|
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means ''surgical excision of a lobe''. This may refer to a lobe of the lung (also simply called a lobectomy), a lobe of the thyroid ( hemithyroidectomy), a lobe of the brain (as in anterior temporal lobectomy), or a lobe of the liver (hepatectomy). __TOC__ Lung lobectomy A lobectomy of the lung is performed in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. It is not performed on patients that have lung cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Tumor size, type, and location are major factors as to whether a lobectomy is performed. This can be due to cancer or smoking. Lung lobectomies are performed on patients as young as eleven or twelve who have no cancer or smoking history, but have conditions from birth or early childhood that necessitate the operation. Such patients will have reduced lung capacity which tends to limit their range of activities through life. They often need to use inhalers on a daily basis, and are often classified as being asthma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
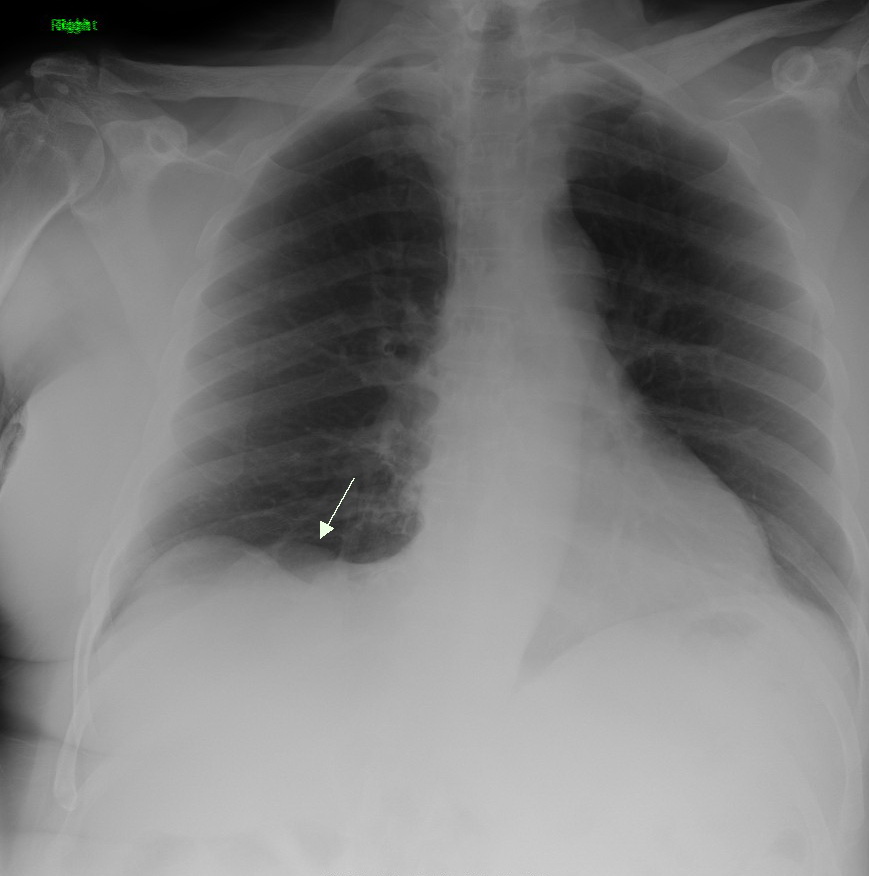
Lobectomy (lung)
Lobectomy of the lung is a surgical operation where a lobe of the lung is removed. It is done to remove a portion of diseased lung, such as early stage lung cancer. In addition to cancer, a lobectomy can also help to treat such things as a fungal infection, emphysema and tuberculosis. Administration The most common type of lobectomy is known as a thoracotomy. When this type of surgery is done the chest is opened up. An incision will be made on the side of the chest where the affected area of the lung is located. The incision will be in between the two ribs located in that area. The surgeon will then be able to have access to the chest cavity once the two involved ribs have been pried open. The surgeon will then be able to remove the lobe where the problem is contained. Another less invasive lobectomy procedure can be performed through a video assisted surgery, where the surgeon does not need to pry the two ribs open in order to get access. A few small incisions are made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Temporal Lobectomy
Anterior temporal lobectomy is the complete or partial removal of the anterior portion of the temporal lobe of the brain. The exact boundaries for removal can vary slightly in practice and between neurosurgeons. It is a treatment option for temporal lobe epilepsy for those in whom anticonvulsant medications do not control epileptic seizures, and who have frequent seizures, and who additionally qualify based on a Wada test, WADA test to localize the dominant hemisphere for language module. __TOC__ Techniques The techniques for removing temporal lobe tissue vary from resection of large amounts of tissue, including lateral temporal cortex along with medial structures, from using more restricted anterior temporal lobectomy (ATL) to more restricted removal of only the medial structures (selective amygdalohippocampectomy). Nearly all reports of seizure outcome following these procedures indicate that the best outcome group includes patients with MRI evidence of Mesial Temporal Sclerosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemithyroidectomy
A thyroidectomy is an operation that involves the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. In general surgery, endocrine or head and neck surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other condition of the thyroid gland (such as hyperthyroidism) or goiter. Other indications for surgery include cosmetic (very enlarged thyroid), or symptomatic obstruction (causing difficulties in swallowing or breathing). Thyroidectomy is a common surgical procedure that has several potential complications or sequelae including: temporary or permanent change in voice, temporary or permanently low calcium, need for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement, bleeding, infection, and the remote possibility of airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. Complications are uncommon when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon. The thyroid produces several hormones, such as thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocellular Adenoma
Hepatocellular adenoma (also known as hepatic adenoma or hepadenoma) is a rare, benign liver tumor. It most commonly occurs in people with elevated systemic levels of estrogen, classically in women taking estrogen-containing oral contraceptive medication. Signs and symptoms About 25–50% of hepatic adenomas cause pain in the right upper quadrant or epigastric region of the abdomen. Since hepatic adenomas can be large (8–15 cm), patients may notice a palpable mass. However, hepatic adenomas are usually asymptomatic, and may be discovered incidentally on imaging ordered for some unrelated reason. Large hepatic adenomas have a tendency to rupture and bleed massively inside the abdomen. If not treated, there is a 30% risk of bleeding. Bleeding may lead to hypotension, tachycardia, and sweating ( diaphoresis). Related Conditions Hepatic adenomas are related to glycogen storage diseases, type 1 diabetes, as well as anabolic steroid use. Diagnosis Hepatic adenoma is usually de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margins Of A Lobectomy
Margin may refer to: Physical or graphical edges *Margin (typography), the white space that surrounds the content of a page *Continental margin, the zone of the ocean floor that separates the thin oceanic crust from thick continental crust *Leaf margin, the edge of a leaf *Resection margin, the tissue near a tumor that is removed to ensure that no cancer cells are left behind Economics and finance *Margin of profit, the fraction of revenue that is left after paying expenses * Margin (economics), a set of constraints conceptualised as a border *Margin (finance), a type of financial collateral used to cover credit risk * ''Margin'' (journal), an economics journal *Contribution margin *Gross margin Figurative edges * Margin (machine learning), the distance between a decision boundary and a data point *Marginal frequency distribution, in statistics ( Frequency distribution § Joint frequency distributions) Other uses * ''Margins'' (film), a 2022 Italian film by Niccolò Falsetti * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatectomy
Hepatectomy is the surgical resection (removal of all or part) of the liver. While the term is often employed for the removal of the liver from a liver transplant donor, this article will focus on partial resections of hepatic tissue and hepatoportoenterostomy. History The first hepatectomies were reported by Dr. Ichio Honjo (1913–1987) of ( Kyoto University) in 1949, and Dr. Jean-Louis Lortat-Jacob (1908–1992) of France in 1952. In the latter case, the patient was a 58-year-old woman diagnosed with colorectal cancer which had metastasized to the liver. Indications Most hepatectomies are performed for the treatment of hepatic neoplasms, both benign or malign. Benign neoplasms include hepatocellular adenoma, hepatic hemangioma and focal nodular hyperplasia. The most common malignant neoplasms (cancers) of the liver are metastases; those arising from colorectal cancer are among the most common, and the most amenable to surgical resection. The most common primary malignant tum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled growth can metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |