|
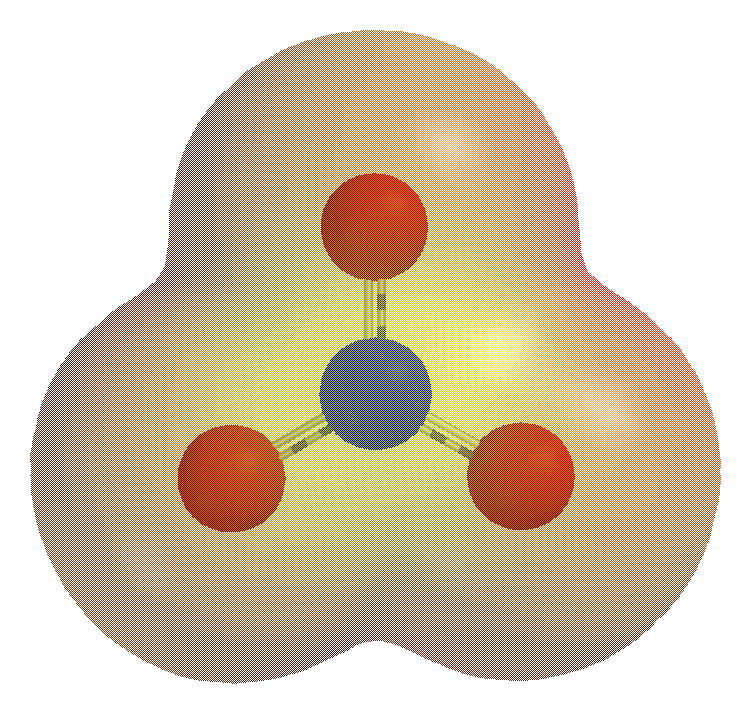
Hydrogencarbonate
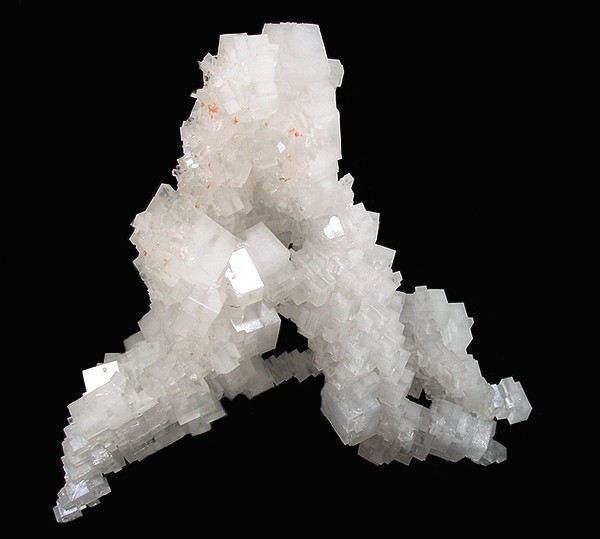
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula . Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemical role in the physiological pH buffering system. The term "bicarbonate" was coined in 1814 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. The name lives on as a trivial name. Chemical properties The bicarbonate ion (hydrogencarbonate ion) is an anion with the empirical formula and a molecular mass of 61.01 daltons; it consists of one central carbon atom surrounded by three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement, with a hydrogen atom attached to one of the oxygens. It is isoelectronic with nitric acid (). The bicarbonate ion carries a negative one formal charge and is an amphiprotic species which has both acidic and basic properties. It is both the conjugate base of carbonic acid (); and the conjugate acid of , the carbonate ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyatomic Ion
A polyatomic ion (also known as a molecular ion) is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that usually has a net charge that is not zero, or in special case of zwitterion wear spatially separated charges where the net charge may be variable depending on acidity conditions. The term molecule may or may not be used to refer to a polyatomic ion, depending on the definition used. The prefix ''poly-'' carries the meaning "many" in Greek, but even ions of two atoms are commonly described as polyatomic. In older literature, a polyatomic ion may instead be referred to as a '' radical'' (or less commonly, as a ''radical group''). In contemporary usage, the term ''radical'' refers to various free radicals, which are species that have an unpaired electron and need not be charged. A simple example of a polyatomic ion is the hydroxide ion, which consists of one oxygen atom and one hydrogen ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group . The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water. In geology and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, , the chief constituent of limestone (as well as the main component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphoterism
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used. Etymology and terminology Amphoteric is derived from the Greek word () meaning "both". Related words in acid-base chemistry are amphichromatic and amphichroic, both describing substances such as acid-base indicators which give one colour on reaction with an acid and another colour on reaction with a base. Amphiprotism Amphiprotism is exhibited by compounds with both Brønsted acidic and basic properties. A prime example is H2O. Amphiprotic molecules can either donate or accept a proton (). Amino acids (and proteins) are amphiprotic molecules because of their amine () and carboxylic acid () groups. Ampholytes Ampholytes are zwitterions ‒ molecules or ions that contain both acidic and basic functional groups. Amino acids have both a basic group and an acidic group . Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonic Acid
Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . The molecule rapidly converts to water and carbon dioxide in the presence of water. However, in the absence of water, it is quite stable at room temperature. The interconversion of carbon dioxide and carbonic acid is related to the breathing cycle of animals and the acidification of natural waters. In biochemistry and physiology, the name "carbonic acid" is sometimes applied to aqueous solutions of carbon dioxide. These chemical species play an important role in the bicarbonate buffer system, used to maintain acid–base homeostasis. Terminology in biochemical literature In chemistry, the term "carbonic acid" strictly refers to the chemical compound with the formula . Some biochemistry literature effaces the distinction between carbonic acid and carbon dioxide dissolved in extracellular fluid. In physiology, carbon dioxide excreted by the lungs may be called ''volatile acid'' or ''respiratory acid''. Anh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extent of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and often determines supply options. Impacts on public health Over time, there has been increasing recognition of the importance of drinking water quality and its impact on public health. This has led to increasing protection and management of water quality. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a creativecommons:by/4.0/, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License The understanding of the links between water quality and healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Dissolved Solids
Total dissolved solids (TDS) is a measure of the dissolved solids, dissolved combined content of all inorganic compound, inorganic and organic compound, organic substances present in a liquid in molecule, molecular, ionized, or micro-granular (sol (colloid), colloidal sol) suspended form. TDS are often measured in parts per million (ppm). TDS in water can be measured using a digital meter. Generally, the operational definition is that the solids must be small enough to survive filtration through a filter with 2-micrometer (nominal size, or smaller) pores. Total dissolved solids are normally discussed only for freshwater systems, as salinity includes some of the ions constituting the definition of TDS. The principal application of TDS is in the study of water quality for streams, rivers, and lakes. Although TDS is not generally considered a primary pollutant (e.g. it is not deemed to be associated with health effects), it is used as an indication of aesthetic characteristics of dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Temperature And Pressure
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), although these are not universally accepted. Other organizations have established a variety of other definitions. In industry and commerce, the standard conditions for temperature and pressure are often necessary for expressing the volumes of gases and liquids and related quantities such as the rate of volumetric flow (the volumes of gases vary significantly with temperature and pressure): standard cubic meters per second (Sm3/s), and normal cubic meters per second (Nm3/s). Many technical publications (books, journals, advertisements for equipment and machinery) simply state "standard cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are '' hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chloride. In an aqueous solution the hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a chemical substance, substance, the solute, to form a solution (chemistry), solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a wikt:saturated#Chemistry, saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be "miscibility, miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Compound
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (Cation, cations) and negatively charged ions (Anion, anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). The constituent ions are held together by Coulomb's law, electrostatic forces termed ionic bonding, ionic bonds. The component ions in a salt can be either inorganic compound, inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic chemistry, organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic ion, monatomic, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic ion, polyatomic, such as ammonium () and carbonate () ions in ammonium carbonate. Salts containing basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−) are classified as Base (chemistry), bases, such as sodium hydroxide and potassium oxide. Individual ions within a salt usually have multiple near neighbours, so they are not considered to be part of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ ( potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− ( chloride ion) and OH− ( hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |