|
Infrared Gas Analyzer
] An infrared gas analyzer measures trace gases by determining the Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of an emitted infrared light source through a certain air sample. Trace gases found in the Earth's atmosphere become excited under specific wavelengths found in the infrared range. The concept behind the technology can be understood as testing how much of the light is absorbed by the air. Different molecules in the air absorb different frequencies of light. Air with much of a certain gas will absorb more of a certain frequency, allowing the sensor to report a high concentration of the corresponding molecule. Infrared gas analyzers usually have two chambers, one is a reference chamber while the other chamber is a measurement chamber. Infrared light is emitted from some type of source on one end of the chamber, passes through a series of chambers that contains given quantities of the various gases in question. Principles of Operation The design from 1975 (pictured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Gas Analyzer
] An infrared gas analyzer measures trace gases by determining the Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of an emitted infrared light source through a certain air sample. Trace gases found in the Earth's atmosphere become excited under specific wavelengths found in the infrared range. The concept behind the technology can be understood as testing how much of the light is absorbed by the air. Different molecules in the air absorb different frequencies of light. Air with much of a certain gas will absorb more of a certain frequency, allowing the sensor to report a high concentration of the corresponding molecule. Infrared gas analyzers usually have two chambers, one is a reference chamber while the other chamber is a measurement chamber. Infrared light is emitted from some type of source on one end of the chamber, passes through a series of chambers that contains given quantities of the various gases in question. Principles of Operation The design from 1975 (pictured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (electromagnetic Radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy — and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A notable effect is attenuation, or the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity (linear absorption), in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. Quantifying absorption Many approaches can potentially quantify radiation absorption, with key examples following. * The absorption coefficient along with some closely related derived quantities * The attenuation coefficient (NB used infrequently with meaning synonymous with "absorption coefficient") * The Molar attenuation coefficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 Terahertz (unit), THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to Wave–particle duality, both those of a wave and of a Subatomic particle, particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelengths
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter ''lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondispersive Infrared Sensor
A nondispersive infrared sensor (or NDIR sensor) is a simple spectroscopic sensor often used as a gas detector. It is non-dispersive in the fact that no dispersive element (e.g a prism or diffraction grating as is often present in other spectrometers) is used to separate out (like a monochromator) the broadband light into a narrow spectrum suitable for gas sensing. The majority of NDIR sensors use a broadband lamp source and an optical filter to select a narrow band spectral region that overlaps with the absorption region of the gas of interest. In this context narrow may be 50-300nm bandwidth. Modern NDIR sensors may use Microelectromechanical systems (MEMs) or mid IR LED sources, with or without an optical filter. Principle The main components of an NDIR sensor are an infrared (IR) source (lamp), a sample chamber or light tube, a light filter and an infrared detector. The IR light is directed through the sample chamber towards the detector. In parallel there is another chamber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detector
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends the information to other electronics, frequently a computer processor. Sensors are always used with other electronics. Sensors are used in everyday objects such as touch-sensitive elevator buttons (tactile sensor) and lamps which dim or brighten by touching the base, and in innumerable applications of which most people are never aware. With advances in micromachinery and easy-to-use microcontroller platforms, the uses of sensors have expanded beyond the traditional fields of temperature, pressure and flow measurement, for example into MARG sensors. Analog sensors such as potentiometers and force-sensing resistors are still widely used. Their applications include manufacturing and machinery, airplanes and aerospace, cars, medicine, robot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch ( psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities (energy, force, torque, light, motion, position, etc.). The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction. Types * Mechanical transducers, so-called as they convert physical quantities into mechanical outputs or vice versa; * Electrical transducers however convert physical quantities into electrical outputs or signals. Examples of these are: ** a thermocouple that changes temperature differences into a small voltage; ** a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT), used to measure displacement (position) changes by means of electrical signals. Sensors, actuators and transceivers Transducers can be categorized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
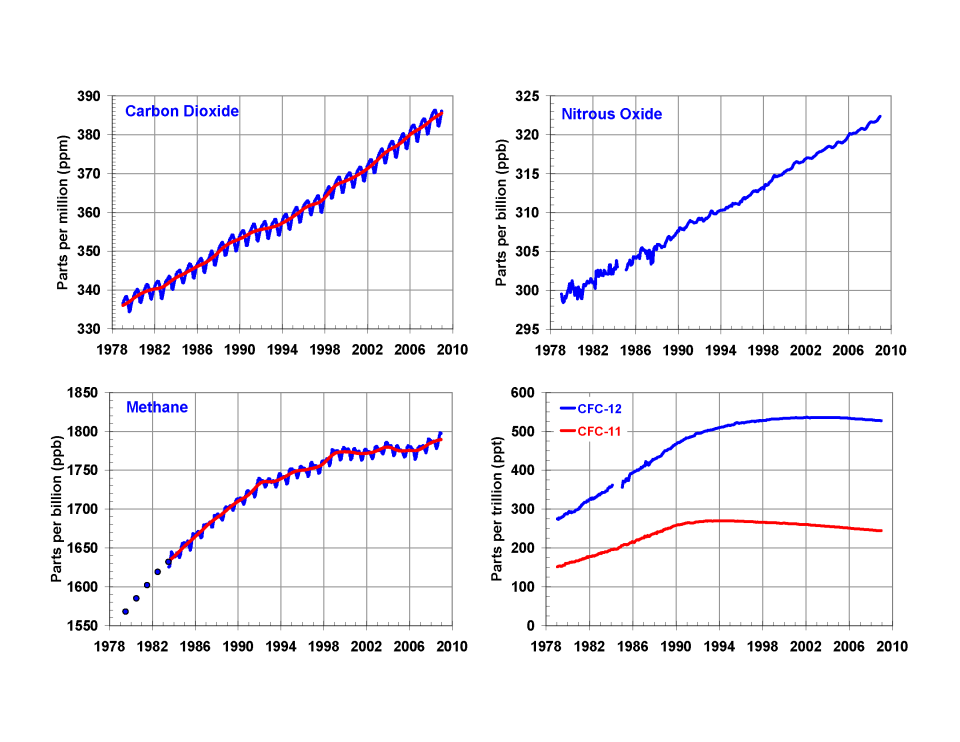
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring
Greenhouse gas monitoring is the direct measurement of greenhouse gas emissions and levels. There are several different methods of measuring carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere, including infrared analyzing and manometry. Methane and nitrous oxide are measured by other instruments. Greenhouse gases are measured from space such as by the Orbiting Carbon Observatory and networks of ground stations such as the Integrated Carbon Observation System. Methodology Carbon dioxide monitoring Manometry Manometry is a key measurement tool for atmospheric carbon dioxide by first measuring the volume, temperature, and pressure of a particular amount of dry air. The air sample is dried by passing it through multiple dry ice traps and then collecting it in a five-liter vessel. The temperature is taken via a thermometer and pressure is calculated using manometry. Then, liquid nitrogen is added, causing the carbon dioxide to condense and become measurable by volume. The idea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |