|
Intramuscular Fat
Intramuscular fat (also known as intramuscular triglycerides, intramuscular triacylglycerol, or intramyocellular triacylglycerol ''IMTG is located inside skeletal muscle fibers. It is stored in lipid droplets that exist in close proximity to the mitochondria, where it serves as an energy store that can be used during exercise. In humans, excess accumulation of intramuscular fat has been associated with conditions such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-lipodystrophy syndrome is associated with over-accumulation of intramuscular fat, which may contribute to AIDS wasting syndrome. Diabetes Increased IMTG was once thought responsible for increased insulin resistance. However, the discovery that athletes as well as obese individuals have high IMTG levels confounded these findings. Instead, IMTG metabolites, such as diacylglycerol and ceramide are responsible for the insulin resistance. Studies demonstrating the effects of IMTGs show that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
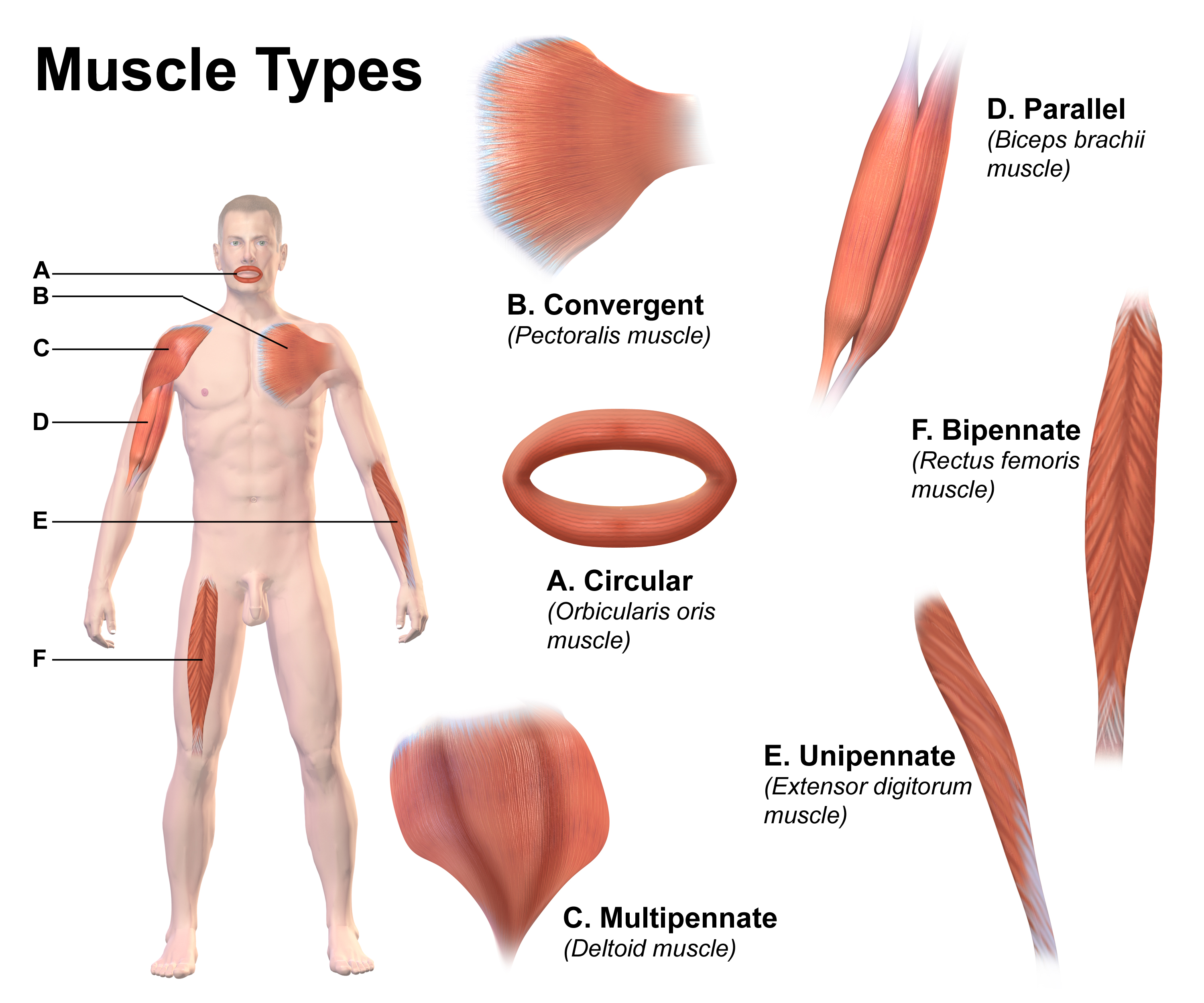
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein
Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes ''SREBF1'' and ''SREBF2''. SREBPs belong to the basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper class of transcription factors. Unactivated SREBPs are attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum membranes. In cells with low levels of sterols, SREBPs are cleaved to a water-soluble N-terminal domain that is translocated to the nucleus. These activated SREBPs then bind to specific sterol regulatory element DNA sequences, thus upregulating the synthesis of enzymes involved in sterol biosynthesis. Sterols in turn inhibit the cleavage of SREBPs and therefore synthesis of additional sterols is reduced through a negative feed back loop. Isoforms Mammalian genomes have two separate SREBP genes ( and ): * SREBP-1 expression produces two different isoforms, SREBP-1a and -1c. These isoforms differ in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Triacylglycerol
A triglyceride (from ''tri-'' and '' glyceride''; also TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver and are a major component of human skin oils. Many types of triglycerides exist. One specific classification focuses on saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats have ''no'' C=C groups; unsaturated fats feature one or more C=C groups. Unsaturated fats tend to have a lower melting point than saturated analogues; as a result, they are often liquid at room temperature. Chemical structure The three fatty acids substituents can be the same, but they are usually different. The positions of the three fatty acids are specified using stereospecific numbering as sn-1, sn-2, and sn-3. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an Branched chain fatty acids, unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important diet (nutrition), dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cell (biology), cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IRS1
Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) is a signaling adapter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IRS1'' gene. It is a 180 kDa protein with amino acid sequence of 1242 residues. It contains a single pleckstrin homology (PH) domain at the N-terminus and a PTB domain ca. 40 residues downstream of this, followed by a poorly conserved C-terminus tail. Together with IRS2, IRS3 (pseudogene) and IRS4, it is homologous to the ''Drosophila'' protein ''chico'', whose disruption extends the median lifespan of flies up to 48%. Similarly, Irs1 mutant mice experience moderate life extension and delayed age-related pathologies. Function Insulin receptor substrate 1 plays a key role in transmitting signals from the insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1) to intracellular pathways PI3K / Akt and Erk MAP kinase pathways. Tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 by insulin receptor (IR) introduces multiple binding sites for proteins bearing SH2 homology domai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols: : This equation can be written in several ways that are nearly equivalent that describe the behaviors of various protonated states of ATP, ADP, and the phosphorylated product. As is clear from the equation, a phosphate group per se is not transferred, but a phosphoryl group (PO3-). Phosphoryl is an electrophile. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. During respiration Phosphorylation is essential to the processes of both anaerobic and aerobic respiration, which involve the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the "high-energy" exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. As a result, kinase produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whether it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of sphingosine and a fatty acid joined by an amide bond. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular lipid signaling, signaling: examples include regulating cell differentiation, differentiation, cell proliferation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of Cell (biology), cells. The word ''ceramide'' comes from the Latin ''cera'' (wax) and ''amide''. Ceramide is a component of vernix caseosa, the waxy or cheese-like white substance found coating the skin of newborn human infants. Pathways for ceramide synthesis There are three major pathways of ceramide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'', meaning a thread-like granule, was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase popularized by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 ''Scientific American'' article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). The multicellular animal '' Henneguya salminicola'' is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles despite a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome. A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
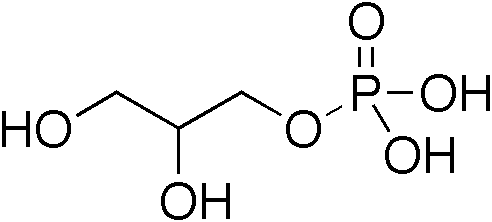
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |