|
Journal Pagination
Pagination, also known as paging, is the process of dividing a document into discrete pages, either electronic pages or printed pages. In reference to books produced without a computer, pagination can mean the consecutive page numbering to indicate the proper order of the pages, which was rarely found in documents pre-dating 1500, and only became common practice c. 1550, when it replaced foliation, which numbered only the front sides of folios. Pagination in word processing, desktop publishing, and digital typesetting Word processing, desktop publishing, and digital typesetting are technologies built on the idea of print as the intended final output medium, although nowadays it is understood that plenty of the content produced through these pathways will be viewed onscreen as electronic pages by most users rather than being printed on paper. All of these software tools are capable of flowing the content through algorithms to decide the pagination. For example, they all inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Page (paper)
A page is one side of a Recto and verso, leaf (a sheet or half-sheet) of paper, parchment or other material (or electronic media) in a book, magazine, newspaper, or other collection of sheets, on which text or illustrations can be printed, written or drawn, to create documents. It can be used as a measure of communicating general quantity of information ("That topic covers twelve pages") or more specific quantity ("there are 535 words in a standard page in twelve point font type"). Etymology The word "page" comes from the Latin term , which means, "a written page, leaf, sheet", which in turn comes from an earlier meaning "to create a row of vines that form a rectangle".Emmanuel Souchier, "Histoires de pages et pages d'histoire", dans iarchive:laventuredesecri0000expo, L'Aventure des écritures, Paris, Bibliothèque nationale de France, 1999. . The Latin word derives from the verb , which means to stake out boundaries when planting vineyards. The page in English lexicon Compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widows And Orphans
In typesetting, widows and orphans are single lines of text from a paragraph that dangle at either the beginning or end of a block of text, or form a very short final line at the end of a paragraph. When split across pages, they occur at either the head or foot of a page (or column), unaccompanied by additional lines from the same paragraph. The pairing of the two terms with their definitions has no consistent standard across the industry; some sources use the opposite meanings as others. Additionally, runts (which varying sources also call widows or orphans) are cases where a paragraph anywhere on a page ends with a very short final line. They give an impression of excessive empty space between that and the following paragraph. Definitions For the purposes of this article, the following meanings are given to the terms. Some sources have these reversed due to a lack of industry standardization. ;Widow (sometimes called orphan): A paragraph-ending line that falls at the begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experience Design
User experience design (UX design, UXD, UED, or XD), upon which is the centralized requirements for "User Experience Design Research" (also known as UX Design Research), defines the experience a user would go through when interacting with a company, its services, and its products. User experience design is a user centered design approach because it considers the user's experience when using a product or platform. Research, data analysis, and test results drive design decisions in UX design rather than aesthetic preferences and opinions, for which is known as UX Design Research. Unlike user interface design, which focuses solely on the design of a computer interface, UX design encompasses all aspects of a user's perceived experience with a product or website, such as its usability, usefulness, desirability, brand perception, and overall performance. UX design is also an element of the customer experience (CX), and encompasses all design aspects and design stages that are around a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interactivity
Across the many fields concerned with interactivity, including information science, computer science, human-computer interaction, communication, and industrial design, there is little agreement over the meaning of the term "interactivity", but most definitions are related to interaction between users and computers and other machines through a user interface. Interactivity can however also refer to interaction between people. It nevertheless usually refers to interaction between people and computers – and sometimes to interaction between computers – through software, hardware, and networks. Multiple views on interactivity exist. In the "contingency view" of interactivity, there are three levels: #Not interactive, when a message is not related to previous messages. #Reactive, when a message is related only to one immediately previous message. #Interactive, when a message is related to a number of previous messages and to the relationship between them. One body of research h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-user
In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrators, database administrators, information technology (IT) experts, software professionals, and computer technicians. End users typically do not possess the technical understanding or skill of the product designers, a fact easily overlooked and forgotten by designers: leading to features creating low customer satisfaction. In information technology, end users are not customers in the usual sense—they are typically employees of the customer. For example, if a large retail corporation buys a software package for its employees to use, even though the large retail corporation was the ''customer'' that purchased the software, the end users are the employees of the company, who will use the software at work. Context End users are one of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Page
A web page (or webpage) is a World Wide Web, Web document that is accessed in a web browser. A website typically consists of many web pages hyperlink, linked together under a common domain name. The term "web page" is therefore a metaphor of paper pages bound together into a book. Navigation Each web page is identified by a distinct URL, Uniform Resource Locator (URL). When the user inputs a URL into their web browser, the browser retrieves the necessary content from a web server and then browser engine, transforms it into an interactive visual representation on the user's screen. If the user point and click, clicks or touchscreen, taps a hyperlink, link, the browser repeats this process to load the new URL, which could be part of the current website or a different one. The browser has web browser#Features, features, such as the address bar, that indicate which page is displayed. Elements A web page is a structured document. The core element is a text file written in the HT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
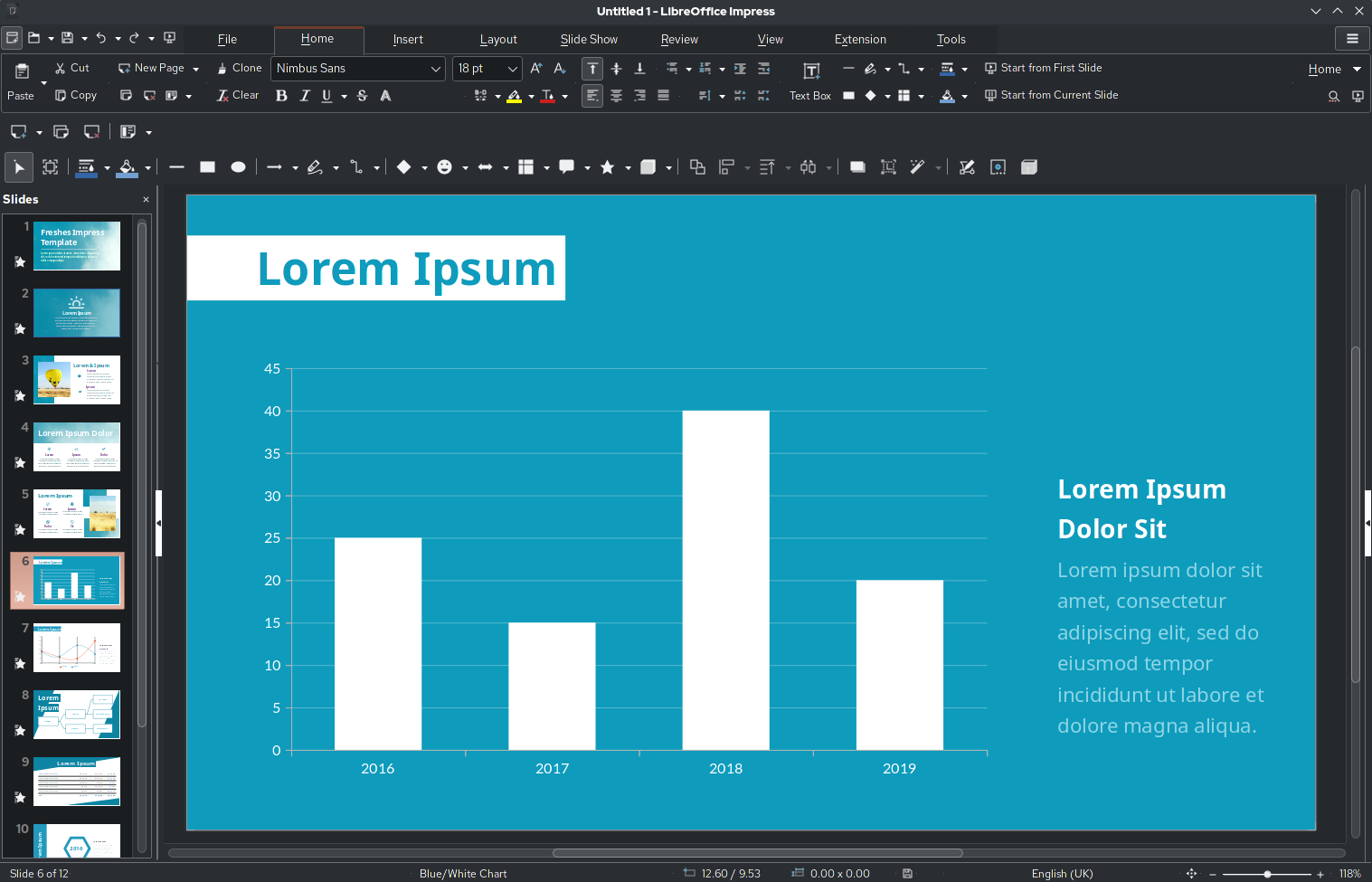
Presentation Software
In computing, a presentation program (also called presentation software) is a software package used to display information in the form of a slide show. It has three major functions: * an editor that allows text to be inserted and formatted * a method for inserting and manipulating graphic images and media clips * a slide-show system to display the content Presentation software can be viewed as enabling a functionally-specific category of electronic media, with its own distinct culture and practices as compared to traditional presentation media (such as blackboards, whiteboards and flip charts). Presentations in this mode of delivery have become pervasive in many aspects of business communication, especially in business planning, as well as in academic-conference and professional conference settings, and in the knowledge economy generally, where ideas are a primary work output. Presentations may also feature prominently in political settings, especially in workplace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Display Technology
A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form (the latter used for example in tactile electronic displays for blind people). When the input information that is supplied has an electrical signal the display is called an '' electronic display''. Common applications for ''electronic visual displays'' are television sets or computer monitors. Types of electronic displays In use These are the technologies used to create the various displays in use today. * Liquid-crystal display (LCD) ** Light-emitting diode (LED) backlit LCD ** Thin-film transistor (TFT) LCD ** Quantum dot (QLED) display * Light-emitting diode (LED) display ** OLED display ** AMOLED display ** Super AMOLED display Segment displays Some displays can show only digits or alphanumeric characters. They are called segment displays, because they are composed of several segments that switch on and off to give appearance of desired glyph. The segments are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Paper
Electronic paper or intelligent paper, is a display device that reflects ambient light, mimicking the appearance of ordinary ink on paper – unlike conventional flat-panel displays which need additional energy to emit their own light. This may make them more comfortable to read, and provide a wider viewing angle than most light-emitting displays. The contrast ratio in electronic displays available as of 2008 approaches newspaper, and newly developed displays are slightly better. An ideal e-paper display can be read in direct sunlight without the image appearing to fade. Technologies include Gyricon, electrophoretics, electrowetting, interferometry, and plasmonics. Many electronic paper technologies hold static text and images indefinitely without electricity. Flexible electronic paper uses plastic substrates and plastic electronics for the display backplane. Applications of e-paper include electronic shelf labels and digital signage, bus station time tables, electronic billboard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recording Format
A recording format is a format for encoding data for storage on a storage medium. The format can be container information such as sectors on a disk, or user/audience information ( content) such as analog stereo audio. Multiple levels of encoding may be achieved in one format. For example, a text encoded page may contain HTML and XML encoding, combined in a plain text file format, using either EBCDIC or ASCII character encoding, on a UDF digitally formatted disk. In electronic media, the primary format is the encoding that requires hardware to interpret (decode) data; while secondary encoding is interpreted by secondary signal processing methods, usually computer software. Recording container formats A container format is a system for dividing physical storage space or virtual space for data. Data space can be divided evenly by a system of measurement, or divided unevenly with meta data. A grid may divide physical or virtual space with physical or virtual (dividers) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer File
A computer file is a System resource, resource for recording Data (computing), data on a Computer data storage, computer storage device, primarily identified by its filename. Just as words can be written on paper, so too can data be written to a computer file. Files can be shared with and transferred between computers and Mobile device, mobile devices via removable media, Computer networks, networks, or the Internet. Different File format, types of computer files are designed for different purposes. A file may be designed to store a written message, a document, a spreadsheet, an Digital image, image, a Digital video, video, a computer program, program, or any wide variety of other kinds of data. Certain files can store multiple data types at once. By using computer programs, a person can open, read, change, save, and close a computer file. Computer files may be reopened, modified, and file copying, copied an arbitrary number of times. Files are typically organized in a file syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Document
An electronic document is a document that can be sent in non-physical means, such as telex, email, and the internet. Originally, any computer data were considered as something internal—the final data output was always on paper. However, the development of computer networks has made it so that in most cases it is much more convenient to distribute electronic documents than printed ones. The improvements in electronic visual display technologies made it possible to view documents on a screen instead of printing them (thus saving paper and the space required to store the printed copies). However, using electronic documents for the final presentation instead of paper has created the problem of multiple incompatible file formats. Even plain text computer files are not free from this problem—e.g. under MS-DOS, most programs could not work correctly with UNIX-style text files (see newline), and for non-English speakers, the different code pages always have been a source of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |