|
Haemagglutinin
In molecular biology, hemagglutinins (or ''haemagglutinin'' in British English) (from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') are receptor-binding membrane fusion glycoproteins produced by viruses in the ''Paramyxoviridae'' family. Hemagglutinins are responsible for binding to receptors on red blood cells to initiate viral attachment and infection. The agglutination (biology), agglutination of red cells occurs when Antibody, antibodies on one cell bind to those on others, causing amorphous aggregates of clumped cells.Hemagglutinins recognize cell-surface glycoconjugates containing sialic acid on the surface of host red blood cells with a low affinity, and use them to enter the endosome of host cells. In the endosome, hemagglutinins are activated at a pH of 5 - 6.5, to undergo conformational changes that enable viral attachment through a fusion peptide. Agglutination and hemagglutinins were discovered by virologist George Hirst (virologist), George K. Hirst in 1941. Alfred Gottschalk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytohaemagglutinin
Phytohaemagglutinin (PHA, or phytohemagglutinin) is a lectin found in plants, especially certain legumes. PHA actually consists of two closely related proteins, called leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) and PHA-E. These proteins cause blood cells to clump together. PHA-E cause erythrocytes (red blood cells) to clump. PHA-L causes leukocytes (white blood cells) to clump. Phytohaemagglutinin has carbohydrate-binding specificity for a complex oligosaccharide containing galactose, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, and mannose. It is found in the highest concentrations in uncooked red kidney beans and white kidney beans (also known as cannellini), and it is also found in lower quantities in many other types of green beans and other common beans (''Phaseolus vulgaris''), as well as broad beans (''Vicia faba'') such as fava beans. It has a number of physiological effects and is used in medical research. In high doses, it is a toxin. The lectin has a number of effects on cell metabolism; it induces mitosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
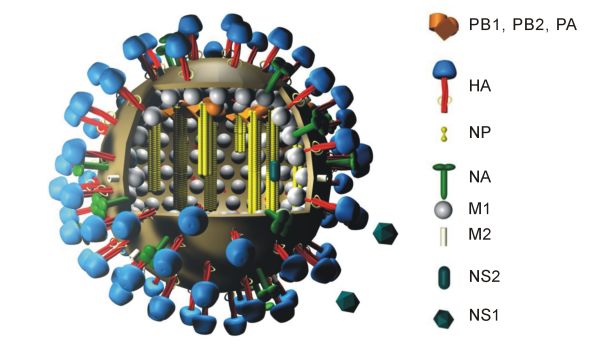
Influenza Hemagglutinin
Influenza hemagglutinin (HA) or haemagglutinin .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> (British English) is a homotrimeric glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza viruses and is integral to its infectivity. Hemagglutinin is a Class I Fusion Protein, having multifunctional activity as both an attachment factor and membrane fusion protein. Therefore, HA is responsible for binding Influenza virus to sialic acid on the surface of target cells, such as cells in the upper respiratory tract or erythrocytes, causing as a result the internalization of the virus. Secondarily, HA is responsible for the fusion of the viral envelope with the late endosomal membrane once exposed to low pH (5.0-5.5). The name "hemagglutinin" comes from the protein's ability to cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to clump together (" agglutinate") ''in vitro''. Subtypes Hemagglutinin (HA) in influenza A has at least 18 different subtypes. These subtypes are named H1 through H18. H16 was discovered in 2004 on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutination (biology)
Agglutination is the clumping of particles. The word ''agglutination'' comes from the Latin '' agglutinare'' (glueing to). Agglutination is the process that occurs if an antigen is mixed with its corresponding antibody called isoagglutinin. This term is commonly used in blood grouping. This occurs in biology in two main examples: # The clumping of cells such as bacteria or red blood cells in the presence of an antibody or complement. The antibody or other molecule binds multiple particles and joins them, creating a large complex. This increases the efficacy of microbial elimination by phagocytosis as large clumps of bacteria can be eliminated in one pass, versus the elimination of single microbial antigens. # When people are given blood transfusions of the wrong blood group, the antibodies react with the incorrectly transfused blood group and as a result, the erythrocytes clump up and stick together causing them to agglutinate. The coalescing of small particles that are susp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase
Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase refers to a single viral protein that has both hemagglutinin and (endo) neuraminidase activity. This is in contrast to the proteins found in influenza, where both functions exist but in two separate proteins. Its neuraminidase domain has the CAZy designation glycoside hydrolase family 83 (GH83). It does show a structural similarity to influenza viral neuraminidase and has a six-bladed beta-propeller structure. This Pfam entry also matches measles hemagglutinin (cd15467), which has a "dead" neuraminidase part repurposed as a receptor binding site. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase allows the virus to stick to a potential host cell, and cut itself loose if necessary. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase can be found in a variety of paramyxoviruses including mumps virus, human parainfluenza virus 3, and the avian pathogen Newcastle disease virus. Types include: * Mumps hemagglutinin-neuraminidase MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming Sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Hirst (virologist)
George Keble Hirst, M.D. (March 2, 1909 – January 22, 1994) was an American virologist and science administrator who was among the first to study the molecular biology and genetics of animal viruses, especially influenza virus. He directed the Public Health Research Institute in New York City (1956–1981), and was also the founding editor-in-chief of ''Virology'', the first English-language journal to focus on viruses. He is particularly known for inventing the hemagglutination assay, a simple method for virus quantification, quantifying viruses, and adapting it into the hemagglutination inhibition assay, which measures virus-specific antibody, antibodies in serum. He was the first to discover that viruses can contain enzymes, and the first to propose that virus genomes can consist of discontinuous segments. ''The New York Times'' described him as "a pioneer in molecular virology." Education and career Hirst was born in Eau Claire, Wisconsin, Eau Claire, Wisconsin, USA, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression. Less commonly seizures, blindness, or inflammation of the brain may occur. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''red measles'', and ''English measles''. Both rubella, also known as ''German measles'', and roseola are different diseases caused by unrelated viruses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza Viruses
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: ''Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', ''Isavirus'', ''Thogotovirus'', and ''Quaranjavirus''. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in birds (see also avian influenza) and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon; the thogotoviruses are arboviruses, infecting vertebrates and invertebrates (such as ticks and mosquitoes). The Quaranjaviruses are also arboviruses, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropods). The four genera of Influenza virus that infect vertebrates, which are identified by antigenic differences in their nucleoprotein and matrix protein, are as follows: * ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' infects humans, other mammals, and birds, and causes all flu pandemics * ''Betainfluenzavirus'' infects humans and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSIRO ScienceImage 354 Influenza Protein Attaching To Cell Membrane
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research. CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO maintains more than 50 sites across Australia and in France, Chile and the United States, employing about 5,500 people. Federally funded scientific research began in Australia years ago. The Advisory Council of Science and Industry was established in 1916 but was hampered by insufficient available finance. In 1926 the research effort was reinvigorated by establishment of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which strengthened national science leadership and increased research funding. CSIR grew rapidly and achieved significant early successes. In 1949, further legislated changes included renaming the organisation as CSIRO. Notable developments by CSIRO have included the invention of atomic absorption spectroscopy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycopeptide
Glycopeptides are peptides that contain carbohydrate moieties ( glycans) covalently attached to the side chains of the amino acid residues that constitute the peptide. Over the past few decades it has been recognised that glycans on cell surface (attached to membrane proteins or lipids) and those bound to proteins (glycoproteins) play a critical role in biology. For example, these constructs have been shown to play important roles in fertilization, the immune system, brain development, the endocrine system, and inflammation. The synthesis of glycopeptides provides biological probes for researchers to elucidate glycan function in nature and products that have useful therapeutic and biotechnological applications. Glycopeptide linkage variety ''N''-Linked glycans ''N''-Linked glycans derive their name from the fact that the glycan is attached to an asparagine (Asn, N) residue, and are amongst the most common linkages found in nature. Although the majority of N-linked glycans ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts General Hospital for managing hospital laboratory information systems. MUMPS technology has since expanded as the predominant database for health information systems and electronic health records in the United States. MUMPS-based information systems run over 40% of the hospitals in the U.S., run across all of the U.S. federal hospitals and clinics, and provide health information services for over 54% of patients across the U.S. A unique feature of the MUMPS technology is its integrated database language, allowing direct, high-speed read-write access to permanent disk storage. This provides tight integration of unlimited applications within a single database, and provides extremely high performance and reliability as an online transaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mumps Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts General Hospital for managing hospital laboratory information systems. MUMPS technology has since expanded as the predominant database for health information systems and electronic health records in the United States. MUMPS-based information systems run over 40% of the hospitals in the U.S., run across all of the U.S. federal hospitals and clinics, and provide health information services for over 54% of patients across the U.S. A unique feature of the MUMPS technology is its integrated database language, allowing direct, high-speed read-write access to permanent disk storage. This provides tight integration of unlimited applications within a single database, and provides extremely high performance and reliability as an online transaction p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Parainfluenza Viruses
Human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs) are the viruses that cause human parainfluenza. HPIVs are a paraphyletic group of four distinct single-stranded RNA viruses belonging to the '' Paramyxoviridae'' family. These viruses are closely associated with both human and veterinary disease. Virions are approximately 150–250 nm in size and contain negative sense RNA with a genome encompassing about 15,000 nucleotides. The viruses can be detected via cell culture, immunofluorescent microscopy, and PCR. HPIVs remain the second main cause of hospitalisation in children under 5 years of age for a respiratory illness (only Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes more respiratory hospitalisations for this age group). Classification The first HPIV was discovered in the late 1950s. The taxonomic division is broadly based on antigenic and genetic characteristics, forming four major serotypes or clades, which today are considered distinct viruses. These include: HPIVs belong to two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |