|
Jins
In traditional Arabic music theory, a jins (, pl. ) is a set of three, four, or five stepwise pitches used to build an Arabic ''maqam'', or melodic mode. They correspond to the English terms trichord, tetrachord, and pentachord. A ''maqam'' is made up of two or more ''ajnas''. Etymology The Arabic word () probably derives from the Greek word () or else from the related Latin word , either way from the same Proto-Indo-European root. The basic meaning is that of a kind, family, or race. The same Arabic word is also used to mean genus in biology, and gender. Meaning of a jins Traditional music theory texts tend to describe a jins as a concrete set of pitches (in many cases a set of exactly four pitches, i.e. a tetrachord), and they are often quick to give mathematically precise intervals for the ideal version of each jins. Their authors were probably influenced by the writings of ancient Greek music theorists going back to Pythagoras (see Tetrachord and Genus (music)), and their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arabic Maqam
In traditional Arabic music, maqam (, literally "ascent"; ') is the system of melodic modes, which is mainly melodic. The word ''maqam'' in Arabic means place, location or position. The Arabic ''maqam'' is a melody type. It is "a technique of improvisation" that defines the pitches, patterns, and development of a piece of music and is "unique to Arabic art music". There are 72 heptatonic tone rows or scales of maqamat. These are constructed from augmented, major, neutral, and minor seconds. Each ''maqam'' is built on a scale, and carries a tradition that defines its habitual phrases, important notes, melodic development and modulation. Both compositions and improvisations in traditional Arabic music are based on the ''maqam'' system. ''Maqamat'' can be realized with either vocal or instrumental music, and do not include a rhythmic component. An essential factor in performance is that each maqam describes the "tonal-spatial factor" or set of musical notes and the rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arabic Music
Arabic music () is the music of the Arab world with all its diverse List of music styles, music styles and genres. Arabic countries have many rich and varied styles of music and also many linguistic Varieties of Arabic, dialects, with each country and region having their own Folk music, traditional music. Arabic music has a long history of interaction with many other regional Music genre, musical styles and genres. It represents the music of all the Member states of the Arab League, peoples that make up the Arab world today. History Pre-Islamic period Pre-Islamic Arabia was the cradle of many intellectual achievements, including music, Music theory, musical theory and the development of musical instruments. In Yemen, the main center of pre-Islamic Arab sciences, literature and arts, musicians benefited from the patronage of the Kings of Sabaeans, Sabaʾ who encouraged the development of music. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Genus (music)
In the musical system of ancient Greece, genus (Greek: γένος 'genos'' pl. γένη 'genē'' Latin: ''genus'', pl. ''genera'' "type, kind") is a term used to describe certain classes of intonations of the two movable notes within a tetrachord. The tetrachordal system was inherited by the Latin medieval theory of scales and by the modal theory of Byzantine music; it may have been one source of the later theory of the jins of Arabic music. In addition, Aristoxenus (in his fragmentary treatise on rhythm) calls some patterns of rhythm "genera". Tetrachords According to the system of Aristoxenus and his followers— Cleonides, Bacchius, Gaudentius, Alypius, Bryennius, and Aristides Quintilianus—the paradigmatic tetrachord was bounded by the fixed tones ''hypate'' and ''mese'', which are a perfect fourth apart and do not vary from one genus to another. Between these are two movable notes, called ''parhypate'' and ''lichanos''. The upper tone, lichanos, can vary over the ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
12 Equal Temperament
12 equal temperament (12-ET) is the musical system that divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are Equal temperament, equally tempered (equally spaced) on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the Twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2 (\sqrt[12] ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. Twelve-tone equal temperament is the most widespread system in music today. It has been the predominant tuning system of Western music, starting with classical music, since the 18th century, and Europe almost exclusively used approximations of it for millennia before that. It has also been used in other cultures. In modern times, 12-ET is usually tuned relative to a standard pitch of 440 Hz, called A440 (pitch standard), A440, meaning one note, A (musical note), A4 (the A in the 4th octave of a typical 88-key piano), is tuned to 440 hertz and all other notes are defined as some multiple of semitones apart from it, ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
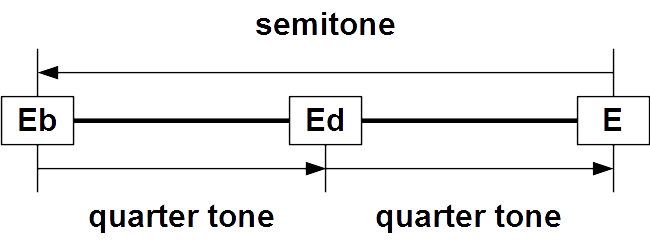
Neutral Second
In music theory, a neutral interval is an interval that is neither a major nor minor, but instead in between. For example, in equal temperament, a major third is 400 cents, a minor third is 300 cents, and a neutral third is 350 cents. A neutral interval inverts to a neutral interval. For example, the inverse of a neutral third is a neutral sixth. Roughly, neutral intervals are a quarter tone sharp from minor intervals and a quarter tone flat from major intervals. In just intonation, as well as in tunings such as 31-ET, 41-ET, or 72-ET, which more closely approximate just intonation, the intervals are closer together. * Neutral second *Neutral third *Neutral sixth * Neutral seventh Second A neutral second or medium second is an interval wider than a minor second and narrower than a major second. Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral seconds: * The intermediate neutral second, called the lesser undecimal neutral second , has a ratio between the higher-frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perfect Fourth
A fourth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending interval from C to the next F is a perfect fourth, because the note F is the fifth semitone above C, and there are four staff positions between C and F. Diminished fourth, Diminished and Tritone, augmented fourths span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (four and six, respectively). The perfect fourth may be derived from the Harmonic series (music), harmonic series as the interval between the third and fourth harmonics. The term ''perfect'' identifies this interval as belonging to the group of perfect intervals, so called because they are neither major nor minor. A perfect fourth in just intonation corresponds to a pitch ratio of 4:3, or about 498 cent (music), cents (), while in equal temperam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Minor Scale
In Classical_music, Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three Scale (music), scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending). These scales contain all three notes of a minor triad: the root (chord), root, a minor third (rather than the major third, as in a Major chord, major triad or major scale), and a perfect fifth (rather than the tritone, diminished fifth, as in a diminished scale or half diminished scale). Minor scale is also used to refer to other scales with this property, such as the Dorian mode or the Pentatonic Scale#Minor pentatonic scale, minor pentatonic scale (see #Other minor scales, other minor scales below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth Degree (music), degree of its relative major, relative major scale. For instance, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perfect Fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so. In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval from the first to the last of the first five consecutive Musical note, notes in a diatonic scale. The perfect fifth (often abbreviated P5) spans seven semitones, while the Tritone, diminished fifth spans six and the augmented fifth spans eight semitones. For example, the interval from C to G is a perfect fifth, as the note G lies seven semitones above C. The perfect fifth may be derived from the Harmonic series (music), harmonic series as the interval between the second and third harmonics. In a diatonic scale, the dominant (music), dominant note is a perfect fifth above the tonic (music), tonic note. The perfect fifth is more consonance and dissonance, consonant, or stable, than any other interval except the unison and the octave. It occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Augmented Second
In Western classical music, an augmented second is an interval created by widening a major second by a chromatic semitone, spanning three semitones and enharmonically equivalent to a minor third in 12-tone equal temperament.Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.54. . Specific example of an A2 not given but general example of major intervals described. For instance, the interval from C to D is a major second, two semitones wide, and the interval from C to D is an augmented second, spanning three semitones. Usage Augmented seconds occur in many scales, including the various modes of the harmonic minor and double harmonic scales. In harmonic minor, the augmented second occurs between the sixth and seventh scale degrees. For example, in the scale of A harmonic minor, the notes F and G form the interval of an augmented second. This distinguishing feature of harmonic minor scales occurs as a consequence of the seventh scale degree having been chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |