|
Isoseismal Map
In seismology, an isoseismal map is used to show lines of equally felt seismic intensity, generally measured on the Modified Mercalli scale. Such maps help to identify earthquake epicenters, particularly where no instrumental records exist, such as for historical earthquakes. They also contain important information on ground conditions at particular locations, the underlying geology, radiation pattern of the seismic waves, and the response of different types of buildings. They form an important part of the macroseismic approach, i.e. that part of seismology dealing with noninstrumental data. The shape and size of the isoseismal regions can be used to help determine the magnitude, focal depth, and focal mechanism of an earthquake. History The first known isoseismal map was produced for the 1810 earthquake in Mór in Hungary, and published by Kitaibel and Tomtsányi in 1814. The first, six-level intensity scale was proposed by Egen in 1828 for an earthquake in Rhineland. Robert M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
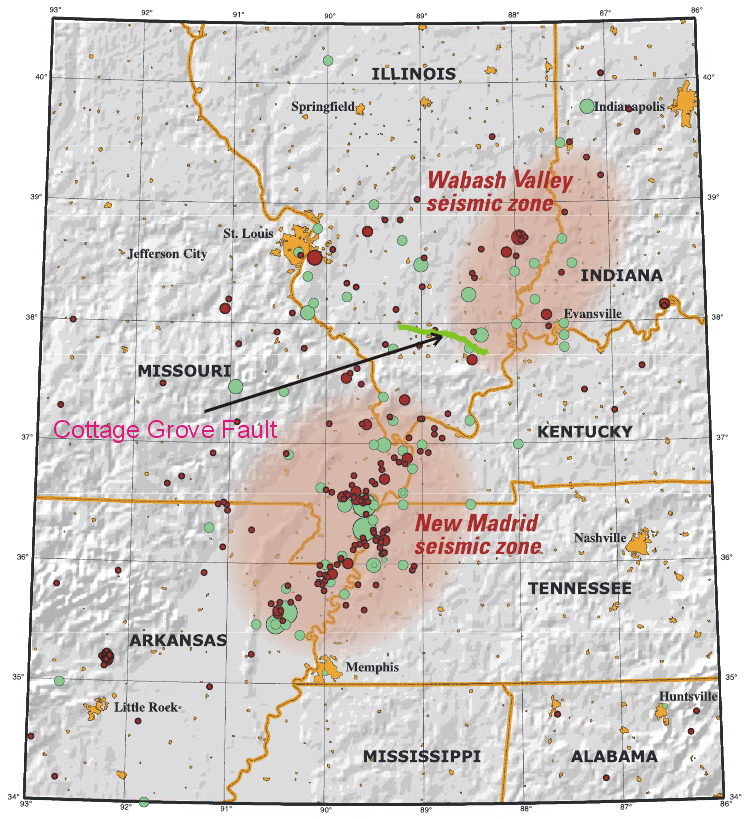
1968 Illinois Earthquake
The 1968 Illinois earthquake (a New Madrid event) was the largest recorded earthquake in the U.S. Midwestern state of Illinois. Striking at 11:02 am on November 9, it measured 5.4 on the Richter scale. Although no fatalities occurred, the event caused considerable structural damage to buildings, including the toppling of chimneys and shaking in Chicago, the region's largest city. The earthquake was one of the most widely felt in U.S. history, largely affecting 23 states over an area of . In studying its cause, scientists discovered the Cottage Grove Fault in the Southern Illinois Basin. Within the region, millions felt the rupture. Reactions to the earthquake varied; some people near the epicenter did not react to the shaking, while others panicked. A future earthquake in the region is extremely likely; in 2005, seismologists and geologists estimated a 90% chance of a magnitude 6–7 tremor before 2055, likely originating in the Wabash Valley seismic zone on the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Mechanism
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the deformation in the source region that generates the seismic waves. In the case of a fault-related event it refers to the orientation of the fault plane that slipped and the slip vector and is also known as a fault-plane solution. Focal mechanisms are derived from a solution of the moment tensor for the earthquake, which itself is estimated by an analysis of observed seismic waveforms. The focal mechanism can be derived from observing the pattern of "first motions", that is, whether the first arriving P waves break up or down. This method was used before waveforms were recorded and analysed digitally and this method is still used for earthquakes too small for easy moment tensor solution. Focal mechanisms are now mainly derived using semi-automatic analysis of the recorded waveforms. Moment tensor solutions The moment tensor solution is typically displayed graphically using a so-called ''beachball'' diagram. The pattern o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriging
In statistics, originally in geostatistics, kriging or Kriging, also known as Gaussian process regression, is a method of interpolation based on Gaussian process governed by prior covariances. Under suitable assumptions of the prior, kriging gives the best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) at unsampled locations. Interpolating methods based on other criteria such as smoothness (e.g., smoothing spline) may not yield the BLUP. The method is widely used in the domain of spatial analysis and computer experiments. The technique is also known as Wiener–Kolmogorov prediction, after Norbert Wiener and Andrey Kolmogorov. The theoretical basis for the method was developed by the French mathematician Georges Matheron in 1960, based on the master's thesis of Danie G. Krige, the pioneering plotter of distance-weighted average gold grades at the Witwatersrand reef complex in South Africa. Krige sought to estimate the most likely distribution of gold based on samples from a few boreholes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1857 Basilicata Earthquake
The 1857 Basilicata earthquake (also known as the Great Neapolitan earthquake) occurred on December 16 in the Basilicata region of Italy southeast of the city of Naples. The epicentre was in Montemurro, on the western border of the modern province of Potenza. Several towns were destroyed, and there were around 11,000 fatalities according to official sources, but unofficial estimates suggest that as many as 19,000 died. At the time it was the third-largest known earthquake and has been estimated to have been of magnitude 7.0 on the moment magnitude scale. Earthquake The principal shock occurred at about 10:15 pm local time on December 16, 1857, with a duration of about 25 seconds. It was preceded by several foreshocks, the largest of which occurred about two minutes before the mainshock. The earthquake was followed by numerous aftershocks, which continued until May 1859, the most damaging of which occurred at about 04:00 local time on December 26. Another damaging aftershock occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Mallet
Robert Mallet (3 June 1810 – 5 November 1881) was an Irish geophysicist, civil engineer, and inventor who distinguished himself in research on earthquakes and is sometimes called the father of seismology. His son, Frederick Richard Mallet was a geologist who worked in India. Early life Mallet was born in Dublin, on 3 June 1810, the son of factory owner John Mallet. He was educated at Trinity College, Dublin, entering it at the age of 16 and graduating in science and mathematics in 1830 at the age of 20. Career Following his graduation, he joined his father's iron foundry business and helped build the firm into one of the most important engineering works in Ireland, supplying ironwork for railway companies, the Fastnet Rock lighthouse, and a swing bridge over the River Shannon at Athlone. He also helped manufacture the characteristic iron railings that surround Trinity College and which bear his family name at the base. Mallet was elected to the Royal Irish Academy in 1832 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section. Term Historically, the Rhinelands refers (physically speaking) to a loosely defined region embracing the land on the banks of the Rhine in Central Europe, which were settled by Ripuarian and Salian Franks and became part of Frankish Austrasia. In the High Middle Ages, numerous Imperial States along the river emerged from the former stem duchy of Lotharingia, without developing any common political or cultural identity. A "Rhineland" conceptualization can be traced to the period of the Holy Roman Empire from the sixteenth until the eighteenth centuries when the Empire's Imperial Estates (territories) were grouped into regional districts in charge of defence and judicial execution, known as Imperial Circles. Three of the ten circles through which the Rhine flowed r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 9 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani people in Hungary, Romani minority. Hungarian language, Hungarian, the Languages of Hungary, official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic languages, Uralic language and among the few non-Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr. The territory of present-day Hungary has for centuries been a crossroads for various peoples, including Celts, Ancient Rome, Romans, Germanic peoples, Germanic trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mór
Mór (german: Moor) is a town in Fejér County, Hungary. Among the smaller towns in the Central Transdanubia Region of Hungary, it lies between the Vértes and Bakony Hills, in the northwestern corner of Fejér County. The historic roots of the present town go back to the Celtic and Roman period. The town is the economical, institutional and cultural centre of the small region of Mór including 13 settlements. The development of the town began with the arrival of ethnic German settlers and Capuchin monks in 1697. The Battle of Mór on December 30, 1848 was a crucial victory for the Austrian Empire's forces in crushing the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. The Wine Region of Mór Antiquarian artefacts show that vine growing occurred even in the Roman period. Vine growing came to stay from the 11th century in this area. The ethnic German settlers and the Capuchin monks started to grow grape vines in the beginning of the 18th century. The oenological boom lasted until the Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focus (earthquake)
In seismology, a hypocenter or hypocentre () is the point of origin of an earthquake or a subsurface nuclear explosion. A synonym is the focus of an earthquake. Earthquakes An earthquake's hypocenter is the position where the strain energy stored in the rock is first released, marking the point where the fault begins to rupture.''The hypocenter is the point within the earth where an earthquake rupture starts. The epicenter is the point directly above it at the surface of the Earth. Also commonly termed the focus.'' This occurs directly beneath the epicenter, at a distance known as the ''hypocentral depth'' or ''focal depth''. The focal depth can be calculated from measurements based on seismic wave phenomena. As with all wave phenomena in physics, there is uncertainty in such measurements that grows with the wavelength In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |