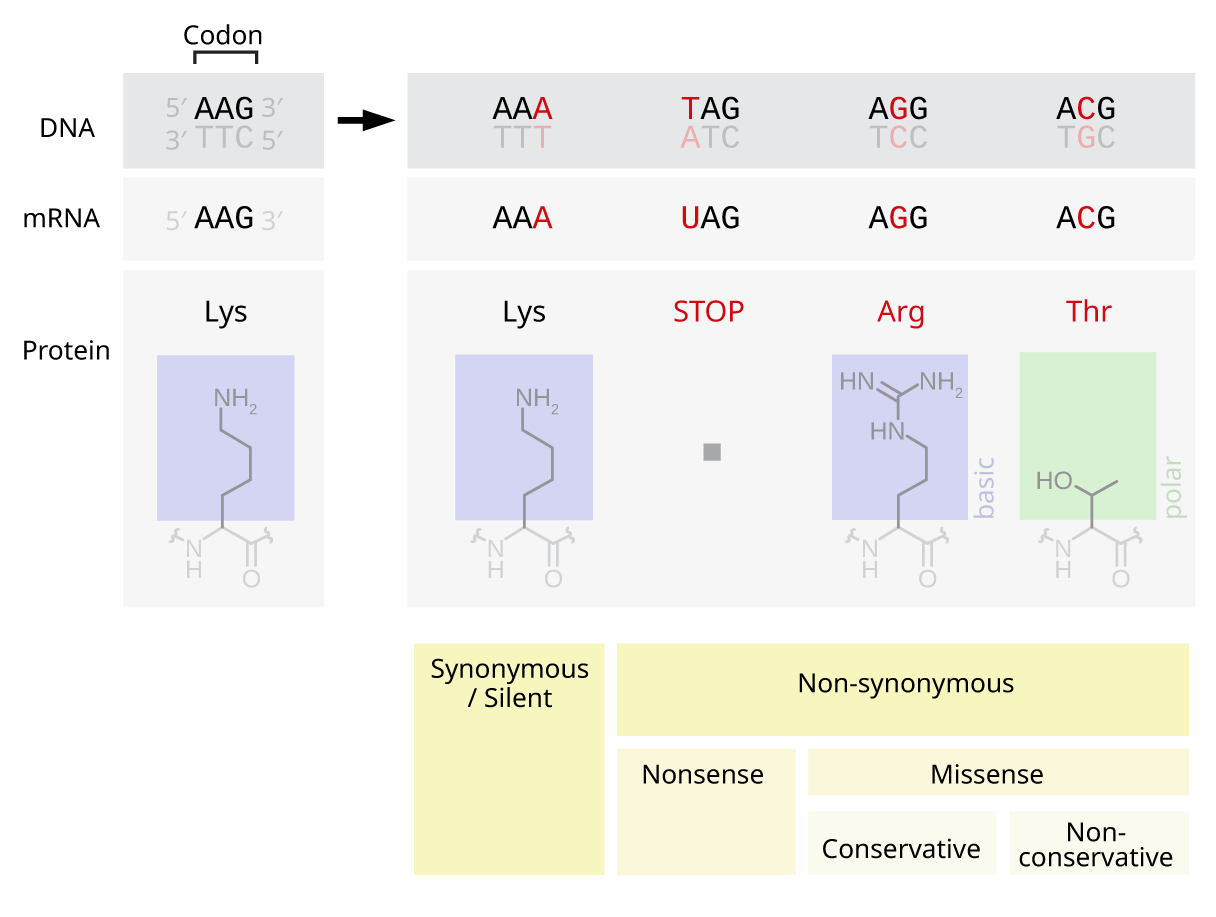
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. Synonymous substitution, synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding site'', and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate, the ''catalytic site''. Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes. Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups (Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- (γ-) amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, Chemical polarity, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid ''Residue (chemistry)#Biochemistry, residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissue (biology), tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyl Carrier Protein
The acyl carrier protein (ACP) is a cofactor of both fatty acid and polyketide biosynthesis machinery. It is one of the most abundant proteins in cells of ''E. coli.'' In both cases, the growing chain is bound to the ACP via a thioester derived from the distal thiol of a 4'-phosphopantetheine moiety. Structure The ACPs are small negatively charged α-helical bundle proteins with a high degree of structural and amino acid similarity. The structures of a number of acyl carrier proteins have been solved using various NMR and crystallography techniques. The ACPs are related in structure and mechanism to the peptidyl carrier proteins (PCP) from nonribosomal peptide synthases. Biosynthesis Subsequent to the expression of the inactive ''apo'' ACP, the 4'-phosphopantetheine moiety is attached to a serine residue. This coupling is mediated by acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS), a 4'-phosphopantetheinyl transferase. 4'-Phosphopantetheine is a prosthetic group of several acyl carrier pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyltransferase
Acyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that acts upon acyl In chemistry, an acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an organyl group () or hydrogen in the case of formyl grou ... groups. Examples include: * Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases * Glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase * Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase * Long-chain-alcohol O-fatty-acyltransferase See also * Acetyltransferase External links * Transferases EC 2.3 {{2.3-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |