|
Manifold Vacuum
Manifold vacuum, or engine vacuum in a petrol engine is the difference in air pressure between the engine's intake manifold and Earth's atmosphere. Manifold vacuum is an effect of a piston's movement on the induction stroke and the airflow through a throttle in the intervening carburetor or throttle body leading to the intake manifold. It is a result of the amount of restriction of airflow through the engine. In some engines, the manifold vacuum is also used as an auxiliary power source to drive engine accessories and for the crankcase ventilation system. Manifold vacuums should not be confused with venturi vacuums, which are an effect exploited in some carburetors to establish a pressure difference roughly proportional to mass airflow and to maintain a somewhat constant air/fuel ratio. It is also used in light airplanes to provide airflow for pneumatic gyroscopic instruments. Overview The rate of airflow through an internal combustion engine is an important factor deter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrol Engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American and Canadian English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as '' E10'' and '' E85''). They may be designed to run on petrol with a higher octane rating, as sold at petrol stations. Most petrol engines use spark ignition, unlike diesel engines which run on diesel fuel and typically use compression ignition. Another key difference to diesel engines is that petrol engines typically have a lower compression ratio. History The first practical petrol engine was built in 1876 in Germany by Nicolaus August Otto and Eugen Langen, although there had been earlier attempts by Étienne Lenoir in 1860, Siegfried Marcus in 1864 and George Brayton in 1873. Design Thermodynamic cycle Most petrol engines use either the four-stroke Otto cycle or the two-stroke cycle. Petrol engines have also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke Engine
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a Thermodynamic power cycle, power cycle with two strokes of the piston, one up and one down, in one revolution of the crankshaft in contrast to a four-stroke engine which requires four strokes of the piston in two crankshaft revolutions to complete a power cycle. During the stroke from bottom dead center to top dead center, the end of the exhaust/intake (or Scavenging (automotive), scavenging) is completed along with the compression of the mixture. The second stroke encompasses the combustion of the mixture, the expansion of the burnt mixture and, near bottom dead center, the beginning of the scavenging flows. Two-stroke engines often have a higher power-to-weight ratio than a four-stroke engine, since their power stroke occurs twice as often. Two-stroke engines can also have fewer moving parts, and thus be cheaper to manufacture and weigh less. In countries and regions with stringe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
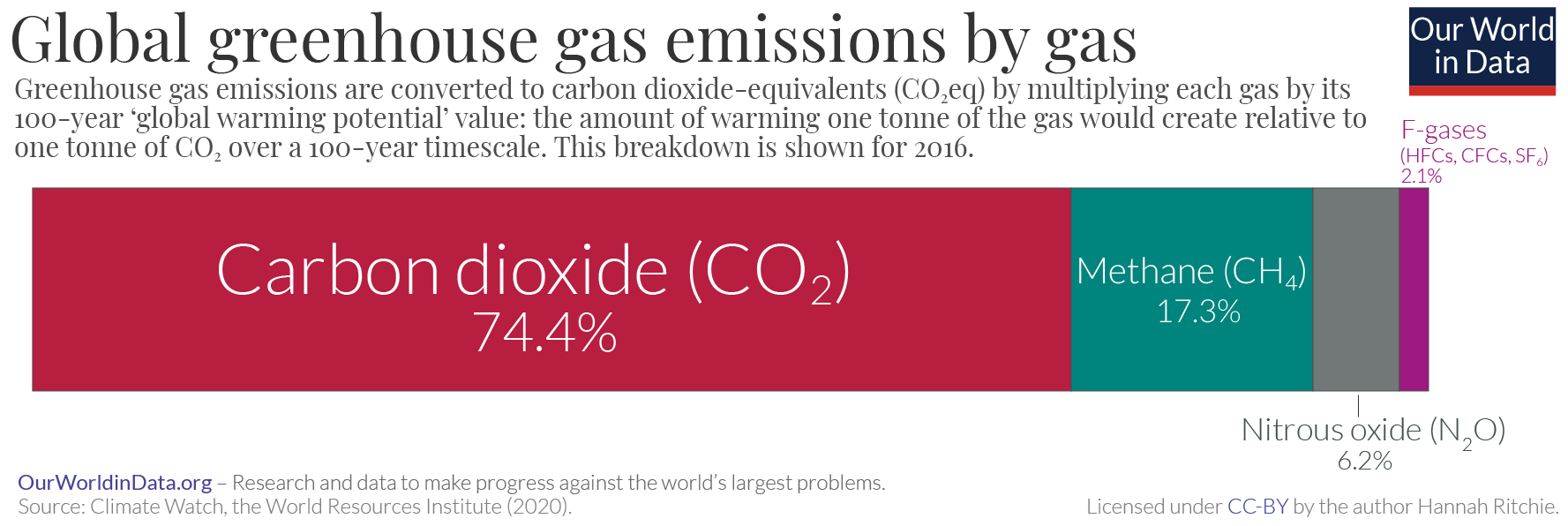
Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (1773±73 ) from fossil fuels and industry, and 219±60 (802±220 ) from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Control Unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also called an engine control module (ECM), is a device that controls various subsystems of an internal combustion engine. Systems commonly controlled by an ECU include the fuel injection and ignition systems. The earliest ECUs (used by aircraft engines in the late 1930s) were mechanical-hydraulic units; however, most 21st-century ECUs operate using digital electronics. Functions The main functions of the ECU are typically: * Fuel injection system * Ignition system * Idle speed control (typically either via an idle air control valve or the electronic throttle system) * Variable valve timing and/or variable valve lift systems The sensors used by the ECU include: * accelerator pedal position sensor * camshaft position sensor * coolant temperature sensor * crankshaft position sensor * knock sensors * inlet manifold pressure sensor ( MAP sensor) * intake air temperature * intake air mass flow rate sensor ( MAF sensor) * oxygen (lambda) s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. Turbochargers are distinguished from superchargers in that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the inv ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement (engine), displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and increase power outputs, especially with reduced engine dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Controls
Car controls are the components in automobiles and other powered road vehicles, such as trucks and buses, used for driving and parking. While controls like steering wheels and pedals have existed since the invention of cars, other controls have developed and adapted to the demands of drivers. For example, manual transmissions became less common as technology relating to automatic transmissions became advanced. Earlier versions of headlights and signal lights were fueled by acetylene or oil. Acetylene was preferred to oil, because its flame is resistant to both wind and rain. Acetylene headlights, which gave a strong green-tinted light, were popular until after World War I; even though the first electric headlights were introduced in 1898 (and those were battery-powered), it wasn't until high-wattage bulbs and more powerful car electrical generating systems were developed in the late 1910s that electric lighting systems entirely superseded acetylene. Steering The first autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Braking
Engine braking occurs when the retarding forces within an internal combustion engine are used to slow down a motor vehicle, as opposed to using additional external braking mechanisms such as friction brakes or magnetic brakes. The term is often confused with several other types of braking, most notably compression-release braking or "jake braking" which uses a different mechanism. Traffic regulations in many countries require trucks to always drive with an engaged gear, which in turn provides a certain amount of engine braking (viscous losses to the engine oil and air pumped through the engine and friction losses to the cylinder walls and bearings) when no accelerator pedal is applied. Engine braking in different engine types Gasoline engines The term "engine braking" refers to the braking effect that occurs in gasoline engines when the accelerator pedal is released. This causes fuel injection to cease and the throttle valve to close almost completely, greatly restricting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Displacement
Variable displacement is an automobile engine technology that allows the engine displacement to change, usually by deactivating cylinders, for improved fuel economy. The technology is primarily used in large multi-cylinder engines. Many automobile manufacturers have adopted this technology as of 2005, although the concept has existed for some time prior to this. Theory of operation Cylinder deactivation is used to reduce the fuel consumption and emissions of an internal combustion engine during light-load operation. In typical light-load driving the driver uses only around 30 percent of an engine’s maximum power. In these conditions, the throttle valve is nearly closed, and the engine needs to work to draw air. This causes an inefficiency known as pumping loss. Some large capacity engines need to be throttled so much at light load that the cylinder pressure at top dead centre is approximately half that of a small 4-cylinder engine. Low cylinder pressure results in lower fuel e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velomobiles), animal-powered transports (e.g. horse-drawn vehicle, horse-drawn carriages/wagons, ox carts, dog sleds), motor vehicles (e.g. motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters) and rail transport, railed vehicles (trains, trams and monorails), but more broadly also includes cable transport (aerial lift, cable cars and elevators), watercraft (ships, boats and underwater vehicles), amphibious vehicles (e.g. screw-propelled vehicles, hovercraft, seaplanes), aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, glider (aircraft), gliders and aerostats) and space vehicles (spacecraft, spaceplanes and launch vehicles). This article primarily concerns the more ubiquitous land vehicles, which can be broadly classified by the type of contact interface with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |