|
Imipenem
Imipenem (trade name Primaxin among others) is a synthetic beta-lactam, β-lactam antibiotic belonging to the carbapenems chemical class. developed by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enzymes produced by many multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, thus playing a key role in the treatment of infections not readily treated with other antibiotics. It is usually administered through intravenous injection. Imipenem was patented in 1975 and approved for medical use in 1985. It was developed via a lengthy trial-and-error search for a more stable version of the natural product thienamycin, which is produced by the bacterium ''Streptomyces cattleya''. Thienamycin has antibacterial activity, but is unstable in aqueous solution, thus it is practically of no medicinal use. Imipenem has a broad spectrum of activity against Aerobic organism, aerobic and Anaerobic organism, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbapenem Antibiotics
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multiple drug resistance, multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins, carbapenems are members of the beta-lactam antibiotics drug class, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antimicrobial resistance, antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams. Carbapenem antibiotics were originally developed at Merck & Co. from the carbapenem thienamycin, a naturally derived product of ''Streptomyces cattleya''. Concern has arisen in recent years over increasing rates of resistance to carbapenems, as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotic ..., carbapenems are members of the beta-lactam antibiotics drug class, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams. Carbapenem antibiotics were originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide Multiple drug resistance, multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a ''Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold () resembles that of a DD-Transpeptidase, DD-transpeptidase, from which the enzyme is thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilastatin
Cilastatin inhibits the human enzyme dehydropeptidase. Uses Dehydropeptidase is an enzyme found in the kidney and is responsible for degrading the antibiotic imipenem. Cilastatin can therefore be combined intravenously with imipenem in order to protect it from degradation, prolonging its antibacterial effect. Imipenem alone is an effective antibiotic and can be given without cilastatin. Cilastatin itself does not have antibiotic activity, although it has been proved to be active against a zinc-dependent beta-lactamase that usually confers antibiotic resistance to certain bacteria, more precisely, the carbapenem family of antibiotics. This property is due to the physicochemical similarities between membrane dipeptidase (MDP), the compound it is usually set to target, and the bacterial metallo-beta-lactamase carried by the CphA gene. The combination allows the antibiotic to be more effective by changing the pharmacokinetics involved. Thus imipenem/cilastatin, like amoxicillin/c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acinetobacter Baumannii
''Acinetobacter baumannii'' is a typically short, almost round, rod-shaped (coccobacillus) Gram-negative bacterium. It is named after the bacteriologist Paul Baumann. It can be an opportunistic pathogen in humans, affecting people with compromised immune systems, and is becoming increasingly important as a hospital-derived ( nosocomial) infection. While other species of the genus '' Acinetobacter'' are often found in soil samples (leading to the common misconception that ''A. baumannii'' is a soil organism, too), it is almost exclusively isolated from hospital environments. Although occasionally it has been found in environmental soil and water samples, its natural habitat is still not known. Bacteria of this genus lack flagella but exhibit twitching or swarming motility, likely mediated by type IV pili. Motility in ''A. baumannii'' may also be due to the excretion of exopolysaccharide, creating a film of high- molecular-weight sugar chains behind the bacterium to move forwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thienamycin
Thienamycin (also known as thienpenem) is one of the most potent naturally produced antibiotics known thus far, discovered in '' Streptomyces cattleya'' in 1976. Thienamycin has excellent activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is resistant to bacterial β-lactamase enzymes. Thienamycin is a zwitterion at pH 7. History In 1976, fermentation broths obtained from the soil bacterium '' Streptomyces cattleya'' were found to be active in a screen for inhibitors of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Initial attempts to isolate the active compound proved difficult due to its chemical instability. After many attempts and extensive purification, the material was finally isolated in >90% purity, allowing for the structural elucidation of thienamycin in 1979. Thienamycin was the first among the naturally occurring class of carbapenem antibiotics to be discovered and isolated. Carbapenems are similar in structure to their antibiotic “cousins” the penicillins. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
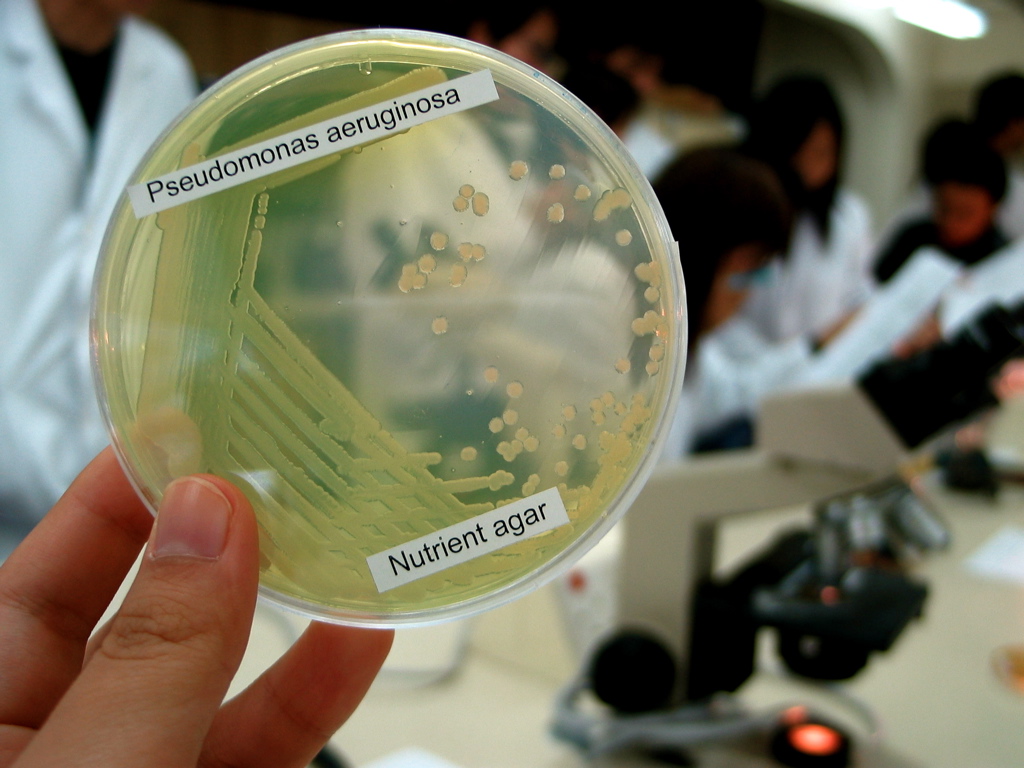
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multiple drug resistance, multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. ''P. aeruginosa'' is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane'' ''– and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization ''P. aeruginosa'' poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acinetobacter
''Acinetobacter'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the wider class of Gammaproteobacteria. ''Acinetobacter'' species are oxidase-negative, exhibit twitching motility, and occur in pairs under magnification. They are important soil organisms, where they contribute to the mineralization of, for example, aromatic compounds. ''Acinetobacter'' species are a key source of infection in debilitated patients in the hospital, in particular the species '' Acinetobacter baumannii''. Description Species of the genus ''Acinetobacter'' are strictly aerobic, nonfermentative, Gram-negative bacilli. They show mostly a coccobacillary morphology on nonselective agar. Rods predominate in fluid media, especially during early growth. The morphology of ''Acinetobacter'' species can be quite variable in Gram-stained human clinical specimens, and cannot be used to differentiate ''Acinetobacter'' from other common causes of infection. Most strains of ''Acinetobacter'', except som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterococcus Faecalis
''Enterococcus faecalis'' – formerly classified as part of the group D '' Streptococcus,'' is a Gram-positive, commensal bacterium naturally inhabiting the gastrointestinal tracts of humans. Like other species in the genus '' Enterococcus'', ''E. faecalis'' is found in healthy humans and can be used as a probiotic. The probiotic strains such as Symbioflor1 and EF-2001 are characterized by the lack of specific genes related to drug resistance and pathogenesis. Despite its commensal role, ''E. faecalis'' is an opportunistic pathogen capable of causing severe infections, especially in the nosocomial (hospital) settings. ''Enterococcus'' spp. is among the leading causes of healthcare-associated infections ranging from endocarditis to urinary tract infections (UTIs). Hospital-acquired UTIs are associated with catheterization because catheters provide an ideal surface for biofilm formation, allowing ''E. faecalis'' to adhere, persist, and evade both the immune response and antibiot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides Fragilis
''Bacteroides fragilis'' is an anaerobic, Gram-negative, pleomorphic to rod-shaped bacterium. It is part of the normal microbiota of the human colon and is generally commensal, but can cause infection if displaced into the bloodstream or surrounding tissue following surgery, disease, or trauma. Habitat ''Bacteroides fragilis'' resides in the human gastrointestinal tract and is essential to healthy gastrointestinal function such as mucosal immunity and host nutrition. As a mesophile, optimal growth occurs at 37 °C and a pH around 7. Morphology Cells of ''B. fragilis'' are rod-shaped to pleomorphic with a cell size range of 0.5–1.5 × 1.0–6.0 μm.''B. fragilis'' is a Gram-negative bacterium and does not possess flagella or cilia making it immotile. However, it does utilize peritrichous fimbriae for adhesion to other molecular structures. ''B. fragilis'' also utilizes a complex series of surface proteins, lipopolysaccharide chains, and outer membrane vesicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramuscular Injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have larger and more numerous blood vessels than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster absorption than subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous or intradermal injections. Medication administered via intramuscular injection is not subject to the first-pass metabolism effect which affects oral medications. Common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle of the upper arm and the gluteal muscle of the buttock. In infants, the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh is commonly used. The injection site must be cleaned before administering the injection, and the injection is then administered in a fast, darting motion to decrease the discomfort to the individual. The volume to be injected in the muscle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia
'' Stenotrophomonas maltophilia'' is an aerobic, nonfermentative, Gram-negative bacterium. It is an uncommon bacterium and human infection is difficult to treat. Initially classified as ''Bacterium bookeri'', then renamed ''Pseudomonas maltophilia'', ''S. maltophilia'' was also grouped in the genus ''Xanthomonas'' before eventually becoming the type species of the genus '' Stenotrophomonas'' in 1993. ''S. maltophilia'' is slightly smaller (0.7–1.8 × 0.4–0.7 μm) than other members of the genus. They are motile due to polar flagella, and grow well on MacConkey agar producing pigmented colonies. ''S. maltophilia'' is catalase-positive, oxidase-negative (which distinguishes it from most other members of the genus) and has a positive reaction for extracellular DNase. ''S. maltophilia'' is ubiquitous in aqueous environments, soil, and plants; it has also been used in biotechnology applications. In immunocompromised patients, ''S. maltophilia'' can lead to nosoco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |