|
Matrigel
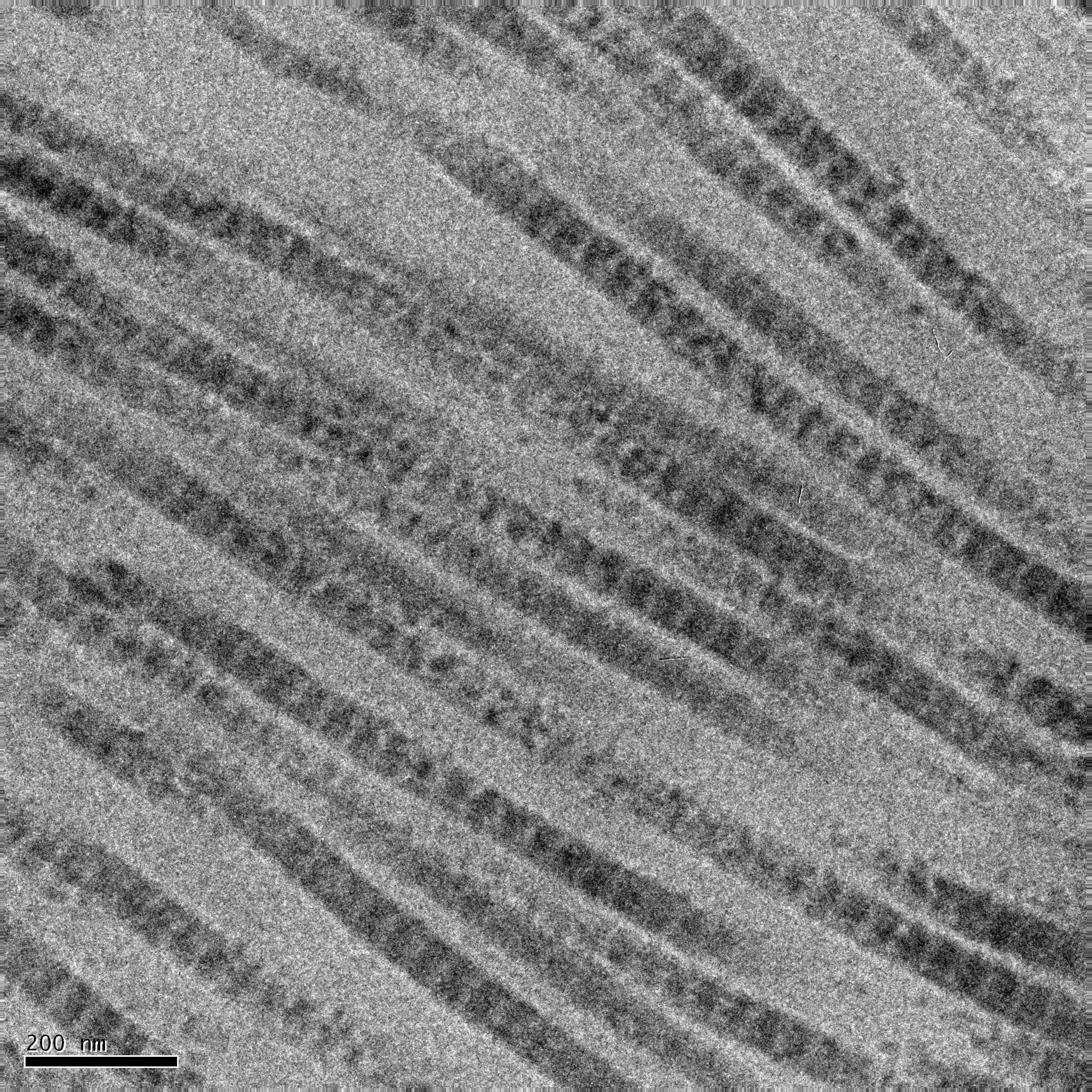
Matrigel is the trade name for the solubilized basement membrane matrix secreted by Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm (EHS) mouse sarcoma cells produced by Corning Life Sciences. Matrigel resembles the laminin/collagen IV-rich basement membrane extracellular environment found in many tissues and is used by cell biologists as a substrate (basement membrane matrix) for culturing cells. Cell culture A common laboratory procedure is to dispense small volumes of chilled (4 °C) liquid Matrigel onto plastic tissue culture labware. When incubated at 37 °C (body temperature) the Matrigel proteins polymerize (solidify) producing a recombinant basement membrane that covers the labware's surface. Cells cultured on Matrigel demonstrate complex cellular behavior that is otherwise difficult to observe under laboratory conditions. For example, endothelial cells create intricate spiderweb-like networks on Matrigel-coated surfaces but not on plastic surfaces. Such networks are highly suggestive of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hynda Kleinman
Hynda K. Kleinman is an American cell biologist who was the chief of the cell biology section at the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research from 1985 to 2006. She co-invented Matrigel. Early life Kleinman was born into a family that valued nature, often gardening, fishing, and hiking. Kleinman's father was a trained geologist and would collect rocks and arrowheads on hikes, which sparked Kleinman's interest in chemical and biological sciences. Life Kleinman received a B.S. in chemistry from Simmons College in 1969 and a M.S. and Ph.D. from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1973. She did postdoctoral training at Tufts University. Kleinman worked at National Institutes of Health (NIH) from 1975 to 2006 in the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) and served as Chief of the Cell Biology Section in NIDCR's Laboratory of Cell and Developmental Biology (1985–2006). Her laboratory was the first to report the wound-healing effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Name
A trade name, trading name, or business name is a pseudonym used by companies that do not operate under their registered company name. The term for this type of alternative name is fictitious business name. Registering the fictitious name with a relevant government body is often required. In a number of countries, the phrase "trading as" (abbreviated to t/a) is used to designate a trade name. In the United States, the phrase "doing business as" (abbreviated to DBA, dba, d.b.a., or d/b/a) is used,Pinkerton's, Inc. v. Superior Court'', 49 Cal. App. 4th 1342, 1348-49, 57 Cal. Rptr. 2d 356, 360 (1996) (collecting cases and explaining term of art "doing business as" (DBA)). among others, such as assumed business name or fictitious business name. In Canada, "operating as" (abbreviated to o/a) and "''trading as''" are used, although "''doing business as''" is also sometimes used. A company typically uses a trade name to conduct business using a simpler name rather than using their for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
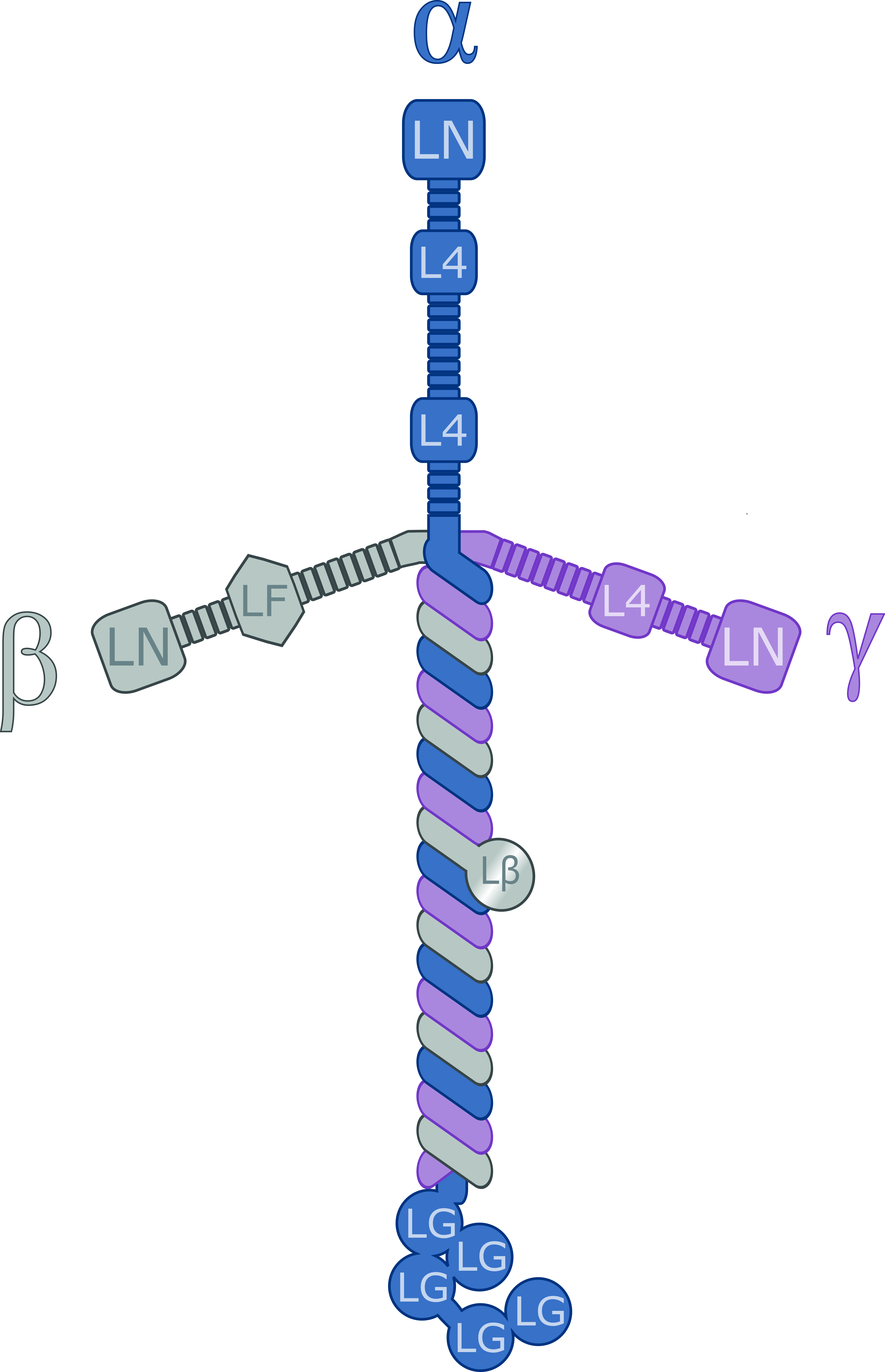
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina (the protein network foundation for most cells and organs). Laminins are vital to biological activity, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa) and possess three different chains (α, β, and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition, e.g. laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect, composing a cruciform structure that is able to bind to other molecules of the extracellular matrix and cell membrane. The three short arms have an affinity for binding to other laminin molecules, conducing sheet formation. The long ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myogel
Myogel is a trade name for a human-based extracellular matrix used in cancer research to provide a 3D cell culture environment for cancer cells. Unlike other synthesized matrices such as matrigel which originated from mice sarcoma, myogel is extracted from a human benign tumor tissue called leiomyoma. Myogel was developed in Tuula Salo's lab at the University of Oulu The University of Oulu () is one of the largest universities in Finland, located in the city of Oulu. It was founded on July 8, 1958. The university has around 14,200 students and 3,800 staff. 21 International Master's Programmes are offer .... The idea started in 2009 by culturing cancer cells on myoma discs. Later in 2015, these myoma tissues were processed following matrigel receipt, to extract a gel form called Myogel. Myogel was compared with matrigel and found to be superior in term of enhancing cancer cells proliferation, migration and invasion. References {{oncology-stub Extracellular matrix Cancer r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluripotent
Cell potency is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types. The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum, begins with totipotency to designate a cell with the most differentiation potential, pluripotency, multipotency, oligopotency, and finally unipotency. Totipotency Totipotency () is the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism. Spores and zygotes are examples of totipotent cells. In the spectrum of cell potency, totipotency represents the cell with the greatest differentiation potential, being able to differentiate into any embryonic cell, as well as any extraembryonic tissue cell. In contrast, pluripotent cells can only differentiate into embryonic cells. A fully differentiated cell can return to a state of totipotency. The conversion to totipotency is complex and not fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Inactive fibroblasts, called 'fibrocytes', are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have less RER. Although disjointed and scattered when covering large spaces, fibroblasts often locally align in parallel clusters when crowded together. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Stem Cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are Cell potency#Pluripotency, pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-Implantation (human embryo), implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post Human fertilization, fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the inner cell mass (embryoblast) using immunosurgery results in destruction of the blastocyst, a process Stem cell controversy, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage have the same moral considerations as embryos in the post-implantation stage of development. Researchers are currently focusing heavily on the therapeutic potential of embryonic stem cells, with clinical use being the goal for many laboratories. Potential uses include the treatment of diabetes and heart disease. The cells are being studied to be used as clinical therapies, models of genetic disorders, and cellular/DNA r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Metabolic composition, however, gets dramatically altered where st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Factors
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for regulating a variety of cellular processes. Growth factors typically act as cell signaling, signaling molecules between cells. Examples are cytokines and hormones that bind to specific receptor (biochemistry), receptors on the surface of their target cell (biology), cells. They often promote cell differentiation and maturation, which varies between growth factors. For example, epidermal growth factor (EGF) enhances osteogenic differentiation (osteogenesis or bone formation), while fibroblast growth factors and vascular endothelial growth factors stimulate blood vessel differentiation (angiogenesis). Comparison to cytokines ''Growth factor'' is sometimes used interchangeably among scientists with the term ''cytokine.'' Historically, cytok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Vitamin C is vital for collagen synthesis. Depending on the degree of biomineralization, mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the Gut (anatomy), gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes 1% to 2% of muscle tissue and 6% by weight of skeletal muscle. The fibroblast is the most common cell creating collagen in animals. Gelatin, which is used in food and industry, is collagen t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nidogen
Nidogens, formerly known as entactins, are a family of sulfated monomeric glycoproteins located in the basal lamina of parahoxozoans. Two nidogens have been identified in humans: nidogen-1 (NID1) and nidogen-2 (NID2). Remarkably, vertebrates are still capable of stabilizing basement membrane in the absence of either identified nidogen. In contrast, those lacking both nidogen-1 and nidogen-2 typically die prematurely during embryonic development as a result of defects existing in the heart and lungs. Nidogen have been shown to play a crucial role during organogenesis in late embryonic development, particularly in cardiac and lung development. Insufficient levels of nidogen in mice causes poorly developed organs such as the lungs and heart, which ultimately ensues to an early death. Due to nidogen being necessary in the formation of basement membranes, serving as a linker protein, and those basement proteins being shown to be necessary during tissue growth, nidogen is crucial for emb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |