|
Interface (chemistry)
In the physical sciences, an interface is the boundary between two spatial regions occupied by different matter, or by matter in different physical states. The interface between matter and air, or matter and vacuum, is called a surface, and studied in surface science. In thermal equilibrium, the regions in contact are called phases, and the interface is called a phase boundary. An example for an interface out of equilibrium is the grain boundary in polycrystalline matter. The importance of the interface depends on the type of system: the bigger the quotient area/volume, the greater the effect the interface will have. Consequently, interfaces are very important in systems with large interface area-to-volume ratios, such as colloids. Interfaces can be flat or curved. For example, oil droplets in a salad dressing are spherical but the interface between water and air in a glass of water is mostly flat. Surface tension is the physical property which rules interface process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Physical Science
Physical science is a branch of natural science that studies abiotic component, non-living systems, in contrast to life science. It in turn has many branches, each referred to as a "physical science", together is called the "physical sciences". Definition Physical science can be described as all of the following: * A branch of outline of science, science (a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes Outline of knowledge, knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe)."... modern science is a discovery as well as an invention. It was a discovery that nature generally acts regularly enough to be described by laws and even by mathematics; and required invention to devise the techniques, abstractions, apparatus, and organization for exhibiting the regularities and securing their law-like descriptions." —p.vii, J. L. Heilbron, (2003, editor-in-chief). ''The Oxford Companion to the History of Modern Science''. New York: Oxford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Pressure
In fluid statics, capillary pressure () is the pressure between two immiscible fluids in a thin tube (see capillary action), resulting from the interactions of forces between the fluids and solid walls of the tube. Capillary pressure can serve as both an opposing or driving force for fluid transport and is a significant property for research and industrial purposes (namely microfluidic design and oil extraction from porous rock). It is also observed in natural phenomena. Definition Capillary pressure is defined as: :p_c=p_-p_ where: :p_ is the capillary pressure :p_ is the pressure of the non-wetting phase :p_ is the pressure of the wetting phase The wetting phase is identified by its ability to preferentially diffuse across the capillary walls before the non-wetting phase. The "wettability" of a fluid depends on its surface tension, the forces that drive a fluid's tendency to take up the minimal amount of space possible, and it is determined by the contact angle of the fluid.F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloidal Chemistry
Interface and colloid science is an interdisciplinary intersection of branches of chemistry, physics, nanoscience and other fields dealing with ''colloids'', heterogeneous systems consisting of a mechanical mixture of particles between 1 nm and 1000 nm dispersed in a continuous medium. A colloidal solution is a heterogeneous mixture in which the particle size of the substance is intermediate between a Solution (chemistry), true solution and a suspension (chemistry), suspension, i.e. between 1–1000 nm. Smoke from a fire is an example of a colloidal system in which tiny particles of solid float in air. Just like true solutions, colloidal particles are small and cannot be seen by the naked eye. They easily pass through filter paper. But colloidal particles are big enough to be blocked by parchment paper or animal membrane. Interface and colloid science has applications and ramifications in the chemical industry, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, ceramics, minerals, nanotec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Phenomenon
Surface science is the study of physical and chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, including solid–liquid interfaces, solid– gas interfaces, solid–vacuum interfaces, and liquid– gas interfaces. It includes the fields of ''surface chemistry'' and '' surface physics''. Some related practical applications are classed as surface engineering. The science encompasses concepts such as heterogeneous catalysis, semiconductor device fabrication, fuel cells, self-assembled monolayers, and adhesives. Surface science is closely related to interface and colloid science. Interfacial chemistry and physics are common subjects for both. The methods are different. In addition, interface and colloid science studies macroscopic phenomena that occur in heterogeneous systems due to peculiarities of interfaces. History The field of surface chemistry started with heterogeneous catalysis pioneered by Paul Sabatier on hydrogenation and Fritz Haber on the Haber proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Biological membranes include cell membranes (outer coverings of cells or organelles that allow passage of certain constituents); nuclear membranes, which cover a cell nucleus; and tissue membranes, such as mucous membrane, mucosae and serous membrane, serosae. Synthetic membranes are made by humans for use in laboratory, laboratories and industry (such as chemical plants). This concept of a membrane has been known since the eighteenth century but was used little outside of the laboratory until the end of World War II. Drinking water supplies in Europe had been compromised by The War and membrane filters were used to test for water safety. However, due to the lack of reliability, slow operation, reduced selectivity and elevated costs, membran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface And Colloid Science
Interface and colloid science is an interdisciplinary intersection of branches of chemistry, physics, nanoscience and other fields dealing with ''colloids'', heterogeneous systems consisting of a mechanical mixture of particles between 1 nm and 1000 nm dispersed in a continuous medium. A colloidal solution is a heterogeneous mixture in which the particle size of the substance is intermediate between a Solution (chemistry), true solution and a suspension (chemistry), suspension, i.e. between 1–1000 nm. Smoke from a fire is an example of a colloidal system in which tiny particles of solid float in air. Just like true solutions, colloidal particles are small and cannot be seen by the naked eye. They easily pass through filter paper. But colloidal particles are big enough to be blocked by parchment paper or animal membrane. Interface and colloid science has applications and ramifications in the chemical industry, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, ceramics, minerals, nanotec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Surface
In physics, a free surface is the surface of a fluid that is subject to zero parallel shear stress, such as the interface between two homogeneous fluids. An example of two such homogeneous fluids would be a body of water (liquid) and the air in the Earth's atmosphere (gas mixture). Unlike liquids, gases cannot form a free surface on their own. Fluidized/ liquified solids, including slurries, granular materials, and powders may form a free surface. A liquid in a gravitational field will form a free surface if unconfined from above. Under mechanical equilibrium this free surface must be perpendicular to the forces acting on the liquid; if not there would be a force along the surface, and the liquid would flow in that direction. Thus, on the surface of the Earth, all free surfaces of liquids are horizontal unless disturbed (except near solids dipping into them, where surface tension distorts the surface in a region called the meniscus). In a free liquid that is not affecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
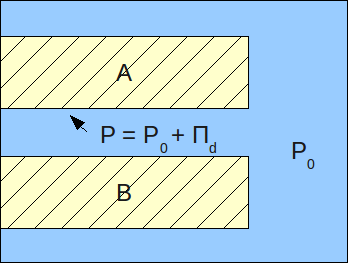
Disjoining Pressure
In surface chemistry, disjoining pressure (symbol ) according to an IUPAC definition arises from an attractive interaction between two surfaces. For two flat and parallel surfaces, the value of the disjoining pressure (i.e., the force per unit area) can be calculated as the derivative of the Gibbs energy of interaction per unit area in respect to distance (in the direction normal to that of the interacting surfaces). There is also a related concept of disjoining force, which can be viewed as disjoining pressure times the surface area of the interacting surfaces. The concept of disjoining pressure was introduced by Derjaguin (1936) as the difference between the pressure in a region of a phase adjacent to a surface confining it, and the pressure in the bulk of this phase. Description Disjoining pressure can be expressed as:Hans-Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, Michael Kappl,"Physics and chemistry of interfaces", John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd., 1 edition, 2003, page 9(Google books)/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Surface
In fluid mechanics and mathematics, a capillary surface is a surface that represents the interface between two different fluids. As a consequence of being a surface, a capillary surface has no thickness in slight contrast with most real fluid interfaces. Capillary surfaces are of interest in mathematics because the problems involved are very nonlinear and have interesting properties, such as discontinuous dependence on boundary data at isolated points. In particular, static capillary surfaces with gravity absent have constant mean curvature, so that a minimal surface is a special case of static capillary surface. They are also of practical interest for fluid management in space (or other environments free of body forces), where both flow and static configuration are often dominated by capillary effects. The stress balance equation The defining equation for a capillary surface is called the stress balance equation, which can be derived by considering the forces and stresses acting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosols
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or human causes. The term ''aerosol'' commonly refers to the mixture of particulates in air, and not to the particulate matter alone. Examples of natural aerosols are fog, mist or dust. Examples of human caused aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at hydroelectric dams, irrigation mist, perfume from atomizers, smoke, dust, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. Several types of atmospheric aerosol have a significant effect on Earth's climate: volcanic, desert dust, sea-salt, that originating from biogenic sources and human-made. Volcanic aerosol forms in the stratosphere after an eruption as droplets of sulfuric acid that can prevail for up to two years, and reflect sunlight, lowering temperature. Desert dust, mineral particles blown to high altitudes, absorb heat and may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window panes, tableware, and optics. Some common objects made of glass are named after the material, e.g., a Tumbler (glass), "glass" for drinking, "glasses" for vision correction, and a "magnifying glass". Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the Melting, molten form. Some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring, and obsidian has been used to make arrowheads and knives since the Stone Age. Archaeological evidence suggests glassmaking dates back to at least 3600 BC in Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, Egypt, or Syria. The earliest known glass objects were beads, perhaps created accidentally during metalworking or the production of faience, which is a form of pottery using lead glazes. Due to its ease of formability int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are ground, polished, or molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices such as telescopes, binoculars, and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from , the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |