|
Limerick (poetry)
A limerick ( ) is a form of verse, usually humorous and frequently rude, in five-line, predominantly trimeter with a strict rhyme scheme of AABBA, in which the first, second and fifth line rhyme, while the third and fourth lines are shorter and share a different rhyme. The following example is a limerick of unknown origin: The form appeared in England in the early years of the 18th century. It was popularized by Edward Lear in the 19th century, although he did not use the term. Gershon Legman, who compiled the largest and most scholarly anthology, held that the true limerick as a folk form is always obscene, and cites similar opinions by Arnold Bennett and George Bernard Shaw, describing the clean limerick as a "periodic fad and object of magazine contests, rarely rising above mediocrity". From a folkloric point of view, the form is essentially transgressive; violation of taboo is part of its function. Form The standard form of a limerick is a stanza of five lines, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick On The Walls Of Limerick
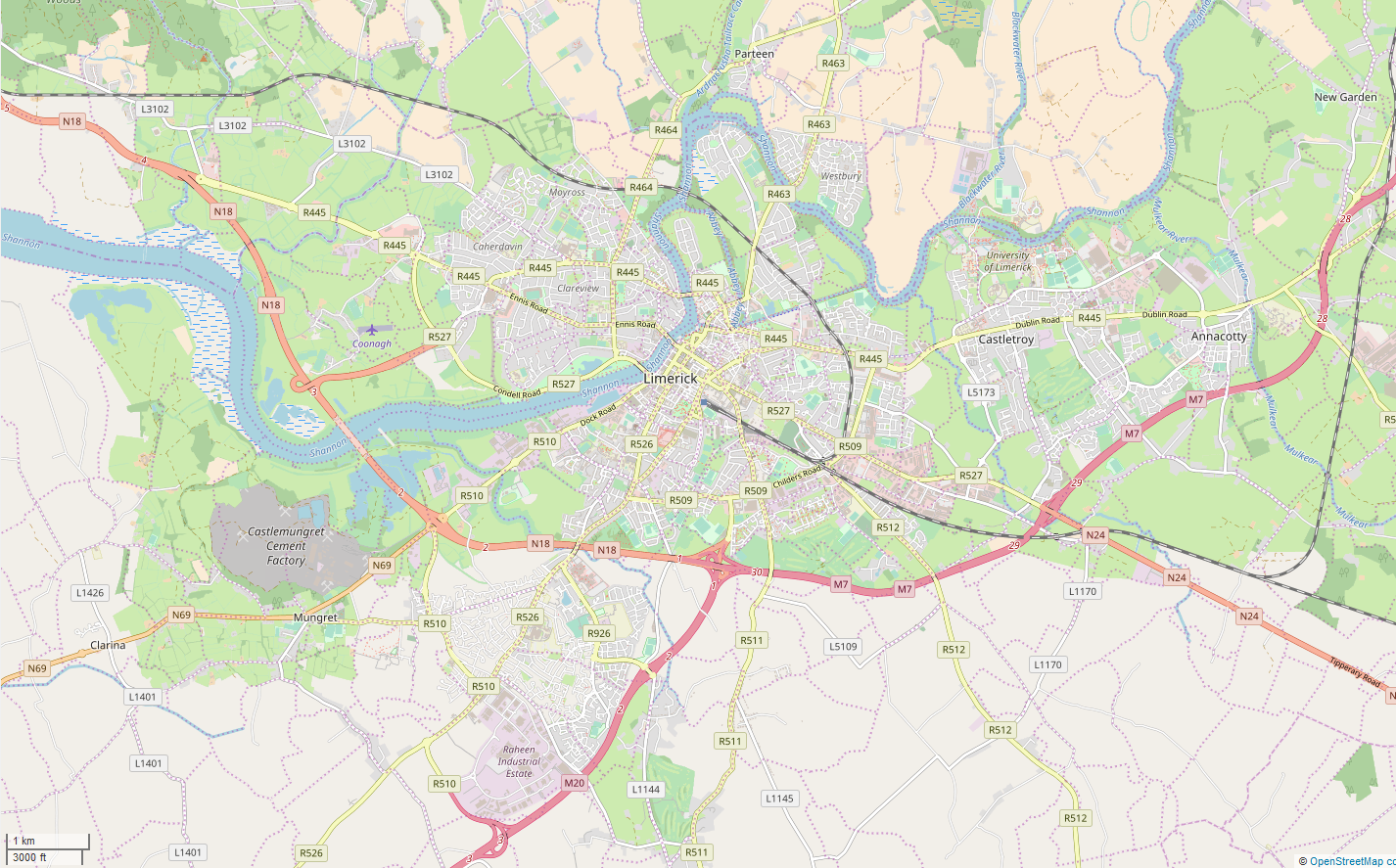
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 census, Limerick is the third-most populous urban area in the state, and the fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland at the 2011 census. The city lies on the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey Rivers. Limerick is also located at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the local authority for the city. Geography and political subdivisions At the 2016 census, the Metropolitan District of Limerick had a population of 104,952. On 1 June 2014 following the merger of Limerick City and County Council, a new Metropolitan District of Limerick was formed within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anapaest
An anapaest (; also spelled anapæst or anapest, also called antidactylus) is a metrical foot used in formal poetry. In classical quantitative meters it consists of two short syllables followed by a long one; in accentual stress meters it consists of two unstressed syllables followed by one stressed syllable. It may be seen as a reversed dactyl. This word comes from the Greek , ''anápaistos'', literally "struck back" and in a poetic context "a dactyl reversed". Because of its length and the fact that it ends with a stressed syllable and so allows for strong rhymes, anapaest can produce a very rolling verse, and allows for long lines with a great deal of internal complexity. Apart from their independent role, anapaests are sometimes used as substitutions in iambic verse. In strict iambic pentameter, anapaests are rare, but they are found with some frequency in freer versions of the iambic line, such as the verse of Shakespeare's last plays, or the lyric poetry of the 19th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 census, Limerick is the third-most populous urban area in the state, and the fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland at the 2011 census. The city lies on the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey Rivers. Limerick is also located at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the local authority for the city. Geography and political subdivisions At the 2016 census, the Metropolitan District of Limerick had a population of 104,952. On 1 June 2014 following the merger of Limerick City and County Council, a new Metropolitan District of Limerick was formed withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Abercrombie (linguist)
David Abercrombie (19 December 1909 – 4 July 1992) was a British phonetician who established the Department of Phonetics at the University of Edinburgh. He was a student of J. R. Firth and Daniel Jones. He retired as Professor of Phonetics in 1980 and died in Edinburgh at the age of 82. Biography Abercrombie was born in Birkenhead on 19 December 1909. His father, Lascelles Abercrombie was a poet and his mother was Catherine, née Gwatkin, one of his three younger siblings was Michael Abercrombie, biologist. He grew up in Ryton, Gloucestershire, before returning to Cheshire on the outbreak of World War I, and moving to Leeds in 1922, when his father became the chair of English Literature at Leeds University , mottoeng = And knowledge will be increased , established = 1831 – Leeds School of Medicine1874 – Yorkshire College of Science1884 - Yorkshire College1887 – affiliated to the federal Victoria University1904 – University of Leeds , t .... He attended Leeds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Song
A drinking song is a song sung while drinking alcohol. Most drinking songs are folk songs or commercium songs, and may be varied from person to person and region to region, in both the lyrics and in the music. In Germany, drinking songs are called ''Trinklieder''. In Sweden, where they are called ''dryckesvisor'', there are drinking songs associated with Christmas, Midsummer, and other celebrations. An example of such a song is " Helan går". In Spain, Asturias, patria querida (the anthem of Asturias) is usually depicted as a drinking song. In France, historical types of drinking songs are Chanson pour boire and Air à boire. History The first record of a drinking song dates to the 11th century, and derives from the Carmina Burana, a 13th-century historical collection of poems, educational songs, love sonnets and "entertainment" or drinking songs. In popular culture Musical artist Homebrew Stew (Rich Stewart) wrote a magazine article in the November 2002 issue of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick (song)
The "Limerick" is a traditional humorous drinking song with many obscene verses. The tune usually used for sung limericks is traditionally "Cielito Lindo," with the words arranged in the form of a limerick. Recorded versions * The Limerick Song has been commercially recorded many times. The earliest version of limericks being sung is 1905 under the title Fol-The-Rol-Lol as sung by Edward M. Favor on Edison records. The earliest date for limericks being sung to the "Gay Caballero" tune is May 11, 1931 on the recording titled Rhymes sung by Jack Hylton which was issued on Decca records. Printed versions The earliest printed date for limericks being sung is 1928 in the book ''A Collection of Sea Songs and Ditties from the Stores of Tom E. Jones''.Jones. Unpaginated. Song #48. Since many of the verses used for this song are bawdy the song tended to get issued in rare, underground mimeographed songbooks. Some of these are (in chronological order): :* 1934. Leech. Variant choruse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrain
A refrain (from Vulgar Latin ''refringere'', "to repeat", and later from Old French ''refraindre'') is the line or lines that are repeated in music or in poetry — the "chorus" of a song. Poetic fixed forms that feature refrains include the villanelle, the virelay, and the sestina. In popular music, the refrain or chorus may contrast with the verse melodically, rhythmically, and harmonically; it may assume a higher level of dynamics and activity, often with added instrumentation. Chorus form, or strophic form, is a sectional and/or additive way of structuring a piece of music based on the repetition of one formal section or block played repeatedly. Usage in history In music, a refrain has two parts: the lyrics of the song, and the melody. Sometimes refrains vary their words slightly when repeated; recognizability is given to the refrain by the fact that it is always sung to the same tune, and the rhymes, if present, are preserved despite the variations of the words. Suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Play
Word play or wordplay (also: play-on-words) is a literary technique and a form of wit in which words used become the main subject of the work, primarily for the purpose of intended effect or amusement. Examples of word play include puns, phonetic mix-ups such as spoonerisms, obscure words and meanings, clever rhetorical excursions, oddly formed sentences, double entendres, and telling character names (such as in the play '' The Importance of Being Earnest'', ''Ernest'' being a given name that sounds exactly like the adjective ''earnest''). Word play is quite common in oral cultures as a method of reinforcing meaning. Examples of text-based ( orthographic) word play are found in languages with or without alphabet-based scripts, such as homophonic puns in Mandarin Chinese. Techniques Some techniques often used in word play include interpreting idioms literally and creating contradictions and redundancies, as in Tom Swifties: :"Hurry up and get to the back of the ship," To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assonance
Assonance is a resemblance in the sounds of words/syllables either between their vowels (e.g., ''meat, bean'') or between their consonants (e.g., ''keep, cape''). However, assonance between consonants is generally called ''consonance'' in American usage. The two types are often combined, as between the words ''six'' and ''switch'', in which the vowels are identical, and the consonants are similar but not completely identical. If there is repetition of the same vowel or some similar vowels in literary work, especially in stressed syllables, this may be termed "vowel harmony" in poetry (though linguists have a different definition of "vowel harmony"). A special case of assonance is rhyme, in which the endings of words (generally beginning with the vowel sound of the last stressed syllable) are identical—as in ''fog'' and ''log'' or ''history'' and ''mystery''. Vocalic assonance is an important element in verse. Assonance occurs more often in verse than in prose; it is used in Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliteration
Alliteration is the conspicuous repetition of initial consonant sounds of nearby words in a phrase, often used as a literary device. A familiar example is "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers". Alliteration is used poetically in various languages around the world, including Arabic, Irish, German, Mongolian, Hungarian, American Sign Language, Somali, Finnish, Icelandic. Historical use The word ''alliteration'' comes from the Latin word ''littera'', meaning "letter of the alphabet". It was first coined in a Latin dialogue by the Italian humanist Giovanni Pontano in the 15th century. Alliteration is used in the alliterative verse of Old English, Old Norse, Old High German, Old Saxon, and Old Irish. It was an important ingredient of the Sanskrit shlokas. Alliteration was used in Old English given names. This is evidenced by the unbroken series of 9th century kings of Wessex named Æthelwulf, Æthelbald, Æthelberht, and Æthelred. These were followed in the 10th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Rhyme
In poetry, internal rhyme, or middle rhyme, is rhyme that occurs within a single line of verse, or between internal phrases across multiple lines. By contrast, rhyme between line endings is known as end rhyme. Internal rhyme schemes can be denoted with spaces or commas between lines. For example, denotes a three-line poem with the same internal rhyme on each line, and the same end rhyme on each line (which does not rhyme with the internal rhyme). Examples The following example is in limerick form. Each stressed syllable rhymes with another stressed syllable using one of three rhyme sets. Each rhyme set is indicated by a different highlight color. Note that the yellow rhyme set provides internal rhyme in lines 1, 2, and 5, and end rhymes in lines 3 and 4, whereas the blue set is entirely internal and the pink is exclusively end rhymes. Each time alie for a She well that her are the Of the , and it , But this will ex More than , so some gape and . Percy Dearmer (1867� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term toponymy come from grc, τόπος / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional discourse among geographers. Top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |