|
Induced Seismicity In Basel
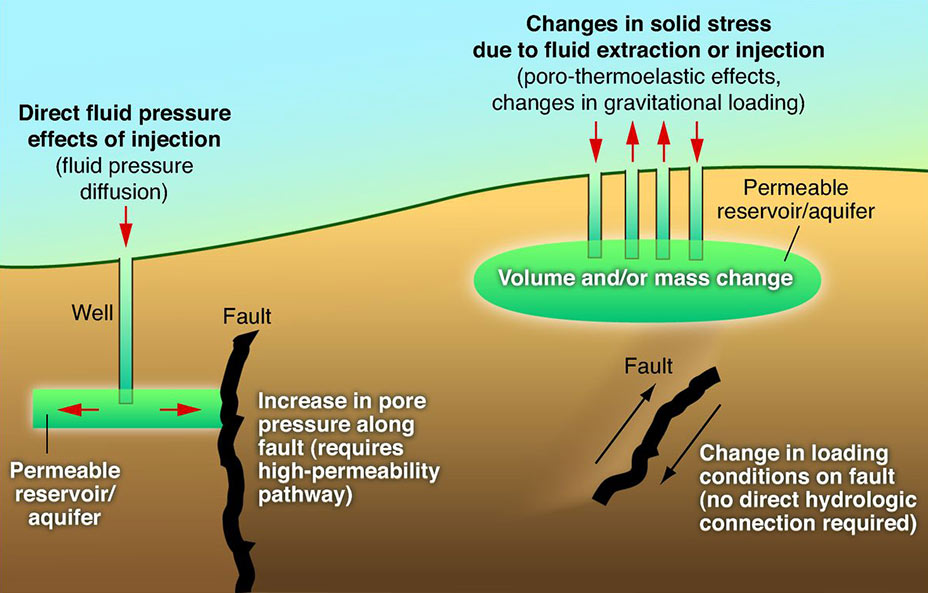
Induced seismicity in Basel led to suspension of its hot dry rock enhanced geothermal systems project. A seismic-hazard evaluation was then conducted, resulting in the cancellation of the project in December 2009. Basel, Switzerland sits atop a historically active fault and most of the city was destroyed in a magnitude 6.5 earthquake in 1356. But the Basel project, although it had established an operational approach for addressing induced earthquakes, had not performed a thorough seismic risk assessment before starting geothermal stimulation. Seismic events in Basel reached the trip point of Richter Magnitude 2.9 six days after the main stimulation was started on December 2, despite precautionary reduction of the injection rate earlier that same day upon reaching earlier "soft" thresholds. However, further tremors exceeding magnitude 3 were recorded on 6 January (measuring 3.1), 16 January 2007 (3.2), and 2 February 2007 (3.2). In all, between December 2006 and March 2007, the six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Seismicity
Induced seismicity is typically minor earthquakes and tremors that are caused by human activity that alters the stresses and strains on Earth's crust. Most induced seismicity is of a low magnitude. A few sites regularly have larger quakes, such as The Geysers geothermal plant in California which averaged two M4 events and 15 M3 events every year from 2004 to 2009. The Human-Induced Earthquake Database (''HiQuake'') documents all reported cases of induced seismicity proposed on scientific grounds and is the most complete compilation of its kind. Results of ongoing multi-year research on induced earthquakes by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) published in 2015 suggested that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma, such as the 1952 magnitude 5.7 El Reno earthquake may have been induced by deep injection of waste water by the oil industry. A huge number of seismic events in fracking states like Oklahoma caused by increasing the volume of injection. "Earthquake rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese , neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS), Saint-Louis (FR-68), Weil am Rhein (DE-BW) , twintowns = Shanghai, Miami Beach , website = www.bs.ch Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label= Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich and Geneva) with about 175,000 inhabitants. The official language of Basel is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many museums, including the Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhanced Geothermal Systems
An enhanced geothermal system (EGS) generates geothermal electricity without the need for natural convective hydrothermal resources. Until recently, geothermal power systems have exploited only resources where naturally occurring heat, water, and rock permeability are sufficient to allow energy extraction. However, by far the most geothermal energy within reach of conventional techniques is in dry and impermeable rock. EGS technologies enhance and/or create geothermal resources in this hot dry rock (HDR) through a variety of stimulation methods, including 'hydraulic stimulation'. Overview When natural cracks and pores do not allow economic flow rates, the permeability can be enhanced by pumping high-pressure cold water down an injection well into the rock. The injection increases the fluid pressure in the naturally fractured rock, triggering shear events that enhance the system's permeability. As long as the injection pressure is maintained, a high matrix permeability is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Fault
An active fault is a fault that is likely to become the source of another earthquake sometime in the future. Geologists commonly consider faults to be active if there has been movement observed or evidence of seismic activity during the last 10,000 years. * Active faulting is considered to be a geologic hazard - one related to earthquakes as a cause. Effects of movement on an active fault include strong ground motion, surface faulting, tectonic deformation, landslides and rockfalls, liquefaction, tsunamis, and seiches. Quaternary faults are those active faults that have been recognized at the surface and which have evidence of movement during the Quaternary Period. Related geological disciplines for ''active-fault'' studies include geomorphology, seismology, reflection seismology, plate tectonics, geodetics and remote sensing, risk analysis, and others. Location Active faults tend to occur in the vicinity of tectonic plate boundaries, and active fault research has foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel Earthquake
The 1356 Basel earthquake is the most significant seismological event to have occurred in Central Europe in recorded history and had a moment magnitude in the range of 6.0–7.1.Centrale Nucléaire de Fessenheim : appréciation du risque sismique RÉSONANCE Ingénieurs-Conseils SA, published 2007-09-05, pages 12, 13 This earthquake, which occurred on 18 October 1356, is also known as the Sankt-Lukas-Tag Erdbeben (English: Earthquake of Saint Luke), as 18 October is the feast day of Saint . Earthquake |
Richter Magnitude Scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 paper, where he called it the "magnitude scale". This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale, denoted as ML or . Because of various shortcomings of the original scale, most seismological authorities now use other similar scales such as the moment magnitude scale () to report earthquake magnitudes, but much of the news media still erroneously refers to these as "Richter" magnitudes. All magnitude scales retain the logarithmic character of the original and are scaled to have roughly comparable numeric values (typically in the middle of the scale). Due to the variance in earthquakes, it is essential to understand the Richter scale uses logarithms simply to make the measurements manageable (i.e., a magnitude 3 quake factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richter Magnitude
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 paper, where he called it the "magnitude scale". This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale, denoted as ML or . Because of various shortcomings of the original scale, most seismological authorities now use other similar scales such as the moment magnitude scale () to report earthquake magnitudes, but much of the news media still erroneously refers to these as "Richter" magnitudes. All magnitude scales retain the logarithmic character of the original and are scaled to have roughly comparable numeric values (typically in the middle of the scale). Due to the variance in earthquakes, it is essential to understand the Richter scale uses logarithms simply to make the measurements manageable (i.e., a magnitude 3 quake factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
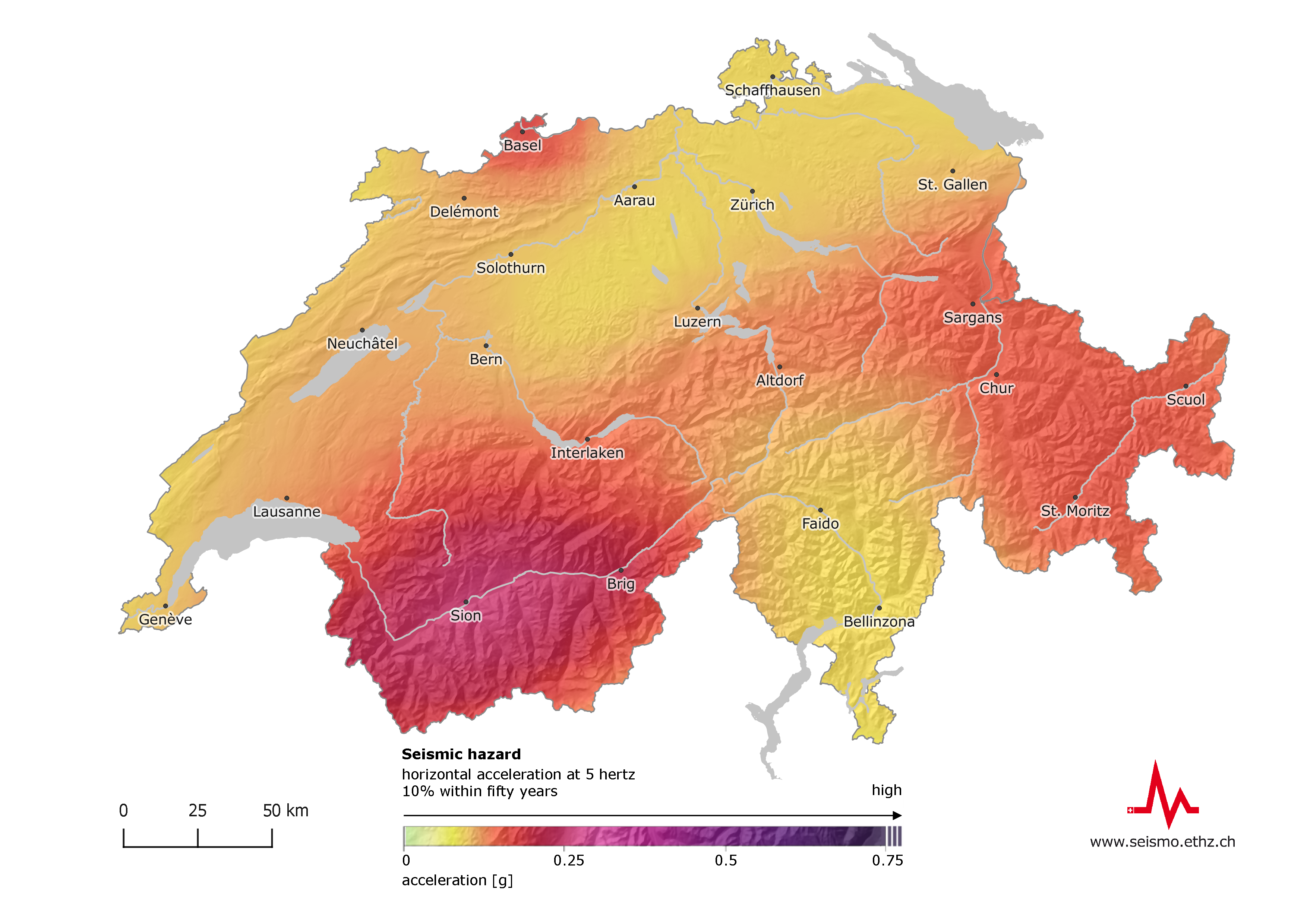
Swiss Seismological Service
The Swiss Seismological Service (german: Schweizerischer Erdbebendienst (SED), french: Service sismologique suisse, it, Servizio sismico svizzero, rm, Servizi da terratrembels svizzer) at ETH Zurich is the federal agency responsible for monitoring earthquakes in Switzerland and its neighboring countries and for assessing Switzerland's seismic hazard. When an earthquake happens, the SED informs the public, authorities, and the media about the earthquake's location, magnitude, and possible consequences. The activities of the SED are integrated in thfederal action plan for earthquake precaution History The beginnings of the SED trace back to the establishment of the Erdbebenkommission in 1878. In 1911 the first earthquake surveillance station of Switzerland was established in Degenried near Zurich. Three years later (1914), the earthquake monitoring mandate was defined in a federal law. Thus, what had been a voluntary activity was transformed into an institution. 1957 the federa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy In Switzerland
The energy sector in Switzerland is, by its structure and importance, typical of a developed country. Apart from hydroelectric power and firewood, the country has few indigenous energy resources: oil products, natural gas and nuclear fuel are imported, so that in 2013 only 22.6% of primary energy consumption were covered by local resources. Final energy consumption in Switzerland has increased more than fivefold since the beginning of the 20th century, from around 170,000 to 896,000 terajoules per year, with the largest share now being captured by transport (35% in 2013). This increase was made in parallel with the strong development of its economy and the increase in population. As the sector is highly liberalised, the federal energy policy aims to accompany the promises made in Kyoto by promoting a more rational use of energy and, particularly since the 1990s, the development of new renewable sources. Thanks to the high share of hydroelectricity (59.6%) and nuclear power (31.7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Sector In Switzerland
The electricity sector in Switzerland relies mainly on hydroelectricity, since the Alps cover almost two-thirds of the country's land mass, providing many large mountain lakes and artificial reservoirs suited for hydro power. In addition, the water masses drained from the Swiss Alps are intensively used by run-of-the-river hydroelectricity (ROR). With 9,052 kWh per person in 2008, the country's electricity consumption is relatively high and was 22% above the European Union's average. In 2013, net generated electricity amounted to 66.2 terawatt-hours (TWh). About 60% of Switzerland's electricity generation comes from renewable sources, most of it from hydro (56.6%), while non-hydro renewables supplied a small contribution of 3.4%. Nuclear contributed 37.6% to the country's electricity production and only about 2.5% were generated by fossil fuel based thermal power stations.Swiss Federal Office of Energy SFOESchweizerische Statistik der erneuerbaren Energien 2013, p. 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |