|
Isopycnic Centrifugation
An isopycnic surface is a surface of constant density inside a fluid. Isopycnic surfaces contrast with isobaric or isothermal surfaces, which describe surfaces of constant pressure and constant temperature respectively. Isopycnic surfaces are sometimes referred to as "iso-density" surfaces, although this is strictly incorrect. Isopycnic typically describes surfaces, not processes. Unless there is a flux of mass into or out of a control volume, a process which occurs at a constant density also occurs at a constant volume and is called an isochoric process and not an isopycnic process. The term "isopycnic" is commonly encountered in the fluid dynamics of compressible fluids, such as in meteorology and geophysical fluid dynamics, astrophysics, or the fluid dynamics of explosions or high Mach number flows.It may also be applied to other situations where a continuous medium has smoothly varying density, such as in the case of an inhomogeneous colloidal suspension. In general isopycni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Purified Viruses
Purified may refer to: *Purified (rapper), Christian hip hop electrohop artist from South Africa, now in Sydney, Australia *Purified (album), ''Purified'' (album), 2005 gospel album by CeCe Winans *"Purified", song by Celldweller from the album ''Blackstar (novel)#Score, Blackstar'' *"Purified", song by Michael W. Smith from the album ''Worship (Michael W. Smith album), Worship'' *"Purified", song by Of Mice & Men from the album ''The Flood (Of Mice & Men album), The Flood'' See also *Purified National Party, a break away from South African National Party which lasted from 1935 to 1948 *Purify (other) *Purification (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are Matter, substances which cannot resist any shear force applied to them. Although the term ''fluid'' generally includes both the liquid and gas phases, its definition varies among branches of science. Definitions of ''solid'' vary as well, and depending on field, some substances can have both fluid and solid properties. Non-Newtonian fluids like Silly Putty appear to behave similar to a solid when a sudden force is applied. Substances with a very high viscosity such as Pitch (resin), pitch appear to behave like a solid (see pitch drop experiment) as well. In particle physics, the concept is extended to include fluidic matters other than liquids or gases. A fluid in medicine or biology refers to any liquid constituent of the body (body fluid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isobaric
*
*
{{disambig ...
Isobar may refer to: * Isobar (meteorology), a line connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure reduced to sea level on the maps. * Isobaric process, a process taking place at constant pressure * Isobar (nuclide), one of multiple nuclides with the same mass but with different numbers of protons (or, equivalently, different numbers of neutrons). See also * Isosurface An isosurface is a three-dimensional analog of an isoline. It is a surface that represents points of a constant value (e.g. pressure, temperature, velocity, density) within a volume of space; in other words, it is a level set of a continuous f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isothermal
An isothermal process is a type of thermodynamic process in which the temperature ''T'' of a system remains constant: Δ''T'' = 0. This typically occurs when a system is in contact with an outside thermal reservoir, and a change in the system occurs slowly enough to allow the system to be continuously adjusted to the temperature of the reservoir through heat exchange (see quasi-equilibrium). In contrast, an ''adiabatic process'' is where a system exchanges no heat with its surroundings (''Q'' = 0). Simply, we can say that in an isothermal process * T = \text * \Delta T = 0 * dT = 0 * For ideal gases only, internal energy \Delta U = 0 while in adiabatic processes: * Q = 0. Etymology The noun '' isotherm'' is derived from the Ancient Greek words (), meaning "equal", and (), meaning "heat". Examples Isothermal processes can occur in any kind of system that has some means of regulating the temperature, including highly structured machines, and even living cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to the Human body, body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bounded organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bounded organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some functional units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst (these could be referred to as membrane bound in the sense that they are attached to (or bound to) the membrane). Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Buoyant Density Centrifugation
Buoyant density centrifugation (also isopycnic centrifugation or equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation) uses the concept of buoyancy to separate molecules in solution by their differences in density. Implementation Historically a cesium chloride (CsCl) solution was often used, but more commonly used density gradients are sucrose or Percoll. This application requires a solution with high density and yet relatively low viscosity, and CsCl suits it because of its high solubility in water, high density owing to the large mass of Cs, as well as low viscosity and high stability of CsCl solutions. The sample is put on top of the solution, and then the tube is spun at a very high speed for an extended time, at times lasting days. The CsCl molecules become densely packed toward the bottom, so a continuous gradient of layers of different densities (and CsCl concentrations) form. Since the original solution was approximately the same density, they go to a level where their density an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Craton
A craton ( , , or ; from "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. Cratons are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots extending several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle. Terminology The term ''craton'' is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons are composed of two layers: a continental '' shield'', in which the basement rock crops out at the surface, and a '' platform'' which o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
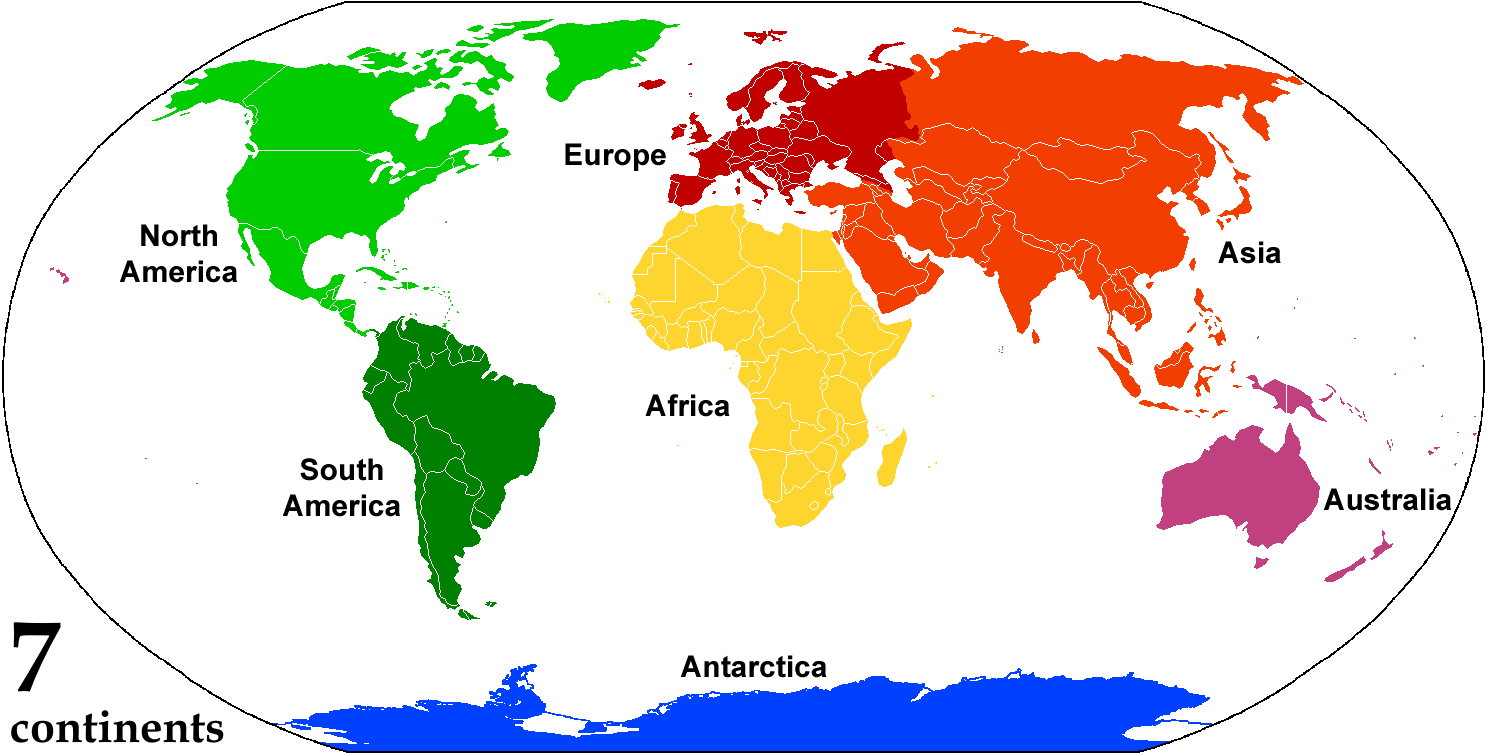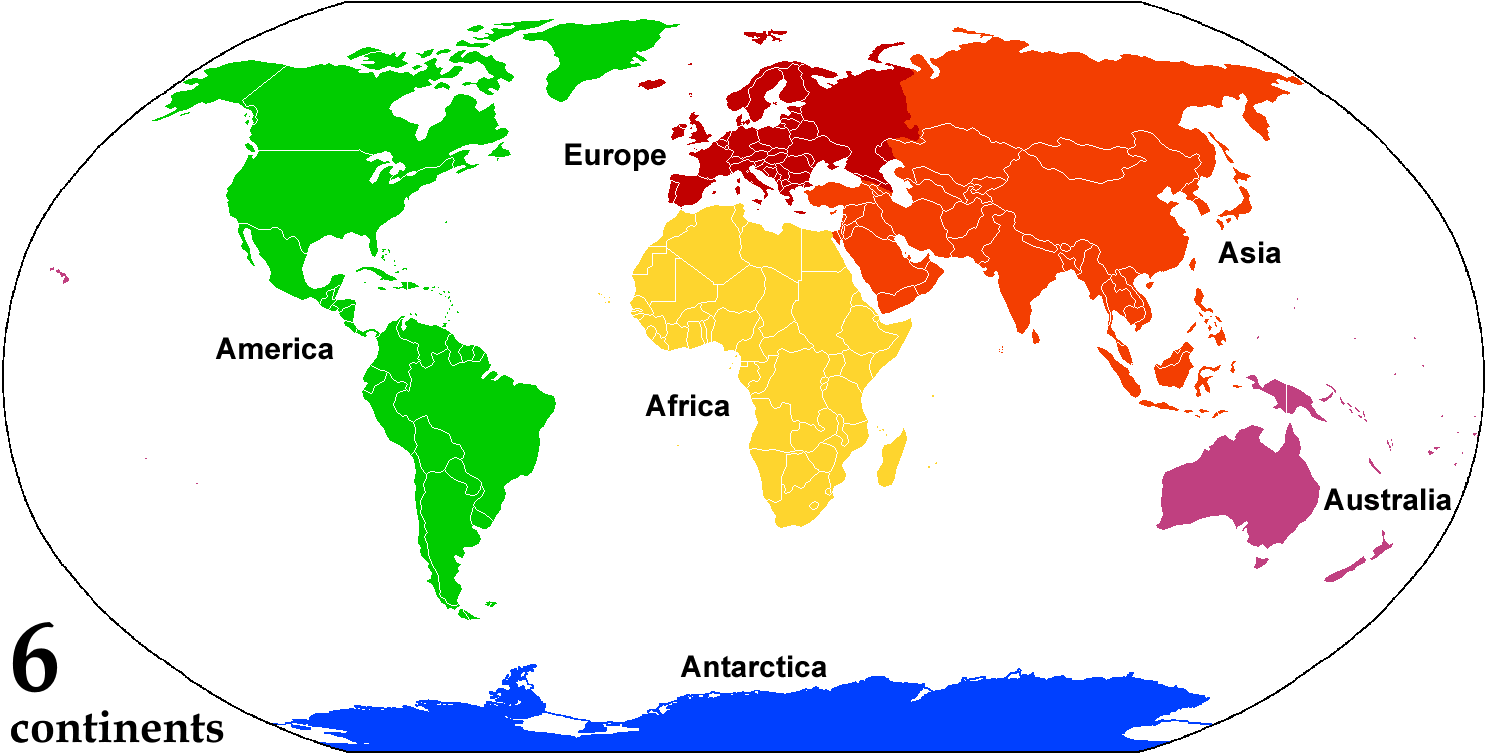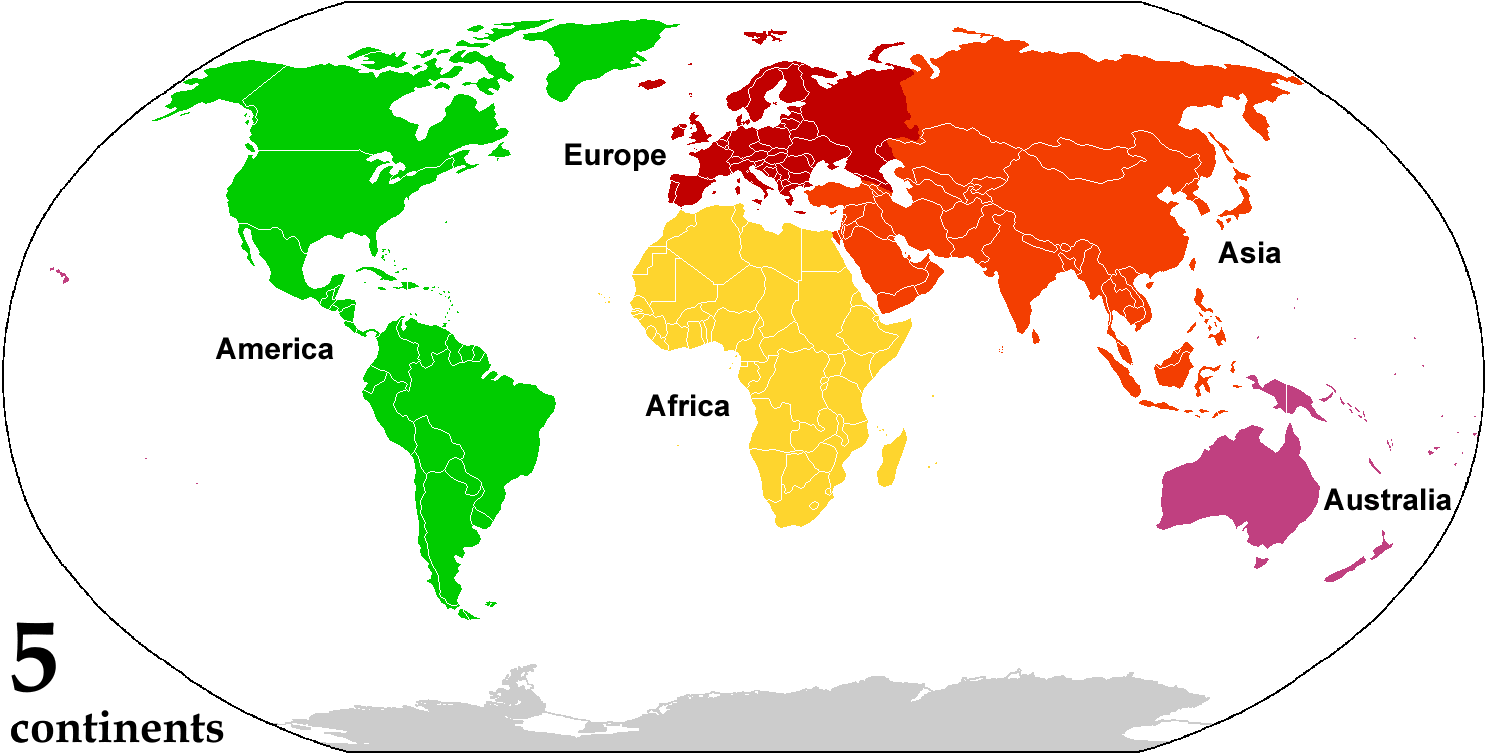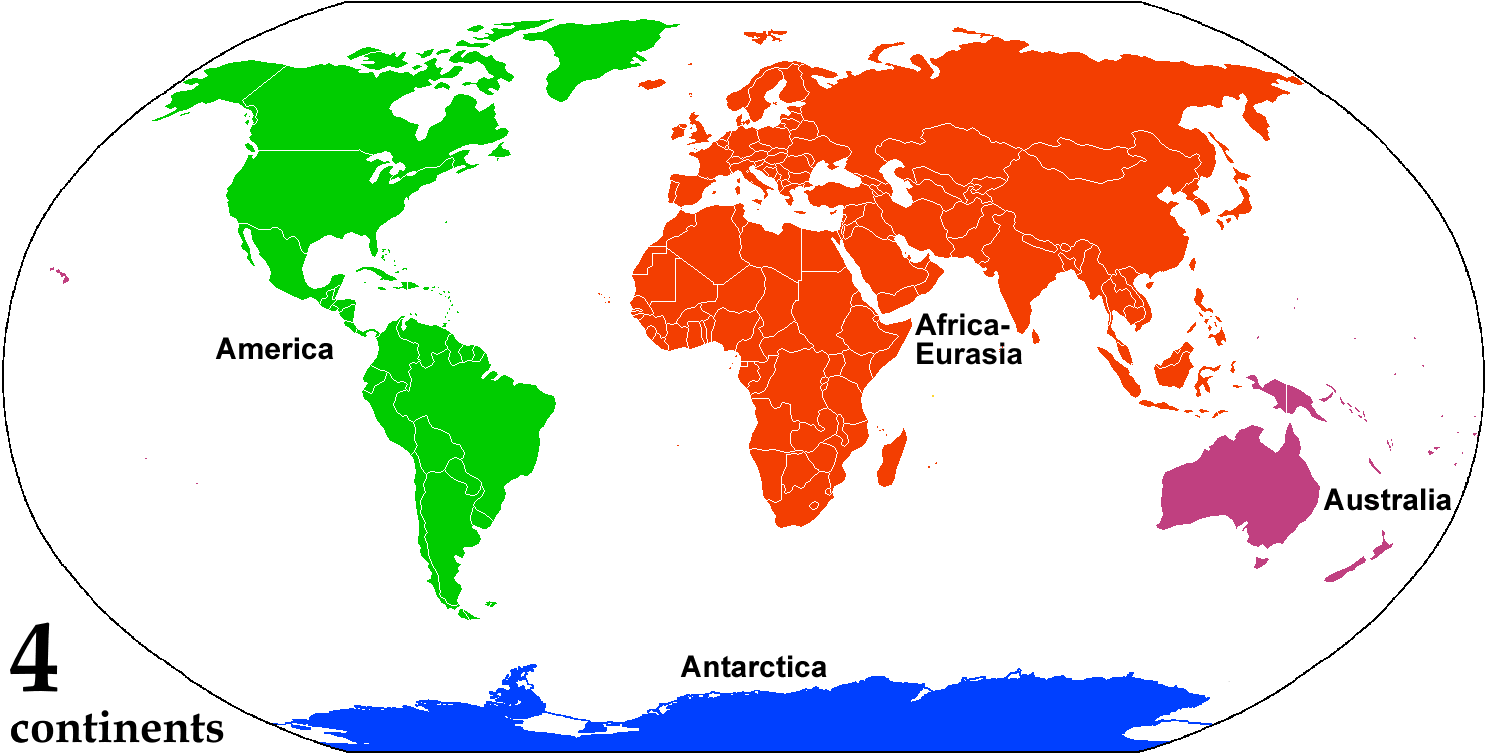
Continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as in the case of Asia or Europe within Eurasia, or a landmass and nearby islands within its continental shelf. Due to these varying definitions, the number of continents varies; up to seven or as few as four geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Most English-speaking world, English-speaking countries recognize seven regions as continents. In order from largest to smallest in area, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (continent), Australia (sometimes called Oceania or Australasia). Different variations with fewer continents merge some of these regions; examples of this are merging Asia and Europe into Eurasia, "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons. These processes include those of mountain-building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Principles of tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles can help geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth-surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shield (geology)
A shield is a large area of exposed Precambrian Crystallinity, crystalline igneous rock, igneous and high-grade metamorphic rock, metamorphic rocks that form tectonics, tectonically stable areas. These rocks are older than 570 million years and sometimes date back to around 2 to 3.5 billion years. They have been little affected by tectonic events following the end of the Precambrian, and are relatively flat regions where mountain building, faulting, and other tectonic processes are minor, compared with the activity at their margins and between tectonic plates. Shields occur on all continents. Terminology The term shield cannot be used interchangeably with the term craton. However, shield can be used interchangeably with the term basement (geology), basement. The difference is that a craton describes a basement overlain by a sedimentary rock, sedimentary platform (geology), platform while shield only describes the basement. The term ''shield'', used to describe this type of ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Platform (geology)
In geology, platform sediments can be classified into the following groups: a "protoplatform" of metamorphosed sediments at the bottom, a "quasiplatform" of slightly deformed sediments, a "cataplatform", and an "orthoplatform" at the top. The Mesoproterozoic Jotnian sediments of the Baltic area are examples of a "quasiplatform". The post-Ordovician The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ... rocks of the South American Platform are examples of an orthoplatform. See also * Carbonate platform * East European Platform * List of shields and cratons References Plate tectonics {{plate-tectonics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |