|
Inositol Monophosphatase
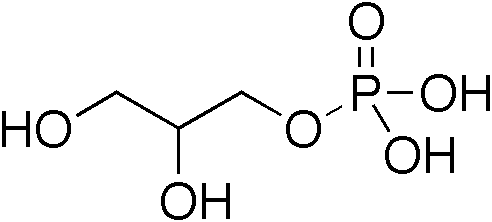
The enzyme Inositol phosphate-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.25) is of the phosphodiesterase family of enzymes. It is involved in the phosphophatidylinositol signaling pathway, which affects a wide array of cell functions, including but not limited to, cell growth, apoptosis, secretion, and information processing. Inhibition of inositol monophosphatase may be key in the action of lithium in treating bipolar disorder, specifically manic depression. The catalyzed reaction: :''myo''-inositol phosphate + H2O \rightleftharpoons ''myo''-inositol + phosphate Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on phosphoric monoester bonds. The systematic name is ''myo''-inositol-phosphate phosphohydrolase. Other names in common use include: * ''myo''-inositol-1(or 4)-monophosphatase, * inositol 1-phosphatase, * L-''myo''-inositol-1-phosphate phosphatase, * ''myo''-inositol 1-phosphatase, * inositol phosphatase, * inositol monophosphate phosphatase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Monophosphatase 1
Inositol monophosphatase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''IMPA1'' gene. Interacting partners IMPA1 has been shown to interact with Bergmann glial S100B and calbindin. Chemical inhibitors L-690,330 is a competitive inhibitor of IMPase activity with very good activity in vitro however with limited bioavailability in vivo. Due to its increased specificity compared to Lithium, L-690,330 has been used extensively in characterizing the results of IMPase inhibition in various cell culture models. L-690,488, a prodrug or L-690,330, has also been developed which has greater cell permeability. Treatment of cortical slices with L-690,488 resulted in accumulation of inositol demonstrating the activity of this inhibitor in tissue. Inhibition of IMPA1 activity can have pleiotropic effects on cellular function, including altering phosphoinositide signalling, autophagy, apoptosis, and other effects. Bipolar disorder Initially it was noticed that several drugs usef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
The enzyme fructose bisphosphatase (EC 3.1.3.11; systematic name D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphohydrolase) catalyses the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate in gluconeogenesis and the Calvin cycle, which are both anabolic pathways: :D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O = D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate Phosphofructokinase (EC 2.7.1.11) catalyses the reverse conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, but this is not just the reverse reaction, because the co-substrates are different (and so thermodynamic requirements are not violated). The two enzymes each catalyse the conversion in one direction only, and are regulated by metabolites such as fructose 2,6-bisphosphate so that high activity of one of them is accompanied by low activity of the other. More specifically, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate allosterically inhibits fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, but activates phosphofructokinase-I. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology Of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is an affective disorder characterized by periods of elevated and depressed mood. The cause and mechanism of bipolar disorder is not yet known, and the study of its biological origins is ongoing. Although no single gene causes the disorder, a number of genes are linked to increase risk of the disorder, and various gene environment interactions may play a role in predisposing individuals to developing bipolar disorder. Neuroimaging and postmortem studies have found abnormalities in a variety of brain regions, and most commonly implicated regions include the ventral prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Dysfunction in emotional circuits located in these regions have been hypothesized as a mechanism for bipolar disorder. A number of lines of evidence suggests abnormalities in neurotransmission, intracellular signalling, and cellular functioning as possibly playing a role in bipolar disorder. Studies of bipolar disorder, particularly neuroimaging studies, are vulnerable to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mood Disorders
A mood disorder, also known as an affective disorder, is any of a group of conditions of mental and behavioral disorder where a disturbance in the person's mood is the main underlying feature. The classification is in the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Mood disorders fall into seven groups, including; abnormally elevated mood, such as mania or hypomania; depressed mood, of which the best-known and most researched is major depressive disorder (MDD) (alternatively known as clinical depression, unipolar depression, or major depression); and moods which cycle between mania and depression, known as bipolar disorder (BD) (formerly known as manic depression). There are several sub-types of depressive disorders or psychiatric syndromes featuring less severe symptoms such as dysthymic disorder (similar to MDD, but longer lasting and more persistent, though often milder) and cyclothymic disorder (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small non-polar molecules. Cells of the barrier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valproate
Valproate (VPA) and its valproic acid, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in those with absence seizures, partial seizures, and generalized seizures. They can be given intravenously or by mouth, and the tablet forms exist in both long- and short-acting formulations. Common side effects of valproate include nausea, vomiting, somnolence, and dry mouth. Serious side effects can include liver failure, and regular monitoring of liver function tests is therefore recommended. Other serious risks include pancreatitis and an increased suicide risk. Valproate is known to cause serious abnormalities in fetuses if taken during pregnancy, and is contra-indicated for women of childbearing age unless the drug is essential to their medical condition. As of 2022 the drug was still prescribed in the UK to potentially pregnant women, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium (medication)
Certain lithium compounds, also known as lithium salts, are used as psychiatric medication, primarily for bipolar disorder and for major depressive disorder. In these disorders, it sometimes reduces the risk of suicide. Lithium is taken orally. Common side effects include increased urination, shakiness of the hands, and increased thirst. Serious side effects include hypothyroidism, diabetes insipidus, and lithium toxicity. Blood level monitoring is recommended to decrease the risk of potential toxicity. If levels become too high, diarrhea, vomiting, poor coordination, sleepiness, and ringing in the ears may occur. Lithium is teratogenic, especially during the first trimester of pregnancy and at higher dosages. The use of lithium while breastfeeding is controversial; however, many international health authorities advise against it, and the long-term outcomes of perinatal lithium exposure have not been studied. The American Academy of Pediatrics lists lithium as contraindic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Triphosphate
Inositol trisphosphate or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate abbreviated InsP3 or Ins3P or IP3 is an inositol phosphate signaling molecule. It is made by hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), a phospholipid that is located in the plasma membrane, by phospholipase C (PLC). Together with diacylglycerol (DAG), IP3 is a second messenger molecule used in signal transduction in biological cells. While DAG stays inside the membrane, IP3 is soluble and diffuses through the cell, where it binds to its receptor, which is a calcium channel located in the endoplasmic reticulum. When IP3 binds its receptor, calcium is released into the cytosol, thereby activating various calcium regulated intracellular signals. Properties Chemical formula and molecular weight IP3 is an organic molecule with a molecular mass of 420.10 g/mol. Its empirical formula is C6H15O15P3. It is composed of an inositol ring with three phosphate groups bound at the 1, 4, and 5 carbon positions, and thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats. Food additive Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides (E471) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIP2 (other)
PIP2, or phosphatidylinositol biphosphate, is the products obtained by cleavage of PIP3, or by phosphorylation of PI(3)P, PI(4)P or PI(5)P. 'PIP2' most frequently refers to: * Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, also known as PI(4,5)P2 The other PIP2 lipids are: * Phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate, also known as PI(3,4)P2 * Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,5)P2) is one of the seven phosphoinositides found in eukaryotic cell membranes. In quiescent cells, the PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels, typically quantified by HPLC, are the lowest amongst the constitutively p ..., also known as PI(3,5)P2 {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig Phospholipids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids. There are thirteen kinds of mammalian phospholipase C that are classified into six isotypes (β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η) according to structure. Each PLC has unique and overlapping controls over expression and subcellular distribution. Variants Mammalian variants The extensive number of functions ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose 6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this way. Because of its prominent position in cellular chemistry, glucose 6-phosphate has many possible fates within the cell. It lies at the start of two major metabolic pathways: glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. In addition to these two metabolic pathways, glucose 6-phosphate may also be converted to glycogen or starch for storage. This storage is in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen for most multicellular animals, and in intracellular starch or glycogen granules for most other organisms. Production From glucose Within a cell, glucose 6-phosphate is produced by phosphorylation of glucose on the sixth carbon. This is catalyzed by the enzyme hexokinase in most cells, and, in higher animals, glucokinase in certain cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |