|
Laminin, Gamma 1
Laminin subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC1'' gene. Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide variety of biological processes including cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, signaling, neurite outgrowth and metastasis. Laminins are composed of 3 non identical chains: laminin alpha, beta and gamma (formerly A, B1, and B2, respectively) and they form a cruciform structure consisting of 3 short arms, each formed by a different chain, and a long arm composed of all 3 chains. Each laminin chain is a multidomain protein encoded by a distinct gene. Several isoforms A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso ... of each chain have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
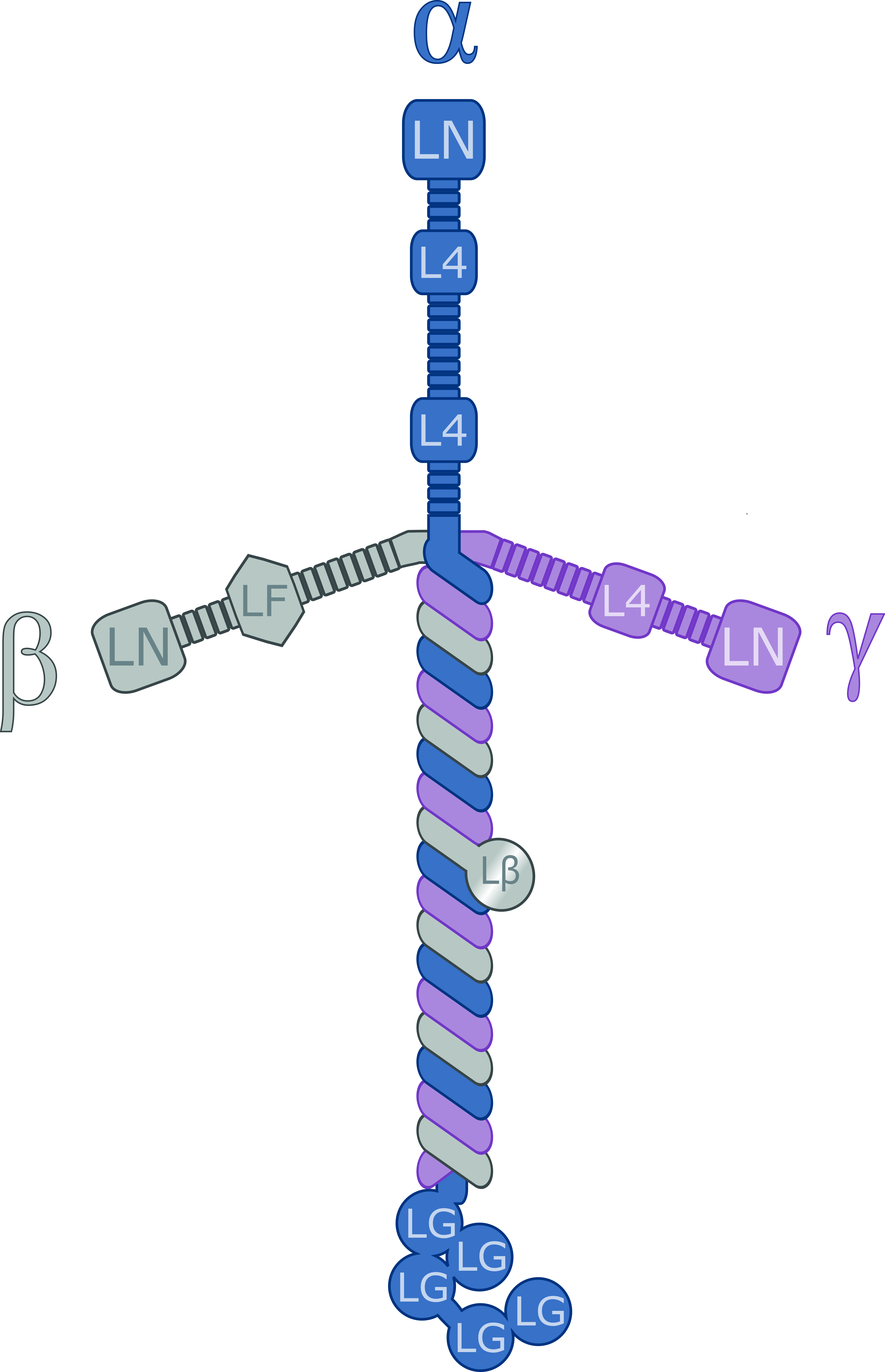
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane and extracellular matrix molecules. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an underlying network of reticular col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments (exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a specific protein in a cell that does not normally express that protein (i.e., heterologous expression), or to sequence or quantify mRNA molecules using DNA based methods (qPCR, RNA-seq). cDNA that codes for a specific protein can be transferred to a recipient cell for expression, often bacterial or yeast expression systems. cDNA is also generated to analyze transcriptomic profiles in bulk tissue, single cells, or single nuclei in assays such as microarrays, qPCR, and RNA-seq. cDNA is also produced naturally by retroviruses (such as HIV-1, HIV-2, simian immunodeficiency virus, etc.) and then integrated into the host's genome, where it creates a provirus. The term ''cDNA'' is also used, typically in a bioinformatics context, to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |