|
Hypothalamic Hormone
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and maternal attachment behaviours, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Structure The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurohormone
A neurohormone is any hormone produced and released by neuroendocrine cells (also called neurosecretory cells) into the blood. By definition of being hormones, they are secreted into the circulation for systemic effect, but they can also have a role of neurotransmitter or other roles such as autocrine (self) or paracrine (local) messenger. The hypothalamus releasing hormones are neurohypophysial hormones in specialized hypothalamic neurons which extend to the median eminence and posterior pituitary. The adrenal medulla produces adrenomedullary hormones in chromaffin cells, cells which are very similar in structure to post-synaptic sympathetic neurons, even though they are not neurons they are derivatives of the neural crest. Enterochromaffin and enterochromaffin-like cells, both being enteroendocrine cells, are also considered neuroendocrine cells due to their structural and functional similarity to chromaffin cells, although they are not derivatives of the neural crest. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
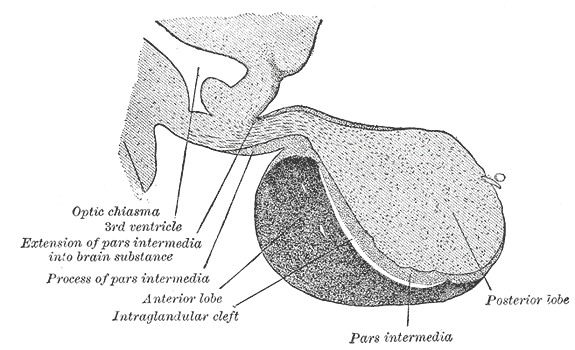
Neurohypophysial Hormone
The neurohypophysial hormones form a family of structurally and functionally related peptide hormones. Their representatives in humans are oxytocin and vasopressin. They are named after the location of their release into the blood, the neurohypophysis (another name for the posterior pituitary). Most of the circulating oxytocin and vasopressin hormones are synthesized in magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the supraoptic nucleus and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. They are then transported in neurosecretory granules along axons within the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial tract by axoplasmic flow to axon terminals forming the pars nervosa of the posterior pituitary. There, they are stored in Herring bodies and can be released into the circulation on the basis of hormonal and synaptic signals with assistance from pituicyte Pituicytes are glial cells of the posterior pituitary. Their main role is to assist in the storage and release of neurohypophysial hormones. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraoptic Nucleus
The supraoptic nucleus (SON) is a nucleus of magnocellular neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus of the mammalian brain. The nucleus is situated at the base of the brain, adjacent to the optic chiasm. In humans, the SON contains about 3,000 neurons. Function The cell bodies produce the peptide hormone vasopressin, which is also known as anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), and the peptide hormone oxytocin. Both of these peptides are released from the posterior pituitary. ADH travels via the bloodstream to its target cells in the papillary ducts in the kidneys, enhancing water reabsorption. OT travels via the bloodstream to act at the mammary glands and the uterus. In the cell bodies, the hormones are packaged in large, membrane-bound vesicles that are transported down the axons to the nerve endings. The secretory granules are also stored in packets along the axon called Herring bodies. Similar magnocellular neurons are also found in the paraventricular nucleus. Signaling Each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraventricular Nucleus
The paraventricular nucleus (PVN, PVA, or PVH) is a nucleus in the hypothalamus. Anatomically, it is adjacent to the third ventricle and many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary. These projecting neurons secrete oxytocin and a smaller amount of vasopressin, otherwise the nucleus also secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the hypophyseal portal system and act on different targets neurons in the anterior pituitary. PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through these different hormones, including osmoregulation, appetite, and the response of the body to stress. Location The paraventricular nucleus lies adjacent to the third ventricle. It lies within the periventricular zone and is not to be confused with the periventricular nucleus, which occupies a more medial position, beneath the third ventricle. The PVN is highly vascularised and is protected by the blood–brain barrier, altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnocellular Neurosecretory Cell
Magnocellular neurosecretory cells are large neuroendocrine cells within the supraoptic nucleus and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. They are also found in smaller numbers in accessory cell groups between these two nuclei, the largest one being the circular nucleus. There are two types of magnocellular neurosecretory cells, oxytocin-producing cells and vasopressin-producing cells, but a small number can produce both hormones. These cells are neuroendocrine neurons, are electrically excitable, and generate action potentials in response to afferent stimulation. Vasopressin is produced from the vasopressin-producing cells via the AVP gene, a molecular output of circadian pathways. Magnocellular neurosecretory cells in rats (where these neurons have been most extensively studied) in general have a single long varicose axon, which projects to the posterior pituitary. Each axon gives rise to about 10,000 neurosecretory terminals and many axon swellings that store very larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to the environment ( entrained by the environment). These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ''circa'', meaning "approximately", and ''dies'', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjusted to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers (German for "time givers"), which include light, temperature and redox cycles. In clinical settings, an abnormal circadian rhythm in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a decreased ability to react to stimuli, but more reactive than a coma or disorders of consciousness, with sleep displaying different, active brain patterns. Sleep occurs in repeating periods, in which the body alternates between two distinct modes: REM sleep and non-REM sleep. Although REM stands for "rapid eye movement", this mode of sleep has many other aspects, including virtual paralysis of the body. Dreams are a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. During sleep, most of the body's systems are in an anabolic state, helping to restore the immune, nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems; these are vital processes that maintain mood, memory, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (medical)
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirst
Thirst is the craving for potable fluids, resulting in the basic instinct of animals to drink. It is an essential mechanism involved in fluid balance. It arises from a lack of fluids or an increase in the concentration of certain osmolites, such as sodium. If the water volume of the body falls below a certain threshold or the osmolite concentration becomes too high, structures in the brain detect changes in blood constituents and signal thirst. Continuous dehydration can cause acute and chronic diseases, but is most often associated with renal and neurological disorders. Excessive thirst, called polydipsia, along with excessive urination, known as polyuria, may be an indication of diabetes mellitus or diabetes insipidus. There are receptors and other systems in the body that detect a decreased volume or an increased osmolite concentration. Some sources distinguish "extracellular thirst" from "intracellular thirst", where extracellular thirst is thirst generated by decreased vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maternal Bond
A maternal bond is the relationship between a mother and her child. While typically associated with pregnancy and childbirth, a maternal bond may also develop in cases where the child is unrelated, such as an adoption. Both physical and emotional factors influence the mother-child bonding process. In separation anxiety disorder a child becomes fearful and nervous when away from a loved one, usually a parent or other caregiver. New mothers do not always experience instant love toward their child. Instead, the bond can strengthen over time. Bonds can take hours, days, weeks, or months to develop. Pregnancy The maternal bond between a woman and her biological child usually begins to develop during pregnancy. The pregnant female adapts her lifestyle to suit the needs of the developing infant. At around 18 to 25 weeks, the mother begins to feel the fetus moving. Similar to seeing her child for the first time in an ultrasound scan, this experience typically leads the mother to feel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunger (motivational State)
Hunger is a sensation that motivates the consumption of food. The sensation of hunger typically manifests after only a few hours without eating and is generally considered to be unpleasant. Satiety occurs between 5 and 20 minutes after eating. There are several theories about how the feeling of hunger arises. The desire to eat food, or appetite, is another sensation experienced with regards to eating. The term ''hunger'' is also the most commonly used in social science and policy discussions to describe the condition of people who suffer from a chronic lack of sufficient food and constantly or frequently experience the sensation of hunger, and can lead to malnutrition. A healthy, well-nourished individual can survive for weeks without food intake (see fasting), with claims ranging from three to ten weeks. Satiety is the opposite of hunger; it is the sensation of feeling full. Hunger pangs The physical sensation of hunger is related to contractions of the stomach muscles. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_Thirst_(1886).jpg)
