|
Hydrops Fetalis
Hydrops fetalis or hydrops foetalis is a condition in the fetus characterized by an accumulation of fluid, or edema, in at least two fetal compartments. By comparison, hydrops allantois or hydrops amnion is an accumulation of excessive fluid in the allantoic or amniotic space, respectively. Signs and symptoms Locations can include the subcutaneous tissue on the scalp, the pleura (pleural effusion), the pericardium (pericardial effusion) and the abdomen (ascites). Edema is usually seen in the fetal subcutaneous tissue, sometimes leading to spontaneous abortion. It is a prenatal form of heart failure, in which the heart is unable to satisfy demand (in most cases abnormally high) for blood flow. Causes Hydrops fetalis usually stems from fetal anemia, when the heart needs to pump a much greater volume of blood to deliver the same amount of oxygen. This anemia can have either an immune or non-immune cause. Non-immune hydrops can also be unrelated to anemia, for example if a fet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergy, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, Abnormality (behavior), dysfunction, distress (medicine), distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injury in humans, injuries, disability, disabilities, Disorder (medicine) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin available for oxygen transport, or abnormalities in hemoglobin that impair its function. The name is derived . When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as Fatigue, tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a Exercise intolerance, reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, lightheadedness, feeling like one is going to pass out, Syncope (medicine), loss of consciousness, and polydipsia, increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably Pallor, pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is a type of supraventricular tachycardia, named for its intermittent episodes of abrupt onset and termination. Often people have no symptoms. Otherwise symptoms may include palpitations, feeling lightheaded, sweating, shortness of breath, and chest pain. The cause is not known. Risk factors include alcohol, psychostimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines, psychological stress, and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, which often is heritability, inherited. The underlying mechanism typically involves an accessory pathway that results in re-entry tachycardia, re-entry. Diagnosis is typically by an electrocardiogram (ECG) which shows narrow QRS complexes and a fast heart rhythm typically between 150 and 240 pulse, beats per minute. Vagal maneuvers, such as the Valsalva maneuver, are often used as the initial treatment. If not effective and the person has a normal blood pressure the medication adenosine may be tried. If aden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, short of breath, or having decreased ability to exercise. Anemia that comes on quickly often has more severe symptoms, including confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out or increased thirst. Anemia is typically significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Children with iron deficiency anemia may have problems with growth and development. There may be additional symptoms depending on the underlying cause. Iron-deficiency anemia is caused by blood loss, insufficient dietary intake, or poor absorption of iron from food. Sources of blood loss can include heavy periods, childbirth, uterine fibroids, stomach ulcers, colon cancer, and urinary tract bleeding. Poor absorption of iron from food may occur as a result of an intesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperdynamic Circulation
Hyperdynamic circulation is abnormally increased circulatory volume. Systemic vasodilation and the associated decrease in peripheral vascular resistance results in decreased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure and decreased blood pressure, presenting usually with a collapsing pulse, but sometimes a bounding pulse. In effort to compensate the heart will increase cardiac output and heart rate, which accounts for the increased pulse pressure and sinus tachycardia. The condition sometimes accompanies septic shock, preeclampsia, and other physiological and psychiatric conditions. __TOC__ Possible causes * Kidney disease * Hypovolemia * Adrenal crisis - especially after fluid replacement * Anemia * Anxiety * Aortic Regurgitation * AV fistulae * Beriberi * Dysautonomia * Erythroderma * Exercise * Liver failure * HydrocephalusGreitz, Dan. Radiological Assessment of hydrocephalus: new theories and implications for therapy. Neurosurg Rev (2004) 27: 145-165. * Hypercapnia * Paget's diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho(D) Immune Globulin
Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIG) is a medication used to prevent RhD isoimmunization in mothers who are RhD negative and to treat idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) in people who are Rh positive. RhIG is commonly referred to as 'anti-D'. It is often given both during and following pregnancy. It may also be used when RhD-negative people are given RhD-positive blood. It is given by injection into muscle or a vein. A single dose lasts 12 weeks. It is made from human blood plasma. Common side effects include fever, headache, pain at the site of injection, and red blood cell breakdown. Other side effects include allergic reactions, kidney problems, and a very small risk of viral infections. In those with ITP, the amount of red blood cell breakdown may be significant. Use is safe with breastfeeding. Rho(D) immune globulin is made up of antibodies to the antigen Rho(D) present on some red blood cells. It is believed to work by blocking a person's immune system from rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
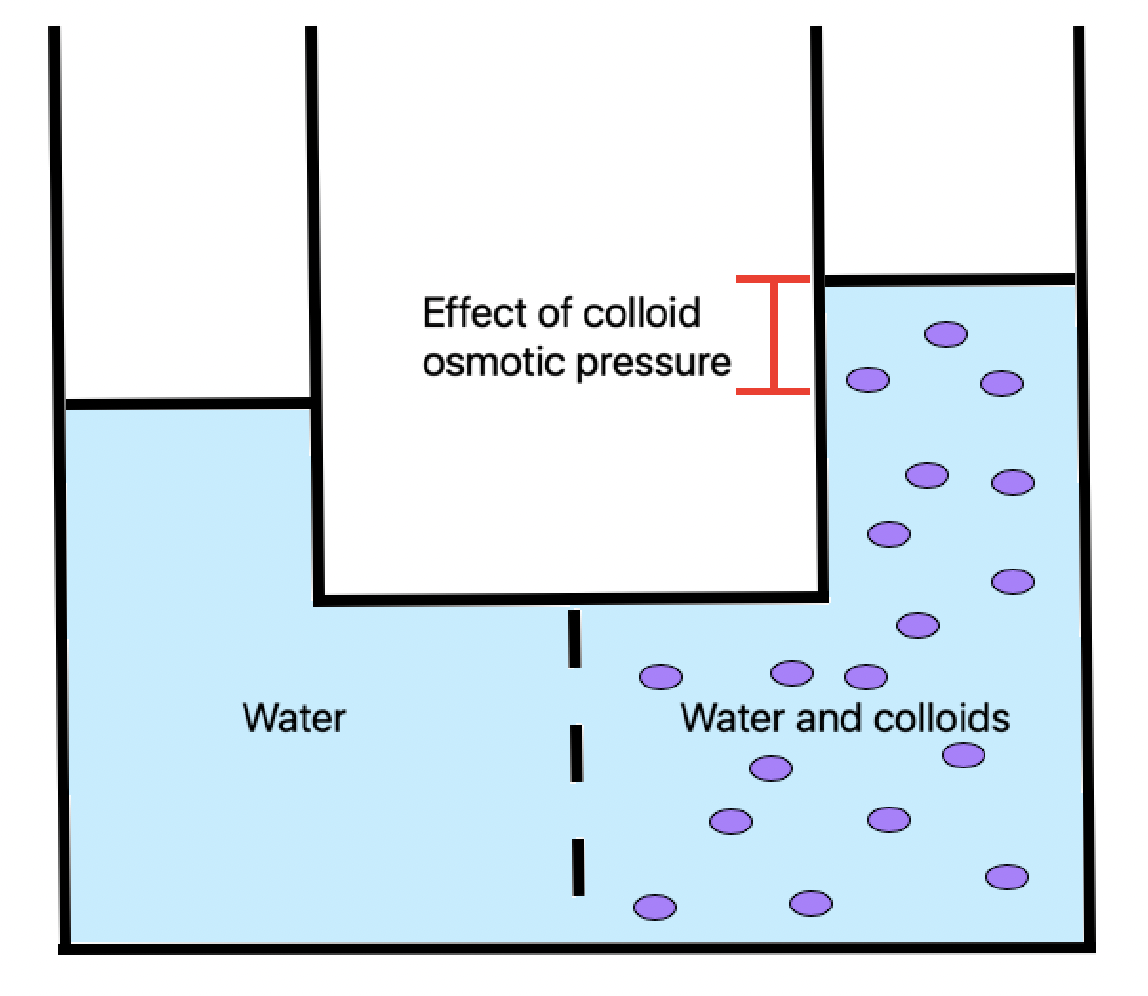
Oncotic Pressure
Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a type of osmotic pressure induced by the plasma proteins, notably albumin, in a blood vessel's plasma (or any other body fluid such as blood and lymph) that causes a pull on fluid back into the capillary. It has an effect opposing both the hydrostatic blood pressure, which pushes water and small molecules out of the blood into the interstitial spaces at the arterial end of capillaries, and the interstitial colloidal osmotic pressure. These interacting factors determine the partitioning of extracellular water between the blood plasma and the extravascular space. Oncotic pressure strongly affects the physiological function of the circulatory system. It is suspected to have a major effect on the pressure across the glomerular filter. However, this concept has been strongly criticised and attention has shifted to the impact of the intravascular glycocalyx layer as the major player. Etymology The word 'oncotic' by definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called ''albuminoids''. A number of blood transport proteins are evolutionarily related in the albumin family, including serum albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, vitamin D-binding protein and afamin. This family is only found in vertebrates. ''Albumins'' in a less strict sense can mean other proteins that coagulate under certain conditions. See ' for lactalbumin, ovalbumin and plant "2S albumin". Function Albumins in general are transport proteins that bind to various ligands and carry them around. Human types include: * Human serum albumin is the main protein of human blood plasma. It m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH or sometimes EH) refers to hematopoiesis occurring outside of the medulla of the bone (bone marrow). It can be physiologic or pathologic. Physiologic EMH occurs during embryonic and fetal development; during this time the main site of fetal hematopoiesis are liver and the spleen. Pathologic EMH can occur during adulthood when physiologic hematopoiesis cannot work properly in the bone marrow and the hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) have to migrate to other tissues in order to continue with the formation of blood cellular components. Pathologic EMH can be caused by myelofibrosis, thalassemias or disorders caused in the hematopoietic system. Physiologic EMH During fetal development, hematopoiesis occurs mainly in the fetal liver and in the spleen followed by localization to the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis also takes place in many other tissues or organs such as the yolk sac, the aorta-gonad mesonephros (AGM) region, and lymph nodes. During develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes. Function Antibodies are major components of humoral immunity. IgG is the main type of antibody found in blood and extracellular fluid, allowing it to control infection of body tissues. By binding many kinds of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, IgG protects the body from infection. It does this through several mechanisms: * IgG-mediated binding of pathogens causes their immobilization and binding together via agglutination; IgG coating of pathogen surfaces (known as opsonization) allows their recognition and ingestion by phagocytic immune cells leading to the elimination of the pathogen itself; * IgG activates the classical pathway of the complement system, a cascade of immune protein product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Each individual antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens, and antigens of virtually any size and chemical composition can be recognized. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each of the branching chains comprising the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" the antigen (or a microbe or an infected cell bearing such an antigen) for attack by cells of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |