|
Lupus Band Test
Lupus band test is done upon skin biopsy, with direct immunofluorescence staining, in which, if positive, IgG and complement depositions are found at the dermoepidermal junction.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. . This test can be helpful in distinguishing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) from cutaneous lupus, because in SLE the lupus band test will be positive in both involved and uninvolved skin, whereas with cutaneous lupus only the involved skin will be positive. The minimum criteria for positivity are:Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2011; 7: 27–32. The lupus band test in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Adam Reich, Katarzyna Marcinow, and Rafal Bialynicki-Birula * In sun-exposed skin: presence of a band of deposits of IgM along the epidermal basement membrane in 50% of the biopsy, intermediate (2+) intensity or more. * In sun-protected skin : presence of interrupted (i.e. less than 50%) de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Immunofluorescence
A direct fluorescent antibody (DFA or dFA), also known as "direct immunofluorescence", is an antibody that has been tagged in a direct fluorescent antibody test. Its name derives from the fact that it directly tests the presence of an antigen with the tagged antibody, unlike western blotting, which uses an indirect method of detection, where the primary antibody binds the target antigen, with a secondary antibody directed against the primary, and a tag attached to the secondary antibody. Commercial DFA testing kits are available, which contain fluorescently labelled antibodies, designed to specifically target unique antigens present in the bacteria or virus, but not present in mammals (Eukaryotes). This technique can be used to quickly determine if a subject has a specific viral or bacterial infection. In the case of respiratory viruses, many of which have similar broad symptoms, detection can be carried out using nasal wash samples from the subject with the suspected infection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IGG Antibodies
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes. Function Antibodies are major components of humoral immunity. IgG is the main type of antibody found in blood and extracellular fluid, allowing it to control infection of body tissues. By binding many kinds of pathogens such as virus A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...es, bacteria, and fungi, IgG protects the body from infection. It does this through several mechanisms: * IgG-mediated binding of pathogens causes their immobilization and binding together via agglutination (biology), agglutinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a mixture of genetics combined with environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk. The mechanism involves an immune response by autoantibodies against a person's own tissues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an underlying network of reticular col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer ( stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
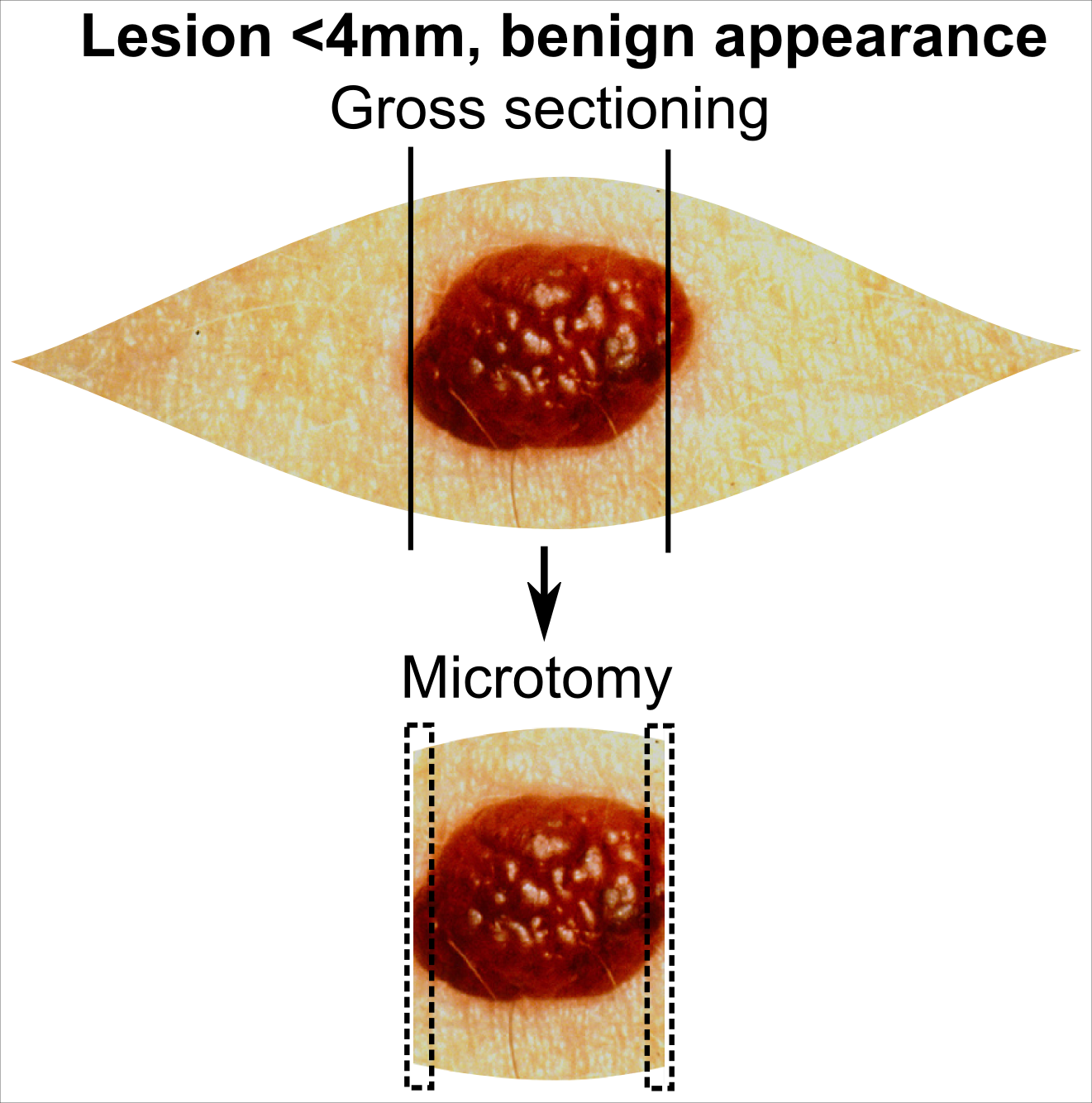
Skin Biopsy
Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. It is commonly performed by dermatologists. Skin biopsies are also done by family physicians, internists, surgeons, and other specialties. However, performed incorrectly, and without appropriate clinical information, a pathologist's interpretation of a skin biopsy can be severely limited, and therefore doctors and patients may forgo traditional biopsy techniques and instead choose Mohs surgery. There are four main types of skin biopsies: shave biopsy, punch biopsy, excisional biopsy, and incisional biopsy. The choice of the different skin biopsies is dependent on the suspected diagnosis of the skin lesion. Like most biopsies, patient consent and anesthesia (usually lidocaine injected into the skin) are prerequisites. Types Shave bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes. Function Antibodies are major components of humoral immunity. IgG is the main type of antibody found in blood and extracellular fluid, allowing it to control infection of body tissues. By binding many kinds of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, IgG protects the body from infection. It does this through several mechanisms: * IgG-mediated binding of pathogens causes their immobilization and binding together via agglutination; IgG coating of pathogen surfaces (known as opsonization) allows their recognition and ingestion by phagocytic immune cells leading to the elimination of the pathogen itself; * IgG activates all the classical pathway of the complement system, a cascade of immune protein pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement System (immunology)
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibody, antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and attack the pathogen's cell membrane. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change during an individual's lifetime. The complement system can, however, be recruited and brought into action by antibodies generated by the adaptive immune system. The complement system consists of a number of small proteins that are synthesized by the liver, and circulate in the blood as inactive Protein precursor, precursors. When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end result of this ''complement activation'' or ''complement fixation'' cascade is stimulation of phagocytes to clear f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermoepidermal Junction
The dermoepidermal junction or dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ) is the area of tissue that joins the epidermal and the dermal layers of the skin. The basal cells in the stratum basale of the epidermis connect to the basement membrane by the anchoring filaments of hemidesmosomes; the cells of the papillary layer of the dermis are attached to the basement membrane by anchoring fibrils, which consist of type VII collagen. Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is a type of severe skin reaction. Together with Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) it forms a spectrum of disease, with TEN being more severe. Early symptoms include fever and flu-like symptoms. A few days later ... are diseases where there is a breakdown of the dermoepidermal junction. References Skin anatomy {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 4
Complement component 4 (C4), in humans, is a protein involved in the intricate complement system, originating from the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system. It serves a number of critical functions in immunity, tolerance, and autoimmunity with the other numerous components. Furthermore, it is a crucial factor in connecting the recognition pathways of the overall system instigated by antibody-antigen (Ab-Ag) complexes to the other effector proteins of the innate immune response. For example, the severity of a dysfunctional complement system can lead to fatal diseases and infections. Complex variations of it can also lead to schizophrenia. The C4 protein was thought to derive from a simple two-locus allelic model, which however has been replaced by a much more sophisticated multimodular RCCX gene complex model which contain long and short forms of the C4A or C4B genes usually in tandem RCCX cassettes with copy number variation, that somewhat parallels variation in the levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |