|
IFood
Heavy isotope diet is the consumption of nutrients in which some atoms are replaced with their heavier non-radioactive isotopes, such as deuterium (2H) or heavy carbon (13C). Biomolecules that incorporate heavier isotopes give rise to more stable molecular structures under certain circumstances, which is hypothesized to increase resistance to damage associated with ageing or diseases. Medicines with some hydrogen atoms substituted with deuterium are called deuterated drugs, while substances that are essential nutrients can be used as food constituents, making this food "isotopic". Consumed with food, these nutrients become building material for the body. The examples are deuterated polyunsaturated fatty acids, essential aminoacids, DNA bases such as cytosine, or heavy water and glucose. Suggested mechanism One of the most pernicious and irreparable types of oxidative damage inflicted by reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon biomolecules involves the carbon-hydrogen bond cleavage ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Linoleate Ordinary And Heavy
Ethyl may refer to: Arts and entertainment *Ethyl Sinclair, a character in the ''Dinosaurs'' television show Science and technology * Ethyl group, an organic chemistry moiety * Ethyl alcohol (or ethanol) * Ethyl Corporation, a fuel additive company ** Tetraethyllead Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula lead, Pb(ethyl group, C2H5)4. It was widely used as a fuel additive for much of the 20th century, first being mixed with gasoline begi ...-treated gasoline See also * Ethel (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
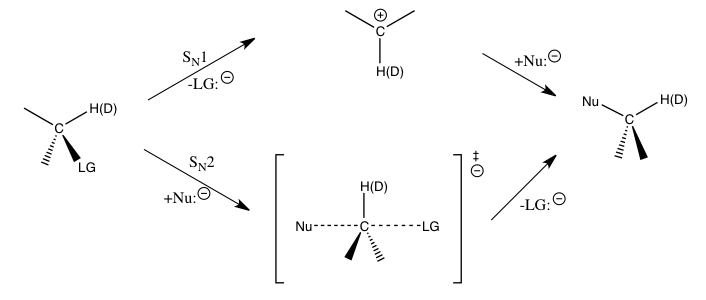
Kinetic Isotope Effect
In physical organic chemistry, a kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is the change in the reaction rate of a chemical reaction when one of the atoms in the reactants is replaced by one of its isotopes. Formally, it is the ratio of rate constants for the reactions involving the light (''k'') and the heavy (''k'') isotopically substituted reactants ( isotopologues): KIE = ''k/k''. This change in reaction rate is a quantum effect that occurs mainly because heavier isotopologues have lower vibrational frequencies than their lighter counterparts. In most cases, this implies a greater energy input needed for heavier isotopologues to reach the transition state (or, in rare cases, dissociation limit), and therefore, a slower reaction rate. The study of KIEs can help elucidate reaction mechanisms, and is occasionally exploited in drug development to improve unfavorable pharmacokinetics by protecting metabolically vulnerable C-H bonds. Background KIE is considered one of the most essential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Extension
Life extension is the concept of extending the human lifespan, either modestly through improvements in medicine or dramatically by increasing the maximum lifespan beyond its generally-settled biological limit of around 125 years. Several researchers in the area, along with "life extensionists", " immortalists", or " longevists" (those who wish to achieve longer lives themselves), postulate that future breakthroughs in tissue rejuvenation, stem cells, regenerative medicine, molecular repair, gene therapy, pharmaceuticals, and organ replacement (such as with artificial organs or xenotransplantations) will eventually enable humans to have indefinite lifespans through complete rejuvenation to a healthy youthful condition (agerasia). The ethical ramifications, if life extension becomes a possibility, are debated by bioethicists. The sale of purported anti-aging products such as supplements and hormone replacement is a lucrative global industry. For example, the industry that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Water
Heavy water (deuterium oxide, , ) is a form of water (molecule), water in which hydrogen atoms are all deuterium ( or D, also known as ''heavy hydrogen'') rather than the common hydrogen-1 isotope (, also called ''protium'') that makes up most of the hydrogen in normal water. The presence of the heavier isotope gives the water different nuclear properties, and the increase in mass gives it slightly different physical and chemical properties when compared to normal water. Deuterium is a heavy Isotopes of hydrogen, hydrogen isotope. Heavy water contains deuterium atoms and is used in nuclear reactors. Semiheavy water (HDO) is more common than pure heavy water, while heavy-oxygen water is denser but lacks unique properties. Tritiated water is radioactive due to tritium content. Heavy water has different physical properties from regular water, such as being 10.6% denser and having a higher melting point. Heavy water is less Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated at a given temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterated Drug
A deuterated drug is a small molecule medicinal product in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms in the drug molecule have been replaced by its heavier stable isotope deuterium. Because of the kinetic isotope effect, deuterium-containing drugs may have significantly lower rates of metabolism, and hence a longer half-life. Mode of action Hydrogen is a chemical element with an atomic number of 1. It has one proton and one electron. Deuterium is the heavier naturally-occurring stable isotope of hydrogen. Deuterium was discovered by Harold Urey in 1931, for which he received the Nobel Prize in 1934. The deuterium isotope effect has become an important tool in the elucidation of the mechanism of chemical reactions. Deuterium contains one proton, one electron, and a neutron, effectively doubling the mass of the deuterium isotope without changing its properties significantly. However, the C–D bond is a bit shorter, and it has reduced electronic polarizability and less hyperconjugati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, pharmaceutical drug, drugs, medical nutrition therapy, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received institutional review board, health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small Pilot experiment, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD) is a rare pervasive developmental disorder that primarily affects the nervous system. Individuals with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy typically do not have any symptoms at birth, but between the ages of about 6 and 18 months they begin to experience delays in acquiring new motor and intellectual skills, such as crawling or beginning to speak. Eventually, they lose previously acquired skills. Presentation Cause This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means two copies of the gene (''PLA2G6'') in each cell are altered. Most often, the parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder each carry one copy of the altered gene but do not show signs and symptoms of the disorder. Pathophysiology Mutations in the '' PLA2G6'' gene have been identified in most individuals with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. The ''PLA2G6'' gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called an A2 phospholipase. This enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedreich’s Ataxia
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is a rare, inherited, autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects the nervous system, causing progressive damage to the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and cerebellum, leading to impaired muscle coordination (''ataxia''). The condition typically manifests in childhood or adolescence, with initial symptoms including difficulty walking, loss of balance, and poor coordination. As the disease progresses, it can also impact speech, vision, and hearing. Many individuals with Friedreich's ataxia develop scoliosis, diabetes, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a serious heart condition that is a leading cause of mortality in patients. Friedreich's ataxia is caused by mutations in the ''FXN'' gene, which result in reduced production of frataxin, a protein essential for mitochondrial function, particularly in iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis. The deficiency of frataxin disrupts cellular energy production and leads to oxidative stress, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RT001
Deulinoleate ethyl (also known as di-deuterated ethyl linoleate, di-deuterated linoleic acid ethyl ester, 11,11-''d''-ethyl linoleate, or ethyl 11,11-''d''-linoleate) is an experimental, orally-bioavailable synthetic deuterated polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), a part of reinforced lipids. It is an isotopologue of linoleic acid, an essential omega-6 PUFA. The deuterated compound, while identical to natural linoleic acid except for the presence of deuterium, is resistant to lipid peroxidation which makes studies of its cell-protective properties worthwhile. Mechanism of action Deulinoleate ethyl is recognized by cells as identical to normal linoleic acid. But when taken up, it is converted into 13,13-''d''-arachidonic acid, a heavy isotope version of arachidonic acid, that gets incorporated into lipid membranes. The deuterated compound resists the non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation (LPO) through isotope effect — a non-antioxidant based mechanism that protects mitochondria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega-6
Omega−6 fatty acids (also referred to as ω−6 fatty acids or ''n''−6 fatty acids) are a family of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) that share a final carbon-carbon double bond in the ''n''−6 position, that is, the sixth bond, counting from the methyl end. Health and medical organizations recommend intake of omega-6 fatty acids as part of healthful dietary patterns. Health effects The American Heart Association "supports an omega-6 PUFA intake of at least 5% to 10% of energy in the context of other AHA lifestyle and dietary recommendations. To reduce omega-6 PUFA intakes from their current levels would be more likely to increase than to decrease risk for coronary heart disease." A 2018 review found that an increased intake of omega−6 fatty acids reduces total serum cholesterol and may reduce myocardial infarction (heart attack), but found no significant change in LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. A 2021 review found that omega−6 supplements do not affect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Development
Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory status, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug. The entire process—from concept through preclinical testing in the laboratory to clinical trial development, including Phase I–III trials—to approved vaccine or drug typically takes more than a decade. New chemical entity development Broadly, the process of drug development can be divided into preclinical and clinical work. Pre-clinical New chemical entities (NCEs, also known as new molecular entities or NMEs) are compounds that emerge from the process of drug discovery. These h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |