|
Intelligence Quotient
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. Originally, IQ was a score obtained by dividing a person's mental age score, obtained by administering an intelligence test, by the person's chronological age, both expressed in terms of years and months. The resulting fraction (quotient) was multiplied by 100 to obtain the IQ score. For modern #Current tests, IQ tests, the test score, raw score is Data transformation (statistics), transformed to a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 15. This results in approximately two-thirds of the population scoring between IQ 85 and IQ 115 and about 2 percent each Intellectual giftedness, above 130 and Intellectual disability, below 70. Scores from intelligence tests are estimates of intelligence. Unlike, for example, distance and mass, a concrete measure of intelligence cannot be achieved given the abstract nature of the concept o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raven Matrix
A raven is any of several large-bodied passerine bird species in the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single Taxon, taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between crows and ravens; the two names are assigned to different species chiefly by size. The largest raven species are the common raven and the thick-billed raven; these are also the largest passerine species. Etymology The term ''raven'' originally referred to the common raven (''Corvus corax''), the widespread species of the Northern Hemisphere. The modern English word ''raven'' has cognates in all other Germanic languages, including Old Norse (and subsequently Icelandic language, modern Icelandic) and Old High German , all of which descend from Proto-Germanic . Collective nouns for a group of ravens include a "conspiracy", a "treachery", a "rave" and an "unkindness"; in practice, most people use the more generic "flock". Extant species * ''Corvus albicollis'' – White-neck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Status
Social status is the relative level of social value a person is considered to possess. Such social value includes respect, honour, honor, assumed competence, and deference. On one hand, social scientists view status as a "reward" for group members who treat others well and take initiative. This is one explanation for its apparent cross-cultural universality. On the other hand, while people with higher status experience a litany of benefits—such as greater health, admiration, resources, influence, and freedom—those with lower status experience poorer outcomes across all of those metrics. Importantly, status is based in widely shared ''beliefs'' about who members of a society judge as more competent or moral. While such beliefs can stem from an impressive performance or success, they can also arise from possessing characteristics a society has deemed meaningful like a person's race or occupation. In this way, status reflects how a society judges a person's relative social worth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-scholarship
Pseudo-scholarship (from pseudo- and scholarship) is a term used to describe work (e.g., publication, lecture) or a body of work that is presented as, but is not, the product of rigorous and objective study or research; the act of producing such work; or the pretended learning upon which it is based. Examples of pseudo-scholarship include: *Pseudoarchaeology * Pseudohistory * Pseudolaw * Pseudolinguistics * Pseudomathematics * Pseudophilosophy *PseudoscienceJeremy Bernstein, ''A Comprehensible World: On Modern Science and Its Origins'', 2nd ed. (New York: Random House, 1967) p. 193 See also * Chaos magic *Conspiracy theory * Counterknowledge * Crackpot index * Crank (person) * Fallacy *Fringe science Fringe science refers to ideas whose attributes include being highly speculative or relying on premises already Objection (argument), refuted. The chance of ideas rejected by editors and published outside the mainstream being correct is remote. Wh ... * Fringe theory * Ignoratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
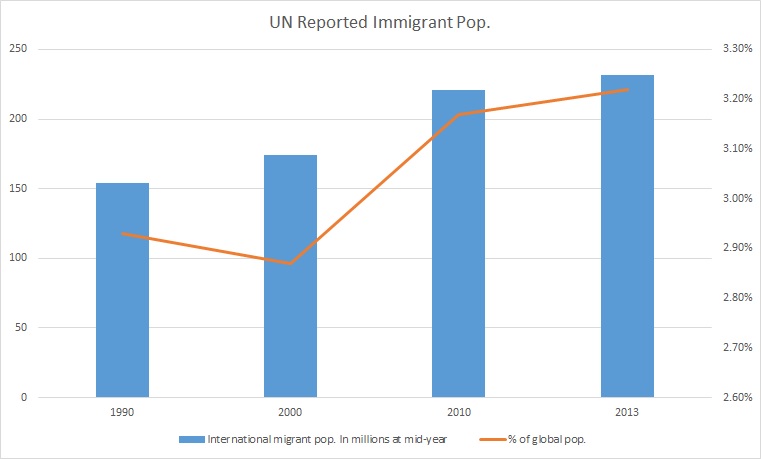
Immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as Permanent residency, permanent residents. Commuting, Commuters, Tourism, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; Seasonal industry, seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racial Segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, such as schools and hospitals by people of different races. Specifically, it may be applied to activities such as eating in restaurants, drinking from water fountains, using public toilets, attending schools, going to movie theaters, riding buses, renting or purchasing homes, renting hotel rooms, going to supermarkets, or attending places of worship. In addition, segregation often allows close contact between members of different racial or ethnic groups in social hierarchy, hierarchical situations, such as allowing a person of one race to work as a servant for a member of another race. Racial segregation has generally been outlawed worldwide. Segregation is defined by the European Commission against Racism and Intolerance as "the act by w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that the Human, human species is divided into biologically distinct taxa called "race (human categorization), races", and that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racial discrimination, racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies can be more extensive than the stunting of life, few injustices deeper than the denial of an opportunity to strive or even to hope, by a limit imposed from without, but falsely identified as lying within". Before the mid-20th century, scientific racism was accepted throughout the scientific community, but it is no longer considered scientific. The division of humankind into biologically separate groups, along with the assignment of particular physical and mental characteristics to these groups through constructing and applying corresponding Scientific modelling, explanatory models, is referred to as racialism, racial realism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claims; reliance on confirmation bias rather than rigorous attempts at refutation; lack of openness to evaluation by other experts; absence of systematic practices when developing hypotheses; and continued adherence long after the pseudoscientific hypotheses have been experimentally discredited. It is not the same as junk science. The demarcation between science and pseudoscience has scientific, philosophical, and political implications. Philosophers debate the nature of science and the general criteria for drawing the line between scientific theories and pseudoscientific beliefs, but there is widespread agreement "that creationism, astrology, homeopathy, Kirlian photography, dowsing, ufology, ancient astronaut theory, Holocaust den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugenics
Eugenics is a set of largely discredited beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter the frequency of various human phenotypes by inhibiting the fertility of those considered inferior, or promoting that of those considered superior. The contemporary history of eugenics began in the late 19th century, when a popular eugenics movement emerged in the United Kingdom, and then spread to many countries, including the United States, Canada, Australia, and most European countries (e.g. Sweden and Germany). In this period, people from across the political spectrum espoused eugenics. Many countries adopted eugenic policies intended to improve the quality of their populations. Historically, the idea of ''eugenics'' has been used to argue for a broad array of practices ranging from prenatal care for mothers deemed genetically desirable to the forced sterilization and murder of those deemed unf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flynn Effect
The Flynn effect is the substantial and long-sustained increase in both fluid and crystallized intelligence test scores that were measured in many parts of the world over the 20th century, named after researcher James Flynn (academic), James Flynn (1934–2020). When intelligence quotient (IQ) tests are initially Standard score#Standardizing in mathematical statistics, standardized using a Sample (statistics), sample of test-takers, by convention the average of the test results is set to 100 and their standard deviation is set to 15 or 16 IQ points. When IQ tests are revised, they are again standardized using a new sample of test-takers, usually born more recently than the first; the average result is set to 100. When the new test subjects take the older tests, in almost every case their average scores are significantly above 100. Test score increases have been continuous and approximately linear from the earliest years of testing to the present. For example, a study published in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation And Dependence
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For example, a person's income in an economic sense may be different from their income as defined by law. An extremely important definition of income is Haig–Simons income, which defines income as ''Consumption + Change in net worth'' and is widely used in economics. For households and individuals in the United States, income is defined by tax law as a sum that includes any wage, salary, profit, interest payment, rent, or other form of earnings received in a calendar year.Case, K. & Fair, R. (2007). ''Principles of Economics''. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. p. 54. Discretionary income is often defined as gross income minus taxes and other deductions (such as mandatory pension contributions), and is widely used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Performance Rating (work Measurement)
Performance rating is the step in the work measurement in which the analyst observes the worker's performance and records a value representing that performance relative to the analyst's concept of standard performance. Performance rating helps people do their jobs better, identifies training and education needs, assigns people to work they can excel in, and maintains fairness in salaries, benefits, promotion, hiring, and firing. Most workers want to know how they are doing on the job. Workers need performance feedback to work effectively. Accessing an employee timely, accurate, constructive feedback is key to effective performance. Motivational strategies such as goal setting depend upon regular performance updates. There are many sources of error with performance ratings, and error can be reduced through rater training and through the use of behaviorally anchored rating scales. In industrial and organizational psychology such scales are used to clearly define the behaviors that co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |