|
Immunohistochemical
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett Coons, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in paraffin, but also cryopreservated (frozen) tissue. Based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromogenic Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Coons, Albert Hewett Coons, Ernst Berliner, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in Paraffin wax, paraffin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunostaining
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods. Techniques Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry or IHC staining of tissue sections (or immunocytochemistry, which is the staining of cells), is perhaps the most commonly applied immunostaining technique. While the first cases of IHC staining used fluorescent dyes (see ''immunofluorescence''), other non-fluorescent methods using enzymes such as peroxidase (see '' immunoperoxidase staining'') and alkaline phosphatase are now used. These enzymes are capable of catalysing reactions that give a coloured product that is easily detectable by ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen Retrieval
Antigen retrieval is a non-enzymatic pretreatment for immunostaining to reduce or eliminate the chemical modifications caused by formalin fixation, through high temperature heating or strong alkaline solution (non-heating). Background In medicine, most surgically removed tissue samples are fixed in formalin (4% formaldehyde) and embedded in paraffin to preserve the morphology for review by pathologists using stains and microscopy to make a diagnosis. However, formaldehyde can induce chemical modifications that reduce the detectability of proteins (antigens) in immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Alber .... Antigen retrieval technique is a non-enzymatic pretreatment for immunostaining to reduce or eliminate these formalin-induced chemical modifications thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
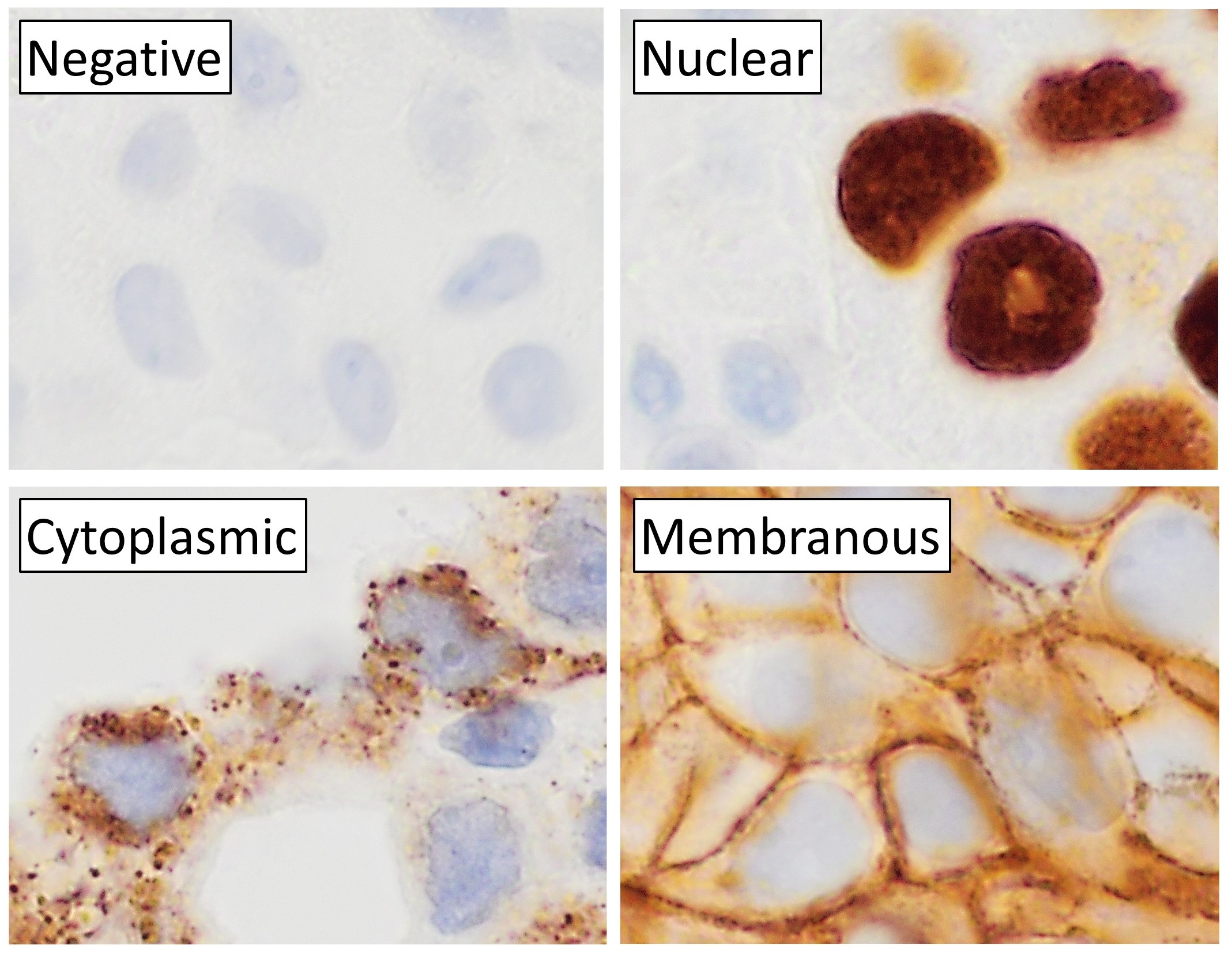
Main Staining Patterns On Immunohistochemistry
Main may refer to: Geography *Main River (other), multiple rivers with the same name *Ma'in, an ancient kingdom in modern-day Yemen * Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province * Spanish Main, the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries *'' The Main'', the diverse core running through Montreal, Quebec, Canada, also separating the Two Solitudes * Main (lunar crater), located near the north pole of the Moon * Main (Martian crater) People and organizations * Main (surname), a list of people with this family name *Main, alternate spelling for the Minaeans, an ancient people of modern-day Yemen * Main (band), a British ambient band formed in 1991 * Chas. T. Main, an American engineering and hydroelectric company founded in 1893 *MAIN (Mountain Area Information Network), former operator of WPVM-LP (MAIN-FM) in Asheville, North Carolina, U.S. * Main Deli Steak House ("The Main"), a smoked-meat delicatessen in Montreal, Quebec, Canada Ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Cd10 Ihc
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescein
Fluorescein is an organic compound and dye based on the xanthene tricyclic structural motif, formally belonging to Triarylmethane dye, triarylmethine dyes family. It is available as a dark orange/red powder slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is used as a fluorescent Flow tracer, tracer in many applications. The color of its aqueous solutions is green by reflection and orange by transmission (its spectral properties are dependent on pH of the solution), as can be noticed in spirit level, bubble levels, for example, in which fluorescein is added as a colorant to the Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol filling the tube in order to increase the visibility of the air bubble contained within. More concentrated solutions of fluorescein can even appear red (because under these conditions nearly all incident emission is re-absorbed by the solution). It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Uses Fluorescein sodium, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive And Negative Controls In Immunohistochemistry
Positive is a property of positivity and may refer to: Mathematics and science * Positive formula, a logical formula not containing negation * Positive number, a number that is greater than 0 * Plus sign, the sign "+" used to indicate a positive number * Positive operator, a type of linear operator in mathematics * Positive result, a result that has been found significant in statistical hypothesis testing * Positive test, a diagnostic test result that indicates some parameter being evaluated was present * Positive charge, one of the two types of electrical charge * Positive (electrical polarity), in electrical circuits * Positive lens, in optics * Positive (photography), a positive image, in which the color and luminance correlates directly with that in the depicted scene * Positive sense, said of an RNA sequence that codes for a protein Philosophy and humanities * Affirmative (policy debate), the team which affirms the resolution * Negative and positive rights, concernin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosciences
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
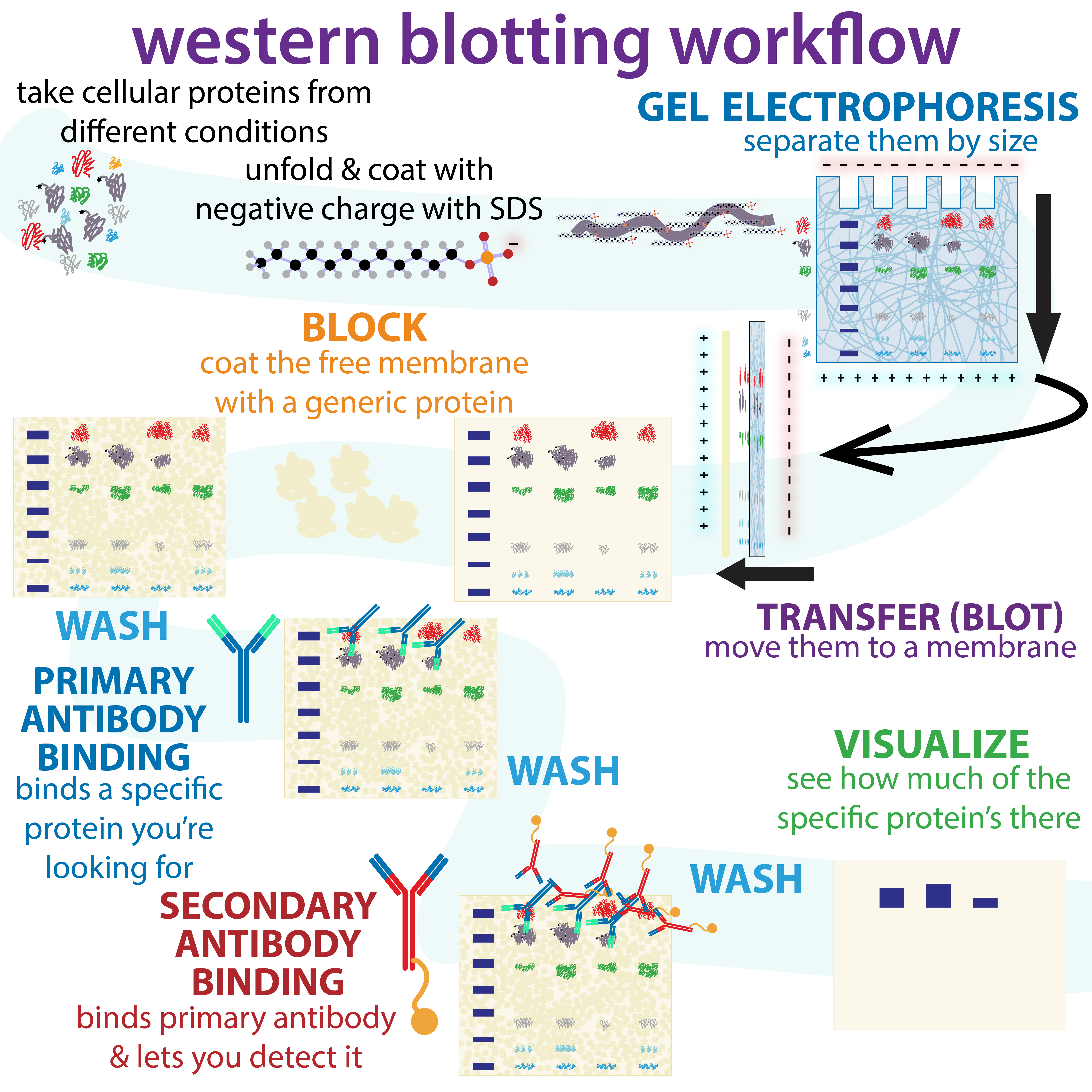
Immunoblotting
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibody. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |