|
Lammerite
Copper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is or . Uses Copper arsenate is an insecticide used in agriculture. It is also used as a herbicide, fungicide, and a rodenticide. It is also used as a poison in slug baits. Copper arsenate can also be a misnomer for copper arsenite, especially when meant as a pigment. Natural occurrences Anhydrous copper arsenate, Cu3(AsO4)2, is found in nature as the mineral lammerite. Copper arsenate tetrahydrate, Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, occurs naturally as the mineral rollandite. Related compounds Copper arsenate hydroxide or basic copper arsenate (Cu(OH)AsO4) is a basic variant with CAS number . It is found naturally as the mineral olivenite. It is used as an insecticide, fungicide, and miticide. Its use is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45% of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water. Although common in nature—both terrestrially and in the outer planets of the Solar System—and in wide use, ammonia is bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miticide
Acaricides are pesticides that kill members of the arachnid subclass ''Acari'', which includes ticks and mites. Acaricides are used both in medicine and agriculture, although the desired selective toxicity differs between the two fields. Terminology More specific words are sometimes used, depending upon the targeted group: * "Ixodicides" are substances that kill ticks. * "Miticides" are substances that kill mites. *The term scabicide is more narrow, and refers to agents specifically targeting ''Sarcoptes''. *The term "arachnicide" is more general, and refers to agents that target arachnids. This term is used much more rarely, but occasionally appears in informal writing. As a practical matter, mites are a paraphyletic grouping, and mites and ticks are usually treated as a single group. Examples Examples include: * Permethrin can be applied as a spray. The effects are not limited to mites: lice, cockroaches, fleas, mosquitos, and other insects will be affected. * Ivermectin can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenical Herbicides
Arsenicals are chemical compounds that contain arsenic. In a military context, the term arsenical refer to toxic arsenic compounds that are used as chemical warfare agents. This include blister agents, blood agents and vomiting agents. Examples Blister agents *Ethyldichloroarsine *Lewisite *Methyldichloroarsine * Phenyldichloroarsine Blood agents *Arsine Vomiting agents * Adamsite * Diphenylchlorarsine *Diphenylcyanoarsine Diphenylcyanoarsine, also called Clark 2 (Chlor-Arsen-Kampfstoff 2, being the successor of Clark 1) by the Germans, was discovered in 1918 by Sturniolo and BellinzoniSturniolo, G. und Bellinzoni, G. (1919); ''Boll. chim. pharm.'', 58, 409–410 an ... * Phenyldichloroarsine References Arsenic compounds Chemical weapons Poisons {{Chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Insecticides
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(II) Compounds
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form (native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, c. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenates
The arsenate ion is . An arsenate (compound) is any compound that contains this ion. Arsenates are salts or esters of arsenic acid. The arsenic atom in arsenate has a valency of 5 and is also known as pentavalent arsenic or As(V). Arsenate resembles phosphate in many respects, since arsenic and phosphorus occur in the same group (column) of the periodic table. Arsenates are moderate oxidizers, with an electrode potential of +0.56 V for reduction to arsenites. Occurrence Arsenates occur naturally in a variety of minerals. Those minerals may contain hydrated or anhydrous arsenates. Unlike phosphates, arsenates are not lost from a mineral during weathering. Examples of arsenate-containing minerals include adamite, alarsite, annabergite, erythrite and legrandite. Where two arsenate ions are required to balance the charge in a formula, it is called diarsenate for example trizinc diarsenate, Zn3(AsO4)2. Ions The word arsenate is derived from arsenic acid, H3AsO4. This moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
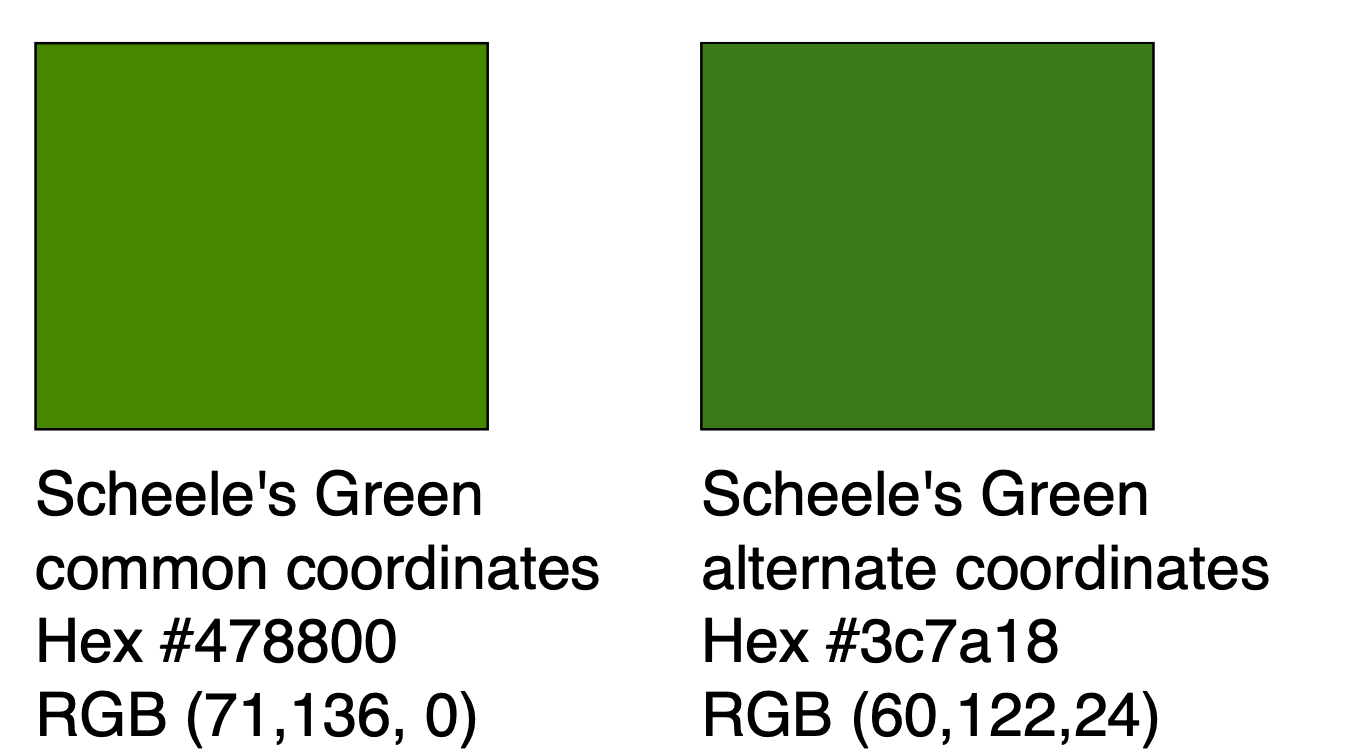
Scheele's Green
Scheele's Green, also called Schloss Green, is chemically a cupric hydrogen arsenite (also called copper arsenite or acidic copper arsenite), . It is chemically related to Paris Green. Scheele's Green was invented in 1775 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. By the end of the 19th century, it had virtually replaced the older green pigments based on copper carbonate. It is a yellowish-green pigment commonly used during the early to mid-19th century in paints as well as being directly incorporated into a variety of products as a colorant. It began to fall out of favor after the 1860s because of its toxicity and the instability of its color in the presence of sulfides and various chemical pollutants. The acutely toxic nature of Scheele's green as well as other arsenic-containing green pigments such as Paris Green may have contributed to the sharp decline in the popularity of the color green in late Victorian society. By the dawn of the 20th century, Scheele's green had completely fallen out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromated Copper Arsenate
Chromated copper arsenate (CCA) is a wood preservative containing compounds of chromium, copper, and arsenic, in various proportions. It is used to impregnate timber and other wood products, especially those intended for outdoor use, in order to protect them from attack by microbes and insects. Like other copper-based wood preservatives, it imparts a greenish tint to treated timber. CCA was invented in 1933 by Indian chemist Sonti Kamesam, and patented in Britain in 1934. It has been used for timber treatment since the mid-1930s, and is marketed under many trade names. In 2003, the United States Environmental Protection Agency and the lumber industry agreed to discontinue the use of CCA-treated wood in most residential construction. This agreement was intended to protect the health of humans and the environment by reducing exposure to the arsenic in CCA-treated wood. As a result of this decision, CCA-treated wood can no longer be used to construct residential structures such as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Arsenate
Calcium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca3(AsO4)2. A colourless salt, it was originally used as a pesticide and as a germicide. It is highly soluble in water, in contrast to lead arsenate, which makes it more toxic. The minerals rauenthalite Ca3(AsO4)2·10H2O and phaunouxite Ca3(AsO4)2·11H2O are hydrates of calcium arsenate. Preparation Calcium arsenate is commonly prepared from disodium hydrogen arsenate and calcium chloride: :2 Na2H sO4 + 3 CaCl2 → 4 NaCl + Ca3 sO4sub>2 + 2 HCl In the 1920s, it was made in large vats by mixing calcium oxide and arsenic oxide. In the United States, 1360 metric tons were produced in 1919, 4540 in 1920, and 7270 in 1922. The composition of commercially available calcium arsenate varies from manufacturer to manufacturer. A typical composition is 80-85% of Ca3(AsO4)2 a basic arsenate probably with a composition of 4CaO.As2O5 together with calcium hydroxide and calcium carbonate. Use as a herbicide It was once a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Arsenate
Lead hydrogen arsenate, also called lead arsenate, acid lead arsenate or LA, chemical formula PbHAsO4, is an inorganic insecticide used primarily against the potato beetle. Lead arsenate was the most extensively used arsenical insecticide.Peryea F.J. 1998. Historical use of lead arsenate insecticides, resulting in soil contamination and implications for soil remediation. Proceedings, 16th World Congress of Soil Science, Montpellier, France. 20-26. Aug. Available online: http://soils.tfrec.wsu.edu/leadhistory.htm Two principal formulations of lead arsenate were marketed: basic lead arsenate (Pb5OH(AsO4)3, CASN: 1327-31-7) and acid lead arsenate (PbHAsO4). Production and structure It is usually produced using the following reaction, which leads to formation of the desired product as a solid precipitate: :Pb(NO3)2 + H3AsO4 → PbHAsO4 +2 HNO3 It has the same structure as the hydrogen phosphate PbHPO4. Like lead sulfate PbSO4, these salts are poorly soluble. Uses As an insecticid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivenite
Olivenite is a copper arsenate mineral, formula Cu2 As O4O H. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system (pseudo-orthorhombic), and is sometimes found in small brilliant crystals of simple prismatic habit terminated by domal faces. More commonly, it occurs as globular aggregates of acicular crystals, these fibrous forms often having a velvety luster; sometimes it is lamellar in structure, or soft and earthy. A characteristic feature, and one to which the name alludes (German, ''Olivenerz'', of A. G. Werner, 1789), is the olive-green color, which varies in shade from blackish-green in the crystals to almost white in the finely fibrous variety known as ''woodcopper''. The hardness is 3, and the specific gravity is 4.3. The mineral was formerly found in some abundance, associated with limonite and quartz, in the upper workings in the copper mines of the St Day district in Cornwall; also near Redruth, and in the Tintic Mining District in Utah. It is a mineral of secondary origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-3D-balls.png)