|
Mismatch Theory
Evolutionary mismatch (also "mismatch theory" or "evolutionary trap") is the evolutionary biology concept that a previously advantageous trait may become maladaptive due to change in the environment, especially when change is rapid. It is said this can take place in humans as well as other animals. Environmental change leading to evolutionary mismatch can be broken down into two major categories: temporal (change of the existing environment over time, e.g. a climate change) or spatial (placing organisms into a new environment, e.g. a population migrating). Since environmental change occurs naturally and constantly, there will certainly be examples of evolutionary mismatch over time. However, because large-scale natural environmental change – like a natural disaster – is often rare, it is less often observed. Another more prevalent kind of environmental change is anthropogenic (human-caused). In recent times, humans have had a large, rapid, and trackable impact on the envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Evolutionary Trap
The term evolutionary trap has retained several definitions associated with different Biology, biological disciplines. Evolutionary biology Within evolutionary biology, this term has been used sporadically to refer to situations in which a pre-existing (and presumably well adapted and successful) trait has become obsolete or maladaptive due to changing biophysical or social environments but evolution, evolved complex behavioral decision-making rules ("Darwinian algorithms") accumulated by prior adaptations now preclude any effective re-adaptation—as organisms can only modify upon or "patch up" existing traits (which essentially have become inherited "baggage") rather than devolution (biology), devolving, removing or "redesigning" a trait (i.e. Dollo's law of irreversibility)—leaving the species hosting the trait struggling to keep up with natural selection and thus vulnerable to competitive disadvantage, extirpation or even extinction. In the 1991 BBC lecture series ''Growing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and sedentism, settlement, making an increasingly large population possible. These settled communities permitted humans to observe and experiment with plants, learning how they grew and developed. This new knowledge led to the domestication of plants into crops. Archaeological data indicate that the domestication of various types of plants and animals happened in separate locations worldwide, starting in the Geologic time scale, geological epoch of the Holocene 11,700 years ago, after the end of the last Ice Age. It was humankind's first historically verifiable transition to agriculture. The Neolithic Revolution greatly narrowed the diversity of foods available, resulting in a decrease in the quality of human nutrition compared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reward System
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and classical conditioning), and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding. The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dopaminergic Pathways
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of projection neurons, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons. There are more than 10 dopaminergic cell groups and pathways. The four major dopaminergic pathways are the mesolimbic pathway, the mesocortical pathway, the nigrostriatal pathway, and the tuberoinfundibular pathway. The mesolimbic pathway and the mesocortical pathway form the mesocorticolimbic system. Two other dopaminergic pathways to be considered are the hypothalamospinal tract and the incertohypothalamic pathway. Parkinson's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), substance use disorders (addiction), and restless legs syndrome (RLS) can be attributed to dysfunction in specific dopaminergic pathways. The dopam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
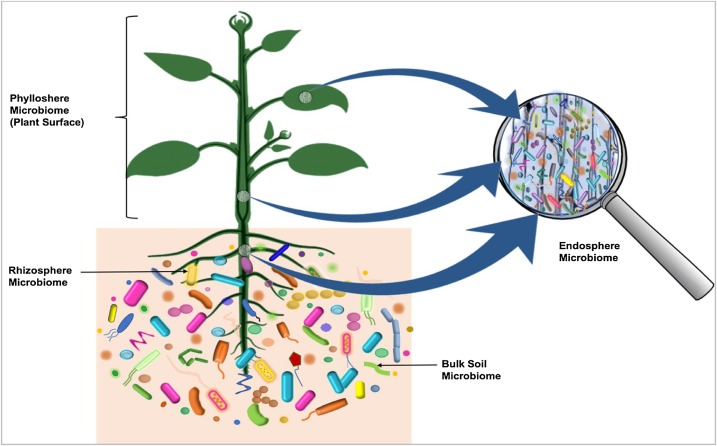
Microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably well-defined habitat which has distinct physio-chemical properties. The term thus not only refers to the microorganisms involved but also encompasses their theatre of activity". In 2020, an international panel of experts published the outcome of their discussions on the definition of the microbiome. They proposed a definition of the microbiome based on a revival of the "compact, clear, and comprehensive description of the term" as originally provided by Whipps ''et al.'', but supplemented with two explanatory paragraphs, the #First explanatory paragraph, first pronouncing the dynamic character of the microbiome, and the #Second explanatory paragraph, second clearly separating the term ''microbiota'' from the term ''microbiome''. Modified text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can for example be in Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic relationships. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined symbiosis as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term is sometimes more exclusively used in a restricted, mutualistic sense, where both symbionts contribute to each other's subsistence. This means that they benefit each other in some way. Symbiosis can be ''obligate'' (or ''obligative''), which means that one, or both of the organisms depend on each other for survival, or ''facultative'' (optional), when they can also subsist independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. Symbionts forming a single body live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, mutualistic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or else the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product ( short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple life fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that there are more than 80 recognized autoimmune diseases, with recent scientific evidence suggesting the existence of potentially more than 100 distinct conditions. Nearly any body part can be involved. Autoimmune diseases are a separate class from autoinflammatory diseases. Both are characterized by an immune system malfunction which may cause similar symptoms, such as rash, swelling, or fatigue, but the cardinal cause or mechanism of the diseases is different. A key difference is a malfunction of the innate immune system in autoinflammatory diseases, whereas in autoimmune diseases there is a malfunction of the adaptive immune system. Symptoms of autoimmune diseases can significantly vary, primarily based on the specific type of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hygiene Hypothesis
In medicine, the hygiene hypothesis states that early childhood exposure to particular microorganisms (such as the gut flora and helminth parasites) protects against allergies by properly tuning the immune system. In particular, a lack of such exposure is thought to lead to poor immune tolerance. The time period for exposure begins before birth and ends at school age. While early versions of the hypothesis referred to microorganism exposure in general, later versions apply to a specific set of microbes that have co-evolved with humans. The updates have been given various names, including the microbiome depletion hypothesis, the microflora hypothesis, and the "old friends" hypothesis. There is a significant amount of evidence supporting the idea that lack of exposure to these microbes is linked to allergies or other conditions, although it is still rejected by many scientists. The term "hygiene hypothesis" has been described as a misnomer because people incorrectly interpret it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the Old age, elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the Vertebral column, spine, the bones of the forearm, the wrist, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, some people may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal peak bone mass, maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after menopause in women due to lower levels of estrogen, and after andropause in older men due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower limbs, which may lead to amputations. A sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Metabolic syndrome is associated with the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. In the U.S., about 25% of the adult population has metabolic syndrome, a proportion increasing with age, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and prediabetes are closely related to one another and have overlapping aspects. The syndrome is thought to be caused by an underlying disorder of energy utilization and storage, but the cause of the syndrome is an area of ongoing medical research. Researchers debate whether a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome implies differential treatment or increases risk of cardiovascular disease beyond what is suggested by the sum of its individual components. Signs and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |