|
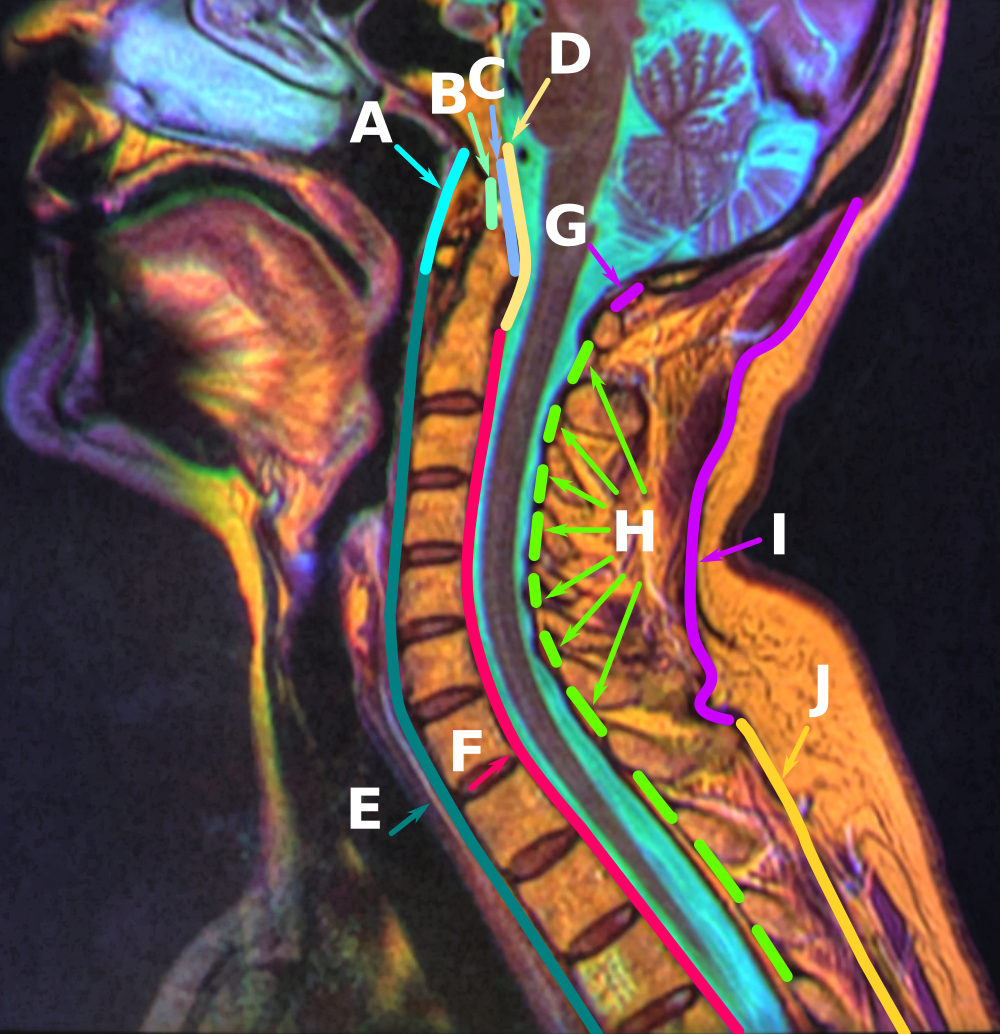
Ligamenta Flava
The ligamenta flava (singular, ''ligamentum flavum'', Latin for ''yellow ligament'') are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They help to preserve upright posture, preventing hyperflexion, and ensuring that the vertebral column straightens after flexion. Hypertrophy can cause spinal stenosis. Structure Each ligamentum flavum connects the laminae two adjacent vertebrae. They begin with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra, continuing down to the junction of the fifth lumbar vertebra and the sacrum. They are best seen from the interior of the vertebral canal. when looked at from the outer surface they appear short, being overlapped by the lamina of the vertebral arch. Each ligament consists of two lateral portions which commence one on either side of the roots of the articular processes, and extend backward to the point where the laminae meet to form the spinous process; the posterior margins of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Arch
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis (anatomy)
In anatomy, the axis (from Latin ''axis'', "axle") or epistropheus is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests. The axis' defining feature is its strong odontoid process (bony protrusion) known as the dens, which rises dorsally from the rest of the bone. Structure The body is deeper in front or in the back and is prolonged downward anteriorly to overlap the upper and front part of the third vertebra. It presents a median longitudinal ridge in front, separating two lateral depressions for the attachment of the longus colli muscles. Odontoid Process of Axis (Dens) The dens, also called the odontoid process or the peg, is the most pronounced projecting feature of the axis. The dens exhibits a slight constriction where it joins the main body of the vertebra. The condition where the dens is separated from the body of the axis is called ''os odontoideum'' and may cause nerve and circulation compression syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. It is named for Atlas of Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the globe, it supports the entire head. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the head to nod up and down on the vertebral column. The dens acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side. The atlas's chief peculiarity is that it has no body. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. The atlas and axis are important neurologically because the brainstem extends down to the axis. Structure Anterior arch The anter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbar
In tetrapod Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ... anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means ''of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum.'' The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lower vertebral column, spine, or as an area of the back in its proximity. In human anatomy the five lumbar vertebrae (vertebrae in the lumbar region of the back) are the largest and strongest in the movable part of the spinal column, and can be distinguished by the absence of a foramen transversarium, foramen in the transverse process, and by the absence of facets on the sides of the body. In most mammals, the lumbar region of the spine curves outward. The actual spinal cord terminates between vertebrae one a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' " breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also called by its Latin names, or , although when used alone, in context, the word ''cervix'' more often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Thus the adjective ''cervical' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Tissue
Elastic fibers (or yellow fibers) are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan. Elastic tissue is classified as "connective tissue proper". Elastic fibers are formed via elastogenesis, a highly complex process involving several key proteins including fibulin-4, fibulin-5, latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 4, and microfibril associated protein 4. In this process tropoelastin, the soluble monomeric precursor to elastic fibers is produced by elastogenic cells and chaperoned to the cell surface. Following excretion from the cell, tropoelastin self associates into ~200 nm particles by coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinous Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Processes
The articular processes or zygapophyses ( Greek ζυγον = " yoke" (because it links two vertebrae) + απο = "away" + φυσις = " process") of a vertebra are projections of the vertebra that serve the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the ''articular facet''.Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 Articular processes spring from the junctions of the pedicles and laminæ, and there are two right and left, and two superior and inferior. These stick out of an end of a vertebra to lock with a zygapophysis on the next vertebra, to make the backbone more stable. * The superior processes or prezygapophysis project upward from a lower vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less backward (oblique coronal plane). * The inferior processes or postzygapophysis project downward from a higher vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less forward and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Canal
The spinal canal (or vertebral canal or spinal cavity) is the canal that contains the spinal cord within the vertebral column. The spinal canal is formed by the vertebrae through which the spinal cord passes. It is a process of the dorsal body cavity. This canal is enclosed within the foramen of the vertebrae. In the intervertebral spaces, the canal is protected by the ligamentum flavum posteriorly and the posterior longitudinal ligament anteriorly. Structure The outermost layer of the meninges, the dura mater, is closely associated with the arachnoid mater which in turn is loosely connected to the innermost layer, the pia mater. The meninges divide the spinal canal into the epidural space and the subarachnoid space. The pia mater is closely attached to the spinal cord. A subdural space is generally only present due to trauma and/or pathological situations. The subarachnoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and contains the vessels that supply the spinal cord, nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |