|
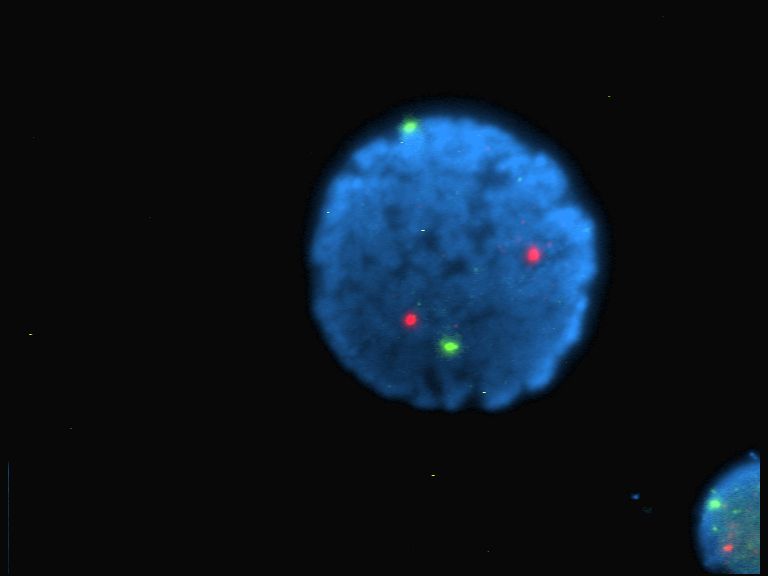
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence (IF) is a light microscopy-based technique that allows detection and localization of a wide variety of target biomolecules within a cell or tissue at a quantitative level. The technique utilizes the binding specificity of antibodies and antigens. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. Several antibodies can recognize the same epitope but differ in their binding affinity. The antibody with the higher affinity for a specific epitope will surpass antibodies with a lower affinity for the same epitope. By conjugating the antibody to a fluorophore, the position of the target biomolecule is visualized by exciting the fluorophore and measuring the emission of light in a specific predefined wavelength using a fluorescence microscope. It is imperative that the binding of the fluorophore to the antibody itself does not interfere with the immunological specificity of the antibody or the binding capacity of its antigen. Immunofluore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Immunostaining
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods. Techniques Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry or IHC staining of tissue sections (or immunocytochemistry, which is the staining of cells), is perhaps the most commonly applied immunostaining technique. While the first cases of IHC staining used fluorescent dyes (see ''immunofluorescence''), other non-fluorescent methods using enzymes such as peroxidase (see '' immunoperoxidase staining'') and alkaline phosphatase are now used. These enzymes are capable of catalysing reactions that give a coloured product that is easily detectable by ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
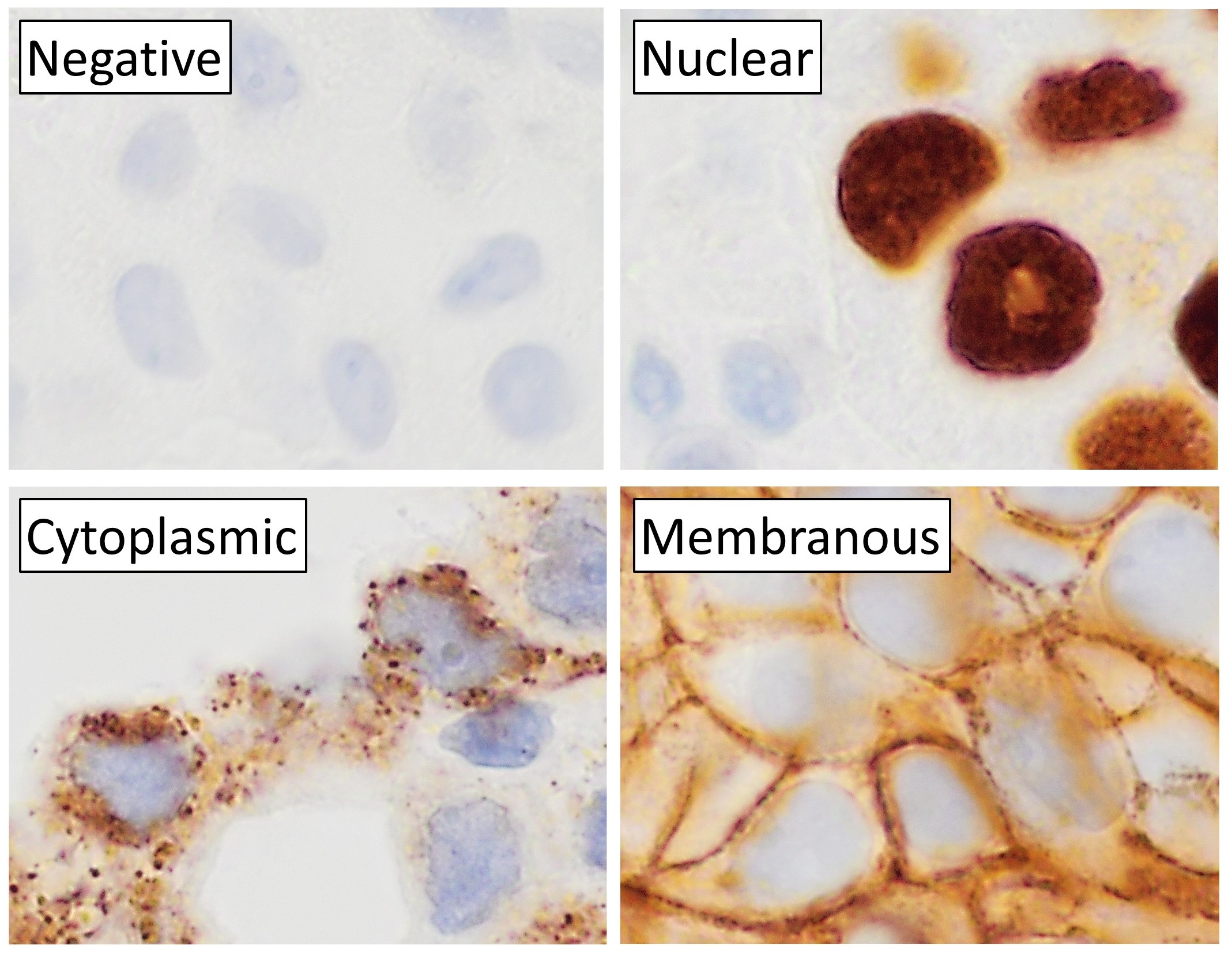
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Coons, Albert Hewett Coons, Ernst Berliner, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in Paraffin wax, paraffin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Each individual antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens, and antigens of virtually any size and chemical composition can be recognized. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each of the branching chains comprising the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" the antigen (or a microbe or an infected cell bearing such an antigen) for attack by cells of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a viru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lupus Band Test
Lupus band test is done upon skin biopsy, with direct immunofluorescence staining, in which, if positive, IgG and complement depositions are found at the dermoepidermal junction.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. . This test can be helpful in distinguishing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) from cutaneous lupus, because in SLE the lupus band test will be positive in both involved and uninvolved skin, whereas with cutaneous lupus only the involved skin will be positive. The minimum criteria for positivity are:Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2011; 7: 27–32. The lupus band test in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Adam Reich, Katarzyna Marcinow, and Rafal Bialynicki-Birula * In sun-exposed skin: presence of a band of deposits of IgM along the epidermal basement membrane in 50% of the biopsy, intermediate (2+) intensity or more. * In sun-protected skin : presence of interrupted (i.e. less than 50%) de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Albert Coons
Albert Hewett Coons (June 28, 1912 – September 30, 1978) was an American physician, pathologist, and immunologist. He was the first person to conceptualize and develop immunofluorescent techniques for labeling antibodies in the early 1940s. Early years Coons was born in Gloversville, New York, on June 28, 1912, the son of Albert Selmser and Marion (née Hewett) Coons. His father was the president of a glove-manufacturing company, and his grandfather, Eugene Coons, was a physician. He was educated in Gloversville public schools, graduated with a B.S. from Williams College (Williamstown, Massachusetts) in 1933, and received his M.D. degree from Harvard Medical School in 1937.McDevitt, H. OAlbert Hewett Coons ''Biographical memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences''. Thereafter, Albert pursued residency training in internal medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. During the final years of his house-officership, Coons joined the Thorndike Memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photobleaching
In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it is permanently unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between the fluorophore and surrounding molecules. Such irreversible modifications in covalent bonds are caused by transition from a singlet state to the triplet state of the fluorophores. The number of excitation cycles to achieve full bleaching varies. In microscopy, photobleaching may complicate the observation of fluorescent molecules, since they will eventually be destroyed by the light exposure necessary to stimulate them into fluorescing. This is especially problematic in time-lapse microscopy. However, photobleaching may also be used prior to applying the (primarily antibody-linked) fluorescent molecules, in an attempt to quench autofluorescence. This can help improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Photobleaching may also be exploited to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Optical Microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast. The object is placed on a stage and may be directly viewed through one or two eyepieces on the microscope. In high-power microscopes, both eyepieces typically show the same image, but with a stereo microscope, slightly different images are used to create a 3-D effect. A camera is typically used to capture the image (micrograph). The sample can be lit in a variety of ways. Transparent objects can be lit from below and solid objects can be lit with light coming through ( bright field) or around ( dark field) the objective lens. Polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to macromolecules, serving as a markers (or dyes, or tags, or reporters) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, such as fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DAPI
DAPI (pronounced 'DAPPY', /ˈdæpiː/), or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, is a fluorescent stain that binds strongly to adenine– thymine-rich regions in DNA. It is used extensively in fluorescence microscopy. As DAPI can pass through an intact cell membrane, it can be used to stain both live and fixed cells, though it passes through the membrane less efficiently in live cells and therefore provides a marker for membrane viability. History DAPI was first synthesised in 1971 in the laboratory of Otto Dann as part of a search for drugs to treat trypanosomiasis. Although it was unsuccessful as a drug, further investigation indicated it bound strongly to DNA and became more fluorescent when bound. This led to its use in identifying mitochondrial DNA in ultracentrifugation in 1975, the first recorded use of DAPI as a fluorescent DNA stain. Strong fluorescence when bound to DNA led to the rapid adoption of DAPI for fluorescent staining of DNA for fluorescence microscopy. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Green Fluorescent Protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victoria'' and is sometimes called ''avGFP''. However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods and lancelets. The GFP from ''A. victoria'' has a major excitation peak at a wavelength of 395 nm and a minor one at 475 nm. Its emission peak is at 509 nm, which is in the lower green portion of the visible spectrum. The fluorescence quantum yield (QY) of GFP is 0.79. The GFP from the sea pansy ('' Renilla reniformis'') has a single major excitation peak at 498 nm. GFP makes for an excellent tool in many forms of biology due to its ability to form an internal chromophore without requiring any accessory cofactors, gene products, or enzymes / substrates other than molecular ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexa Fluor
The Alexa Fluor family of fluorescent dyes is a series of dyes invented by Molecular Probes, now a part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, and sold under the Invitrogen brand name. Alexa Fluor dyes are frequently used as cell and tissue labels in fluorescence microscopy and cell biology. Alexa Fluor dyes can be conjugated directly to primary antibodies or to secondary antibodies to amplify signal and sensitivity or other biomolecules. The excitation and emission spectra of the Alexa Fluor series cover the visible spectrum and extend into the infrared. The individual members of the family are numbered according roughly to their excitation maxima in nanometers. History Richard and Rosaria Haugland, the founders of Molecular Probes, are well known in biology and chemistry for their research into fluorescent dyes useful in biological research applications. At the time that Molecular Probes was founded, such products were largely unavailable commercially. A number of fluorescent d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |