|
Joint Hypothesis Problem
The joint hypothesis problem is the problem that testing for market efficiency is difficult, or even impossible. Any attempts to test for market (in)efficiency must involve asset pricing models so that there are expected returns to compare to real returns. It is not possible to measure 'abnormal' returns without expected returns predicted by pricing models. Therefore, anomalous market returns may reflect market inefficiency, an inaccurate asset pricing model or both. This problem is discussed in Fama's (1970) influential review of the theory and evidence on efficient markets, and was often used to argue against interpreting early stock market anomalies as mispricing. Other arguments used by efficient market advocates include the Roll critique, which points at that testing a specific asset pricing model, the Capital asset pricing model In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is a model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Efficiency
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asset Pricing Models
In financial economics, asset pricing refers to a formal treatment and development of two main pricing principles, outlined below, together with the resultant models. There have been many models developed for different situations, but correspondingly, these stem from either general equilibrium asset pricing or rational asset pricing, the latter corresponding to risk neutral pricing. Investment theory, which is near synonymous, encompasses the body of knowledge used to support the decision-making process of choosing investments, and the asset pricing models are then applied in determining the asset-specific required rate of return on the investment in question, or in pricing derivatives on these, for trading or hedging. (See also .) General Equilibrium Asset Pricing Under General equilibrium theory prices are determined through market pricing by supply and demand. Here asset prices jointly satisfy the requirement that the quantities of each asset supplied and the quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
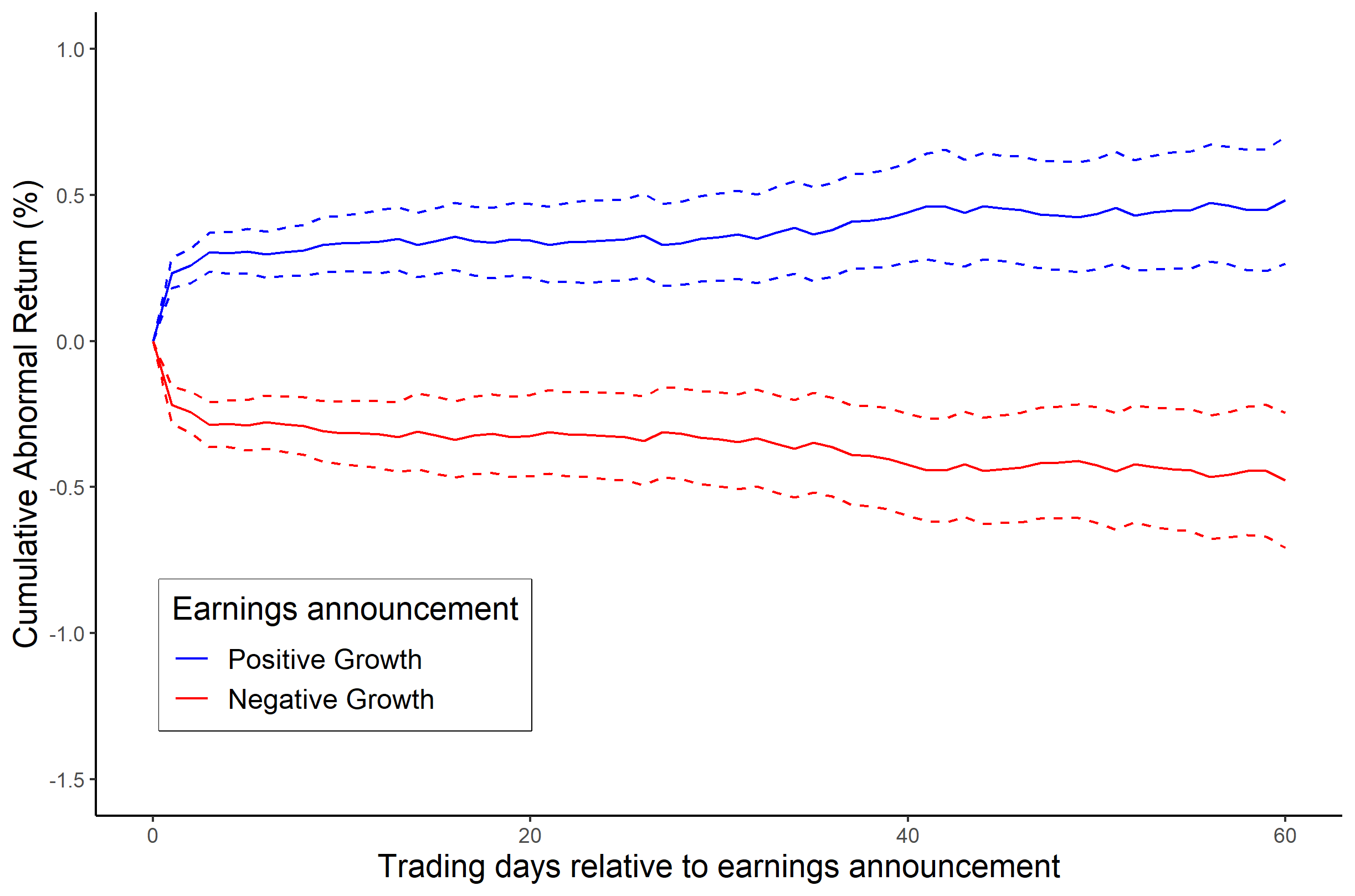
Market Anomaly
A market anomaly in a financial market is predictability that seems to be inconsistent with (typically risk-based) theories of asset prices. Standard theories include the capital asset pricing model and the Fama-French Three Factor Model, but a lack of agreement among academics about the proper theory leads many to refer to anomalies without a reference to a benchmark theory (Daniel and Hirschleifer 2015 and Barberis 2018, for example). Indeed, many academics simply refer to anomalies as "return predictors", avoiding the problem of defining a benchmark theory. Academics have documented more than 150 return predictors (see '' List of Anomalies Documented in Academic Journals).'' These "anomalies", however, come with many caveats. Almost all documented anomalies focus on illiquid, small stocks. Moreover, the studies do not account for trading costs. As a result, many anomalies do not offer profits, despite the presence of predictability. Additionally, return predictability decli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roll's Critique
Roll's critique is a famous analysis of the validity of empirical tests of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) by Richard Roll. It concerns methods to formally test the statement of the CAPM, the equation :E(R_i) = R_f + \beta_(R_m) - R_f\, This equation relates an asset's expected return E(R_i) to the asset's sensitivity \beta_ to the market portfolio return R_m. The market return is defined as the wealth-weighted sum of all investment returns in the economy. Roll's critique makes two statements regarding the market portfolio: 1. Mean-variance tautology: Any mean-variance efficient portfolio R_p satisfies the CAPM equation ''exactly'': :E(R_i) = R_f + \beta_ (R_p) - R_f,. (A portfolio is mean-variance efficient if there is no portfolio that has a higher return and lower risk than those for the efficient portfolio.) Mean-variance efficiency of the market portfolio is equivalent to the CAPM equation holding. This statement is a mathematical fact, requiring ''no'' model assu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Asset Pricing Model
In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is a model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, to make decisions about adding assets to a well-diversified portfolio. The model takes into account the asset's sensitivity to non-diversifiable risk (also known as systematic risk or market risk), often represented by the quantity beta (β) in the financial industry, as well as the expected return of the market and the expected return of a theoretical risk-free asset. CAPM assumes a particular form of utility functions (in which only first and second moments matter, that is risk is measured by variance, for example a quadratic utility) or alternatively asset returns whose probability distributions are completely described by the first two moments (for example, the normal distribution) and zero transaction costs (necessary for diversification to get rid of all idiosyncratic risk). Under these conditions, CAPM shows that the cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotheses
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the assumption in a (possibly counterfactual) ''What If'' question. The adjective ''hypothetical'', meaning "ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |