|
Joint Product
In Economics, joint product is a product that results jointly with other products from processing a common input; this common process is also called joint production.Wouters, Mark; Selto, Frank H.; Hilton, Ronald W.; Maher, Michael W. (2012): ''Cost Management: Strategies for Business Decisions'', International Edition, Berkshire (UK), p. 532. A joint product can be the output of a process with fixed or variable proportions. Examples * The processing of crude oil can result in the joint products naphtha, gasoline, jet fuel, kerosene, diesel, heavy fuel oil and asphalt, as well as other petrochemical derivatives. The refinery process has variable proportions depending on the distilling temperatures and cracking intensity. * Cogeneration delivers the joint products of heat and power; trigeneration provides cold, heat and power. With extraction steam turbines, cogeneration has variable proportions; with an internal combustion engine the proportions of heat and power are fixed. * In a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (business)
In marketing, a product is an object, or system, or service made available for consumer use as of the consumer demand; it is anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer. In retailing, products are often referred to as '' merchandise'', and in manufacturing, products are bought as raw materials and then sold as finished goods. A service is also regarded as a type of product. In project management, products are the formal definition of the project deliverables that make up or contribute to delivering the objectives of the project. A related concept is that of a sub-product, a secondary but useful result of a production process. Dangerous products, particularly physical ones, that cause injuries to consumers or bystanders may be subject to product liability. Product classification A product can be classified as tangible or intangible. A tangible product is an actual physical object that can be perceived by touch such as a build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
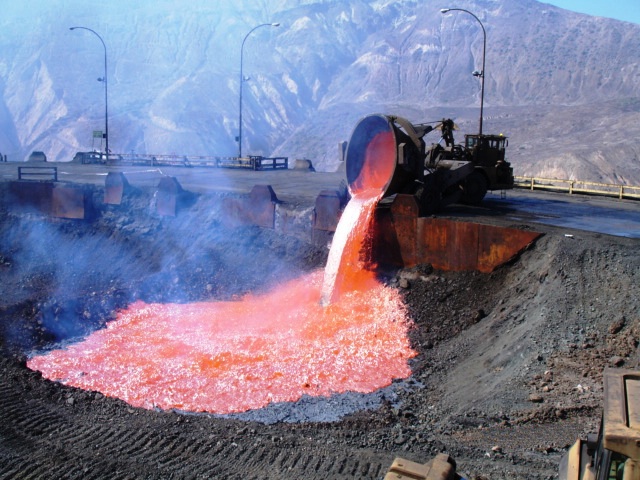
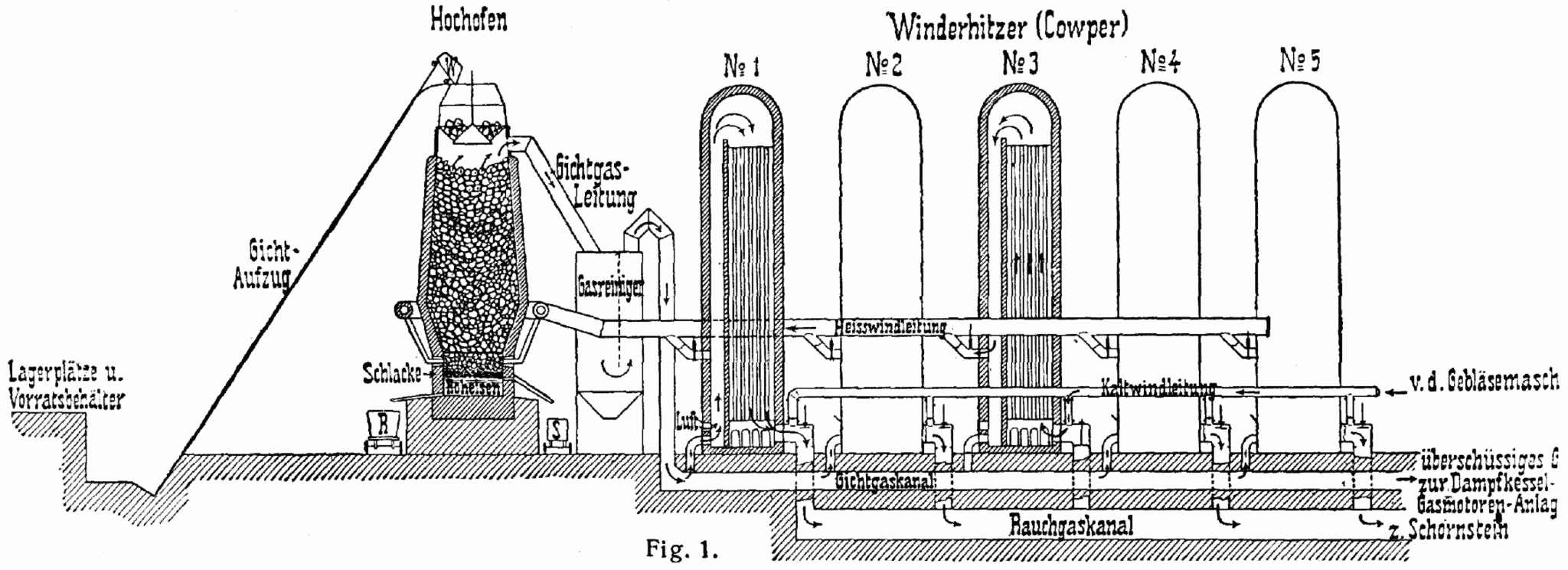
Pig Iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silica and other constituents of dross, which makes it brittle and not useful directly as a material except for limited applications. The traditional shape of the molds used for pig iron ingots is a branching structure formed in sand, with many individual ingots at right angles to a central channel or "runner", resembling a litter of piglets being nursed by a sow. When the metal had cooled and hardened, the smaller ingots (the "pigs") were simply broken from the runner (the "sow"), hence the name "pig iron". As pig iron is intended for remelting, the uneven size of the ingots and the inclusion of small amounts of sand cause only insignificant problems considering the ease of casting and handling them. History Smelting and producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride salts like ammonium chloride ( sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and hydrochloric acid (in the form of ). However, the nature of free chlorine gas as a separate substance was only recognised aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloralkali Process
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor alkali) is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), which are commodity chemicals required by industry. Thirty five million tons of chlorine were prepared by this process in 1987. The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in this process are widely used in the chemical industry. Usually the process is conducted on a brine (an aqueous solution of NaCl), in which case sodium hydroxide (NaOH), hydrogen, and chlorine result. When using calcium chloride or potassium chloride, the products contain calcium or potassium instead of sodium. Related processes are known that use molten NaCl to give chlorine and sodium metal or condensed hydrogen chloride to give hydrogen and chlorine. The process has a high energy consumption, for example around of electricity per tonne of sodium hydroxide produced. Because the proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowper Stove
A regenerative heat exchanger, or more commonly a regenerator, is a type of heat exchanger where heat from the hot fluid is intermittently stored in a thermal storage medium before it is transferred to the cold fluid. To accomplish this the hot fluid is brought into contact with the heat storage medium, then the fluid is displaced with the cold fluid, which absorbs the heat. In regenerative heat exchangers, the fluid on either side of the heat exchanger can be the same fluid. The fluid may go through an external processing step, and then it is flowed back through the heat exchanger in the opposite direction for further processing. Usually the application will use this process cyclically or repetitively. Regenerative heating was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution when it was used in the hot blast process on blast furnaces. It was later used in Glass melting furnace, glass melting furnaces and steel making, to increase the efficiency of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction Material
This is a list of building materials. Many types of building materials are used in the construction industry to create buildings and structures. These categories of materials and products are used by architects and construction project managers to specify the materials and methods used for building projects. Some building materials like cold rolled steel framing are considered modern methods of construction, over the traditionally slower methods like blockwork and timber. Many building materials have a variety of uses, therefore it is always a good idea to consult the manufacturer to check if a product is best suited to your requirements. Catalogs Catalogs distributed by architectural product suppliers are typically organized into these groups. Industry standards The Construction Specifications Institute maintains the following industry standards: * MasterFormat 50 standard divisions of building materials - 2004 edition (current in 2009) *16 Divisions Original 16 division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blast Furnace Gas
Blast furnace gas (BFG) is a by-product of blast furnaces that is generated when the iron ore is reduced with coke to metallic iron. It has a very low heating value, about 93 BTU/cubic foot (3.5 MJ/m3), because it consists of about 51 vol% nitrogen and 22 vol% carbon dioxide, which are not flammable. The rest amounts to around 22 vol% carbon monoxide, which has a fairly low heating value already and 5 vol% hydrogen. Per ton of steel produced via the blast furnace route, 2.5 to 3.5 ton of blast furnace gas is produced. It is commonly used as a fuel within the steel works, but it can be used in boilers and power plants equipped to burn it. It may be combined with natural gas or coke oven gas before combustion or a flame support with richer gas or oil is provided to sustain combustion. Particulate matter is removed so that it can be burned more cleanly. Blast furnace gas is sometimes flared without generating heat or electricity. Blast furnace gas is generated at higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting ( pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-products of recovering non-ferrous materials like copper, nickel, zinc and phosphorus). Within these general categories, slags can be further categorized by their precursor and processing conditions (e.g., Blast furnace (BF) slags, air-cooled blast furnace (ACBF) slag, basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag, and electric arc furnace (EAF) slag) . Due to the large demand for these materials, slag production has also significantly increased throughout the years despite recycling (most notably in the iron and steelmaking industries) and upcycling efforts. The World Steel Association (WSA) estimates that 600 kg of by-products (~90 wt% is slags) are generated per tonne of steel produced. Composition Slag is usually a mixture of metal oxides and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blast Furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric pressure. In a blast furnace, fuel ( coke), ores, and flux ( limestone) are continuously supplied through the top of the furnace, while a hot blast of air (sometimes with oxygen enrichment) is blown into the lower section of the furnace through a series of pipes called tuyeres, so that the chemical reactions take place throughout the furnace as the material falls downward. The end products are usually molten metal and slag phases tapped from the bottom, and waste gases ( flue gas) exiting from the top of the furnace. The downward flow of the ore along with the flux in contact with an upflow of hot, carbon monoxide-rich combustion gases is a countercurrent exchange and chemical reaction process. In contrast, air furnaces (such as reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |