|
Monoamine Nuclei
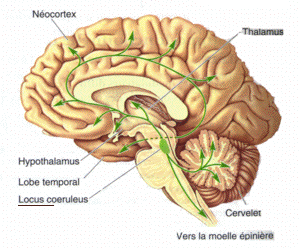
Monoamine nuclei are clusters of cells that primarily use monoamine neurotransmitters to communicate. The raphe nuclei, ventral tegmental area, and locus coeruleus have been included in texts about monoamine nuclei. These nuclei receive a variety of inputs including from other monoamines, as well as from glutaminergic, GABAergic, and substance p related pathways. The catacholaminergic pathways mainly project upwards into the cortical and limbic regions, power sparse descending axons have been observed in animals models. Both ascending and descending serotonergic pathways project from the raphe nuclei. Raphe nuclei in the obscurus, pallid us, and magnus descend into the brainstem and spinal cord, while the raphe ponds, raphe dorsals, and nucleus centralism superior projected up into the medial forebrain bundle before branching off. Monoamine nuclei have been studied in relation to major depressive disorder Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin. All monoamines are derived from aromatic amino acids like phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan by the action of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase enzymes. They are deactivated in the body by the enzymes known as monoamine oxidases which clip off the amine group. Monoaminergic systems, i.e., the networks of neurons that use monoamine neurotransmitters, are involved in the regulation of processes such as emotion, arousal, and certain types of memory. It has also been found that monoamine neurotransmitters play an important role in the secretion and production of neurotrophin-3 by astrocytes, a chemical which maintains neuron integrity and provides neurons with trophic support. Drugs used to increase or reduce the effect of monoamine neurotransmitters are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
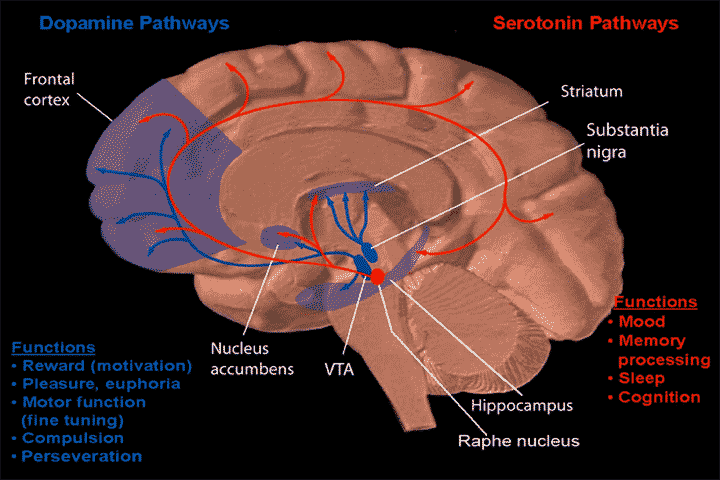
Raphe Nuclei
The raphe nuclei (, "seam") are a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem. They have 5-HT1 receptors which are coupled with Gi/Go-protein-inhibiting adenyl cyclase. They function as autoreceptors in the brain and decrease the release of serotonin. The anxiolytic drug Buspirone acts as partial agonist against these receptors. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act in these nuclei, as well as at their targets. Anatomy The raphe nuclei are traditionally considered to be the medial portion of the reticular formation, and appear as a ridge of cells in the center and most medial portion of the brain stem. In order from caudal to rostral, the raphe nuclei are known as the '' nucleus raphe obscurus'', the '' nucleus raphe pallidus'', the '' nucleus raphe magnus'', the '' nucleus raphe pontis'', the '' median raphe nucleus'', ''dorsal raphe nucleus'', ''caudal linear nucleus''. In the first systematic examination of the raph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Tegmental Area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is the origin of the dopaminergic cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and other dopamine pathways; it is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. The VTA plays an important role in a number of processes, including reward cognition ( motivational salience, associative learning, and positively-valenced emotions) and orgasm, among others, as well as several psychiatric disorders. Neurons in the VTA project to numerous areas of the brain, ranging from the prefrontal cortex to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between. Structure Neurobiologists have often had great difficulty distinguishing the VTA in humans and other primate brains from the substantia nigra (SN) and surrounding nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus Coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system in the reticular formation. The locus coeruleus, which in Latin means "blue spot", is the principal site for brain synthesis of norepinephrine (noradrenaline). The locus coeruleus and the areas of the body affected by the norepinephrine it produces are described collectively as the locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system or LC-NA system. Norepinephrine may also be released directly into the blood from the adrenal medulla. Anatomy The locus coeruleus (LC) is located in the posterior area of the rostral pons in the lateral floor of the fourth ventricle. It is composed of mostly medium-size neurons. Melanin granules inside the neurons contribute to its blue colour. Thus, it is also known as the ''blue nucleus'', or the ''nucleus pigmentosus pontis'' (hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid. It is non-essential and conditionally essential in humans, meaning the body can usually synthesize sufficient amounts of it, but in some instances of stress, the body's demand for glutamine increases, and glutamine must be obtained from the diet. It is encoded by the codons CAA and CAG. It is named after glutamic acid, which in turn is named after its discovery in cereal proteins, gluten. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid. The dietary sources of glutamine include especially the protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables like beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices and also in wheat, papaya, Brussels sprouts, celery, kale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABA
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, γ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. GABA is sold as a dietary supplement in many countries. It has been traditionally thought that exogenous GABA (i.e., taken as a supplement) does not cross the blood–brain barrier, but data obtained from more recent research (2010s) in rats describes the notion as being unclear. The carboxylate form of GABA is γ-aminobutyrate. Function Neurotransmitter Two general classes of GABA receptor are known: * GABAA in which the receptor is part of a ligand-gated ion channel complex * GABAB metabotropic receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors that open or close ion channels via intermediaries (G proteins) Neurons that produce GABA as their output are called GABAergic neurons, and have chiefly inhibitory action at receptors in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance P
Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide (a peptide composed of a chain of 11 amino acid residues) and a type of neuropeptide, belonging to the tachykinin family of neuropeptides. It acts as a neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator. Substance P and the closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after alternative splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows: * Arg Pro Lys Pro Gln Gln Phe Phe Gly Leu Met (RPKPQQFFGLM) with an amide group at the C-terminus. Substance P is released from the terminals of specific sensory nerves. It is found in the brain and spinal cord and is associated with inflammatory processes and pain. Discovery The original discovery of Substance P (SP) was in 1931 by Ulf von Euler and John H. Gaddum as a tissue extract that caused intestinal contraction ''in vitro''. Its tissue distribution and biologic actions were further investigated over the follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Forebrain Bundle
The medial forebrain bundle (MFB) is a neural pathway containing fibers from the basal olfactory regions, the periamygdaloid region and the septal nuclei, as well as fibers from brainstem regions, including the ventral tegmental area and nigrostriatal pathway. Anatomy The MFB passes through the lateral hypothalamus and the basal forebrain in a rostral-caudal direction. The MFB has its main projections to these regions of Brodmann areas (BA) 8, 9, 10, 11, 11m. The superior frontal region of MFB projects to BA 8, 9, 10; the rostral middle frontal projects to dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (BA 9, 10); lateral orbitofrontal of MFB shows its projections to nucleus accumbens septi (NAC) and ventral striatum as subcortical reward associated structures. It contains both ascending and descending fibers. The mesolimbic pathway, which is a collection of dopaminergic neurons that projects from the ventral tegmental area to the nucleus accumbens, is a component pathway of the MFB. The MFB i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Depressive Disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this syndrome, symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The disorder causes the second-most years lived with disability, after low back pain, lower back pain. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by family or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubmed Equitativa Hormonal
PubMed is an openly accessible, free database which includes primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintains the database as part of the Entrez system of information retrieval. From 1971 to 1997, online access to the MEDLINE database was provided via computer and phone lines primarily through institutional facilities, such as university libraries. PubMed, first released in January 1996, ushered in the era of private, free, home- and office-based MEDLINE searching. The PubMed system was offered free to the public starting in June 1997. Content In addition to MEDLINE, PubMed provides access to: * older references from the print version of ''Index Medicus'', back to 1951 and earlier * references to some journals before they were indexed in Index Medicus and MEDLINE, for instance ''Science'', ''BMJ'', and ''Annals of Surgery'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |