|
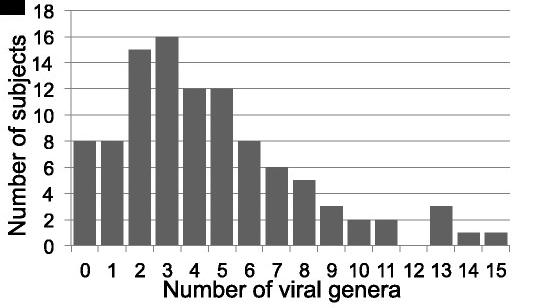
Human Virome
The human virome is the total collection of viruses in and on the human body. Viruses in the human body may infect both human cells and other microbes such as bacteria (as with bacteriophages). Some viruses cause disease, while others may be asymptomatic. Certain viruses are also integrated into the human genome as proviruses or endogenous viral elements. Viruses evolve rapidly and hence the human virome changes constantly. Every human being has a unique virome with a unique balance of species. Lifestyle, age, geographic location, and even the season of the year can affect an individual's exposure to viruses, and one's susceptibility to any disease that might be caused by those viruses is also affected by pre-existing immunity and both viral and human genetics. The human virome is far from being completely explored and new viruses are discovered frequently. Unlike the roughly 40 trillion bacteria in a typical human microbiome, an estimate of the number of viral particles in a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virome
Virome refers to the assemblage of viruses that is often investigated and described by metagenomic sequencing of viral nucleic acids that are found associated with a particular ecosystem, organism or holobiont. The word is frequently used to describe environmental viral shotgun metagenomes. Viruses, including bacteriophages, are found in all environments, and studies of the virome have provided insights into nutrient cycling, development of immunity, and a major source of genes through lysogenic conversion. Also, the human virome has been characterized in nine organs (colon, liver, lung, heart, brain, kidney, skin, blood, hair) of 31 Finnish individuals using qPCR and NGS methodologies. History The first comprehensive studies of viromes were by shotgun community sequencing, which is frequently referred to as metagenomics. In the 2000s, the Rohwer lab sequenced viromes from seawater, marine sediments, adult human stool, infant human stool, soil, and blood. This group also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Human Herpesvirus 7
Human herpesvirus 7 (HHV-7) is one of nine known members of the ''Herpesviridae'' family that infects humans. HHV-7 is a member of ''Betaherpesvirinae'', a subfamily of the ''Herpesviridae'' that also includes HHV-6 and ''Cytomegalovirus'' (HHV-5 or HCMV). HHV-7 often acts together with HHV-6, and the viruses together are sometimes referred to by their genus, '' Roseolovirus''. HHV-7 was first isolated in 1990 from CD4+ T cells taken from peripheral blood lymphocytes. Signs and symptoms Both HHV-6B and HHV-7, as well as other viruses, can cause a skin condition in infants known as exanthema subitum, although HHV-7 causes the disease less frequently than HHV-6B. HHV-7 infection also leads to or is associated with a number of other symptoms, including acute febrile respiratory disease, fever, rash, vomiting, diarrhea, low lymphocyte counts, and febrile seizures, though most often no symptoms present at all. There are indications that HHV-7 can contribute to the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roseolovirus
''Roseolovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Herpesvirales'', in the family ''Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily ''Betaherpesvirinae''. There are currently six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: HHV-6: sixth disease (roseola infantum, exanthema subitum); HHV-7: symptoms analog to the 'sixth disease'. Species The genus consists of the following six species: * '' Roseolovirus humanbeta7'' * '' Roseolovirus humanbeta6a'' * '' Roseolovirus humanbeta6b'' * '' Roseolovirus macacinebeta9'' * '' Roseolovirus muridbeta3'' * '' Roseolovirus suidbeta2'' Structure Viruses in ''Roseolovirus'' are enveloped, with icosahedral, spherical to pleomorphic, and round geometries, and T=16 symmetry. The diameter is around 150-200 nm. Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 200kb in length. Life cycle Viral replication is nuclear, and is lysogenic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral glycoproteins to host recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Human Virome 2 1
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Circovirus
''Circovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Circoviridae''. Birds (such as pigeons and ducks) and pigs serve as natural hosts, though dogs have been shown to be infected as well. Circoviruses are single stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. There are 70 species in this genus. Some members of this genus cause disease: PCV-1 is non pathogenic, while PCV-2 causes postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS). Structure Viruses in ''Circovirus'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedrals capsids that have T=1 symmetry. The diameter is around 17 nm. Genomes are circular and non-segmented. The virions of Circoviruses are surprisingly small, with diameters ranging from 17 up to 22 nm. Genome Circovirus has a monopartite, circular, and ssDNA genome of between 1759 and 2319nt, making it possibly the virus of shortest genome size in mammal viruses. The virus replicates through an dsDNA intermediate initiated by the Rep protein. Two major genes are transcribed from open rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parvoviridae
Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family ''Parvoviridae''. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the protein the viral capsid is made of. The coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form into Stem-loop, hairpin loops that are important during replication. Parvovirus virions are small compared to most viruses, at 23–28 nanometers in diameter, and contain the genome enclosed in an icosahedral capsid that has a rugged surface. Parvoviruses enter a host cell by endocytosis, travelling to the nucleus where they wait until the cell enters its replication stage. At that point, the genome is uncoated and the coding portion is replicated. Viral messenger RNA (mRNA) is then Transcription (biology), transcribed and Translation (biology), translated, resulting in NS1 initiating replication. During replication, the hairpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anelloviridae
''Anelloviridae'' is a family of viruses. They are classified as vertebrate viruses and have a non-enveloped capsid, which is round with isometric, icosahedral symmetry and has a triangulation number of 3. The name is derived from Italian ''anello'' 'ring', referring to the circular genome of anelloviruses. It is the sole representative of its own phylum, ''Commensaviricota'' (from its "commensal" lifestyle in the human virome + -viricota). Genome The genome is not segmented and contains a single molecule of circular, negative-sense, single-stranded DNA. The complete genome is 3000–4000 nucleotides long. They also contain a non-coding region with one to two 80–110 nt sequences that contain high GC content, forming a secondary structure of stems and loops. The genome has ORFs and a high degree of genetic diversity. Although the mechanism of replication has not been studied heavily, anelloviridae appears to use the rolling circle mechanism where first ssDNA is converted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adenoviridae
Adenoviruses (members of the family (biology), family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nanometer, nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of Adenovirus infection, illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a Immunodeficiency, weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genus, genera: * ''Aviadenovirus'' * ''Barthadenovirus'' * ''Ichtadenovirus'' * ''Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * ''Siadenovirus'' * ''Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polyomaviridae
''Polyomaviridae'' is a family of DNA viruses whose natural hosts are mammals and birds. As of 2024, there are eight recognized genera. Fourteen species are known to infect humans, while others, such as Simian Virus 40, have been identified in humans to a lesser extent. Most of these viruses are very common and typically asymptomatic in most human populations studied. BK virus is associated with nephropathy in renal transplant and non-renal solid organ transplant patients, JC virus with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, and Merkel cell virus with Merkel cell cancer. Structure and genome Polyomaviruses are non-enveloped double-stranded DNA viruses with circular genomes of around 5000 base pairs. With such a small size, they are ranked among the smallest known double stranded DNA viruses. The genome is packaged in a viral capsid of about 40-50 nanometers in diameter, which is icosahedral in shape (T=7 symmetry). The capsid is composed of 72 pentameric capsom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Papillomaviridae
''Papillomaviridae'' is a family of non- enveloped double-stranded DNA viruses whose members are known as papillomaviruses. Several hundred species of papillomaviruses, traditionally referred to as "types", have been identified infecting all carefully inspected mammals, but also other vertebrates such as birds, snakes, turtles and fish. Infection by most papillomavirus types, depending on the type, is either asymptomatic (e.g. most Beta-PVs) or causes small benign tumors, known as papillomas or warts (e.g. human papillomavirus 1, HPV6 or HPV11). Papillomas caused by some types, however, such as human papillomaviruses 16 and 18, carry a risk of becoming cancerous. Papillomaviruses are usually considered as highly host- and tissue- tropic, and are thought to rarely be transmitted between species. Papillomaviruses replicate exclusively in the basal layer of the body surface tissues. All known papillomavirus types infect a particular body surface, typically the skin or mucosal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Herpesviridae
''Orthoherpesviridae'', previously named and more widely known as ''Herpesviridae'', is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are commonly known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ἕρπειν ( 'to creep'), referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster ( shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established ''Herpesvirus'' as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. Since then, the number of identified herpesviruses has grown to more than 100. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections. Nine herpesvirus types are known to primarily infect humans, at least five of which are extremely widespread among most human populations, and which cause common diseases: herpes simplex 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2, also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |