|
Lunar Geologic Timescale
The lunar geological timescale (or selenological timescale) divides the history of Earth's Moon into five generally recognized periods: the Copernican, Eratosthenian, Imbrian ( Late and Early epochs), Nectarian, and Pre-Nectarian. The boundaries of this time scale are related to large impact events that have modified the lunar surface, changes in crater formation through time, and the size-frequency distribution of craters superposed on geological units. The absolute ages for these periods have been constrained by radiometric dating of samples obtained from the lunar surface. However, there is still much debate concerning the ages of certain key events, because correlating lunar regolith samples with geological units on the Moon is difficult, and most lunar radiometric ages have been highly affected by an intense history of bombardment. Lunar stratigraphy The primary geological processes that have modified the lunar surface are impact cratering and volcanism, and by using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Map Of The Near Side Of The Moon
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other Astronomical object, astronomical objects, the features or rock (geology), rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth science, Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the Relative dating, relative and Geochronology, absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Mare
The lunar maria (; singular: mare ) are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient asteroid impacts on the far side on the Moon that triggered volcanic activity on the opposite (near) side. They were dubbed , Latin for 'seas', by early astronomers who mistook them for actual seas. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich composition, and hence appear dark to the naked eye. The maria cover about 16% of the lunar surface, mostly on the side visible from Earth. The few maria on the far side are much smaller, residing mostly in very large craters. The traditional nomenclature for the Moon also includes one (ocean), as well as features with the names ('lake'), ('marsh'), and ('bay'). The last three are smaller than maria, but have the same nature and characteristics. The names of maria refer to sea features ( Mare Humorum, Mare Imbrium, Mare Insularum, Mare Nubium, Mare Spumans, Mare Undarum, Mare Vaporum, Oceanus Proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mare Imbrium
Mare Imbrium (Latin ''imbrium'', the "Sea of Showers" or "Sea of Rains", "Sea of Tears") is a vast lava plain within the Imbrium Basin on the Moon and is one of the larger craters in the Solar System. The Imbrium Basin formed from the collision of a proto-planet during the Late Heavy Bombardment. Basaltic lava later flooded the giant crater to form the flat volcanic plain seen today. The basin's age has been estimated using uranium–lead dating methods to approximately 3.9 billion years ago, and the diameter of the impactor has been estimated to be 250 ± 25 km. The Moon's maria (plural of mare) have fewer features than other areas of the Moon because molten lava pooled in the craters and formed a relatively smooth surface. Mare Imbrium is not as flat as it was originally thought, because later events have altered its surface. Origin Mare Imbrium formed when a proto-planet from the asteroid belt collided with the moon during the Late Heavy Bombardment. The impact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basin Groups
Basin Groups refers to 9 subdivisions of the lunar Pre-Nectarian geologic period. It is the second era of the Hadean. Definition The motivation for creating the Basin Groups subdivisions was to place 30 pre-Nectarian impact basins into 9 relative age groups. The relative age of the first basin in each group is based on crater densities and superposition relationships, whereas the other basins are included based on weaker grounds. Basin Group 1 has no official age for its base, and the boundary between Basin Group 9 and the Nectarian period is defined by the formation of the Nectaris impact basin. The age of the Nectaris basin is somewhat contentious, with the most frequently cited numbers placing it at 3.92 Ga, or more infrequently at 3.85 Ga. Recently, however, it has been suggested that the Nectaris basin could be, in fact, much older and might have formed at ~4.1 Ga. Basin Groups are not used as a geologic period on any of the United States Geological Survey lunar geologic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptic Era
Cryptic may refer to: In science: * Cryptic species complex, a group of species that are very difficult to distinguish from one another * Crypsis, the ability of animals to blend in to avoid observation * Cryptic era, earliest period of the Earth In music: * ''Cryptic'' (album), by Edge of Sanity * Cryptic, a Minnesota-based music group formed by Brownmark In games and entertainment: * Cryptic crossword, a type of word puzzle, known colloquially as ''Cryptics'' * Cryptic Studios Cryptic Studios is an American video game developer specializing in massively multiplayer online role-playing games. It is headquartered in Los Gatos, California and was a wholly owned Perfect World subsidiary, and is now owned by Embracer Gro ..., video game developer * Cryptics, characters from the role playing game, '' Demon: The Fallen'' {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
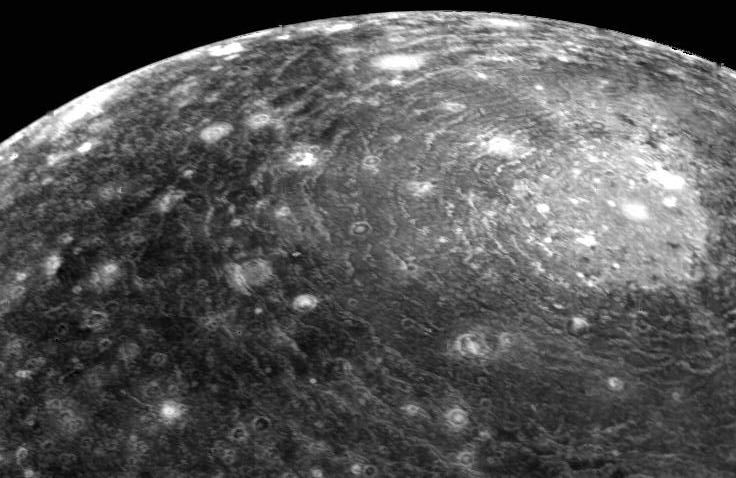
South Pole–Aitken Basin
The South Pole–Aitken basin (SPA Basin, ) is an immense impact crater on the far side of the Moon. At roughly in diameter and between deep, it is one of the largest known impact craters in the Solar System. It is the largest, oldest, and deepest basin recognized on the Moon. It is estimated that it was formed 4.2 to 4.3 billion years ago, during the Pre-Nectarian epoch. It was named for two features on opposite sides of the basin: the lunar South Pole at one end and the crater Aitken on the northern end. The outer rim of this basin can be seen from Earth as a huge mountain chain located on the Moon's southern limb, sometimes informally called "Leibnitz mountains". On 3 January 2019, the Chang'e 4, a Chinese spacecraft, landed in the basin, specifically within a crater called Von Kármán. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Side Of The Moon
The near side of the Moon is the lunar hemisphere that always faces towards Earth, opposite to the far side. Only one side of the Moon is visible from Earth because the Moon rotates on its axis at the same rate that the Moon orbits the Earth—a situation known as tidal locking. The Moon is directly illuminated by the Sun, and the cyclically varying viewing conditions cause the lunar phases. Sometimes the dark portion of the Moon is faintly visible due to earthshine, which is indirect sunlight reflected from the surface of Earth and onto the Moon. Since the Moon's orbit is both somewhat elliptical and inclined to its equatorial plane, libration allows up to 59% of the Moon's surface to be viewed from Earth (though only half at any moment from any point). Orientation The image of the Moon here is drawn as is normally shown on maps, that is with north on top and west to the left. Astronomers traditionally turn the map to have south on top to correspond with the northern-h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-ring Impact Basin
A multi-ringed basin (also a multi-ring impact basin) is not a simple bowl-shaped crater, or a peak ring crater, but one containing multiple concentric topographic rings; a multi-ringed basin could be described as a massive impact crater, surrounded by circular chains of mountains resembling rings on a bull's-eye. A multi-ringed basin may have an area of many thousands of square kilometres. An impact crater of diameter bigger than about is referred to as a ''basin''. __TOC__ The structure of multi-ring basins In adjacent rings, the ratio of the diameters approximates :1 ≈ 1.41 to 1.''Moons & Planets'', William K. Hartmann, 2005, p.255ff Formation To start, a peak ring crater has * one peak-ring, i.e., a crater rim, which is generally circular, ''and'' * a mountainous region which surrounds the basin center. A multi-ringed basin has an important difference, which is multiple peak-rings. In extremely large collisions, following the impact the rebound of the surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mare Nectaris
Mare Nectaris (Latin ''nectaris'', the "Sea of Nectar") is a small lunar mare or sea (a volcanic lava plain noticeably darker than the rest of the Moon's surface) located south of Mare Tranquillitatis southwest of Mare Fecunditatis, on the near side of the moon. Montes Pyrenaeus borders the mare to the east and Sinus Asperitatis fuses to its northwestern edge. It is 84,000 square kilometers in size. Several large craters are situated at the borders of Mare Nectaris. The biggest one is lava-filled Fracastorius (124 km), which fuses with southern coast of the Sea. A prominent trio of 100-km craters Theophilus, Cyrillus and Catharina is located near northwestern coast. Other notable feature is a "ghost crater" Daguerre, almost entirely covered with lava, in the northern part of Mare Nectaris. Mare Nectaris is located in the central part of 860-km-diameter impact basin, which was formed 3.8–3.9 billion years ago. This event marks the beginning of Nectarian period of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Recovery And Interior Laboratory
The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) was an American lunar science mission in NASA's Discovery Program which used high-quality gravitational field mapping of the Moon to determine its interior structure. The two small spacecraft GRAIL A (Ebb) and GRAIL B (Flow) were launched on 10 September 2011 aboard a single launch vehicle: the most-powerful configuration of a Delta II, the 7920H-10. GRAIL A separated from the rocket about nine minutes after launch, GRAIL B followed about eight minutes later. They arrived at their orbits around the Moon 25 hours apart. The first probe entered orbit on 31 December 2011 and the second followed on 1 January 2012. The two spacecraft impacted the Lunar surface on December 17, 2012. Overview Maria Zuber of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology was GRAIL's principal investigator. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory managed the project. NASA budgeted US$496 million for the program to include spacecraft and instrument development, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rift Valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear depression may subsequently be further deepened by the forces of erosion. More generally the valley is likely to be filled with sedimentary deposits derived from the rift flanks and the surrounding areas. In many cases rift lakes are formed. One of the best known examples of this process is the East African Rift. On Earth, rifts can occur at all elevations, from the sea floor to plateaus and mountain ranges in continental crust or in oceanic crust. They are often associated with a number of adjoining subsidiary or co-extensive valleys, which are typically considered part of the principal rift valley geologically. Earth's rift valleys The most extensive rift valley is located along the crest of the mid-ocean ridge system and is the result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanus Procellarum
Oceanus Procellarum ( la, Ōceanus procellārum, lit=Ocean of Storms) is a vast lunar mare on the western edge of the near side of the Moon. It is the only one of the lunar maria to be called an "Oceanus" (ocean), due to its size: Oceanus Procellarum is the largest of the maria ("seas"), stretching more than across its north–south axis and covering roughly , accounting for 10.5% of the total lunar surface area. Characteristics Like all lunar maria, Oceanus Procellarum was formed by ancient volcanic eruptions resulting in basaltic floods that covered the region in a thick, nearly flat layer of solidified magma. Basalts in Oceanus Procellarum have been estimated to be as young as one billion years old. Unlike the other lunar maria, however, Oceanus Procellarum may or may not be contained within a single, well-defined impact basin. Around its edges lie many minor bays and seas, including Sinus Roris to the north, and Mare Nubium and Mare Humorum to the south. To the northeas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

.gif)



.png)