|
Homotopy Groups
In mathematics, homotopy groups are used in algebraic topology to classify topological spaces. The first and simplest homotopy group is the fundamental group, denoted \pi_1(X), which records information about Loop (topology), loops in a Mathematical space, space. Intuitively, homotopy groups record information about the basic shape, or ''Hole (topology), holes'', of a topological space. To define the ''n''th homotopy group, the base-point-preserving maps from an N-sphere, ''n''-dimensional sphere (with base point) into a given space (with base point) are collected into equivalence classes, called homotopy classes. Two mappings are homotopic if one can be continuously deformed into the other. These homotopy classes form a group (mathematics), group, called the ''n''th homotopy group, \pi_n(X), of the given space ''X'' with base point. Topological spaces with differing homotopy groups are never homeomorphic, but topological spaces that homeomorphic have the same homotopy groups. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homotopy Groups Of Spheres
In the mathematical field of algebraic topology, the homotopy groups of spheres describe how spheres of various dimensions can wrap around each other. They are examples of topological invariants, which reflect, in algebraic terms, the structure of spheres viewed as topological spaces, forgetting about their precise geometry. Unlike homology groups, which are also topological invariants, the homotopy groups are surprisingly complex and difficult to compute. The -dimensional unit sphere — called the -sphere for brevity, and denoted as — generalizes the familiar circle () and the ordinary sphere (). The -sphere may be defined geometrically as the set of points in a Euclidean space of dimension located at a unit distance from the origin. The -th ''homotopy group'' summarizes the different ways in which the -dimensional sphere can be mapped continuously into the sphere . This summary does not distinguish between two mappings if one can be continuously deformed to the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is a Set (mathematics), set with an Binary operation, operation that combines any two elements of the set to produce a third element within the same set and the following conditions must hold: the operation is Associative property, associative, it has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element. For example, the integers with the addition, addition operation form a group. The concept of a group was elaborated for handling, in a unified way, many mathematical structures such as numbers, geometric shapes and polynomial roots. Because the concept of groups is ubiquitous in numerous areas both within and outside mathematics, some authors consider it as a central organizing principle of contemporary mathematics. In geometry, groups arise naturally in the study of symmetries and geometric transformations: The symmetries of an object form a group, called the symmetry group of the object, and the transformations of a given type form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedge Sum
In topology, the wedge sum is a "one-point union" of a family of topological spaces. Specifically, if ''X'' and ''Y'' are pointed spaces (i.e. topological spaces with distinguished basepoints x_0 and y_0) the wedge sum of ''X'' and ''Y'' is the quotient space of the disjoint union of ''X'' and ''Y'' by the identification x_0 \sim y_0: X \vee Y = (X \amalg Y)\;/, where \,\sim\, is the equivalence closure of the relation \left\. More generally, suppose \left(X_i\right)_ is an indexed family of pointed spaces with basepoints \left(p_i\right)_. The wedge sum of the family is given by: \bigvee_ X_i = \coprod_ X_i\;/, where \,\sim\, is the equivalence closure of the relation \left\. In other words, the wedge sum is the joining of several spaces at a single point. This definition is sensitive to the choice of the basepoints \left(p_i\right)_, unless the spaces \left(X_i\right)_ are homogeneous. The wedge sum is again a pointed space, and the binary operation is associative and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homotopy Group Addition
In topology, two continuous functions from one topological space to another are called homotopic (from and ) if one can be "continuously deformed" into the other, such a deformation being called a homotopy ( ; ) between the two functions. A notable use of homotopy is the definition of homotopy groups and cohomotopy groups, important invariants in algebraic topology. In practice, there are technical difficulties in using homotopies with certain spaces. Algebraic topologists work with compactly generated spaces, CW complexes, or spectra. Formal definition Formally, a homotopy between two continuous functions ''f'' and ''g'' from a topological space ''X'' to a topological space ''Y'' is defined to be a continuous function H: X \times ,1\to Y from the product of the space ''X'' with the unit interval , 1to ''Y'' such that H(x,0) = f(x) and H(x,1) = g(x) for all x \in X. If we think of the second parameter of ''H'' as time then ''H'' describes a ''continuous def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary (topology)
In topology and mathematics in general, the boundary of a subset of a topological space is the set of points in the Closure (topology), closure of not belonging to the Interior (topology), interior of . An element of the boundary of is called a boundary point of . The term boundary operation refers to finding or taking the boundary of a set. Notations used for boundary of a set include \operatorname(S), \operatorname(S), and \partial S. Some authors (for example Willard, in ''General Topology'') use the term frontier instead of boundary in an attempt to avoid confusion with a Manifold#Manifold with boundary, different definition used in algebraic topology and the theory of manifolds. Despite widespread acceptance of the meaning of the terms boundary and frontier, they have sometimes been used to refer to other sets. For example, ''Metric Spaces'' by E. T. Copson uses the term boundary to refer to Felix Hausdorff, Hausdorff's border, which is defined as the intersection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
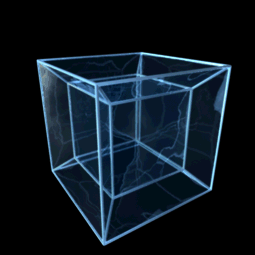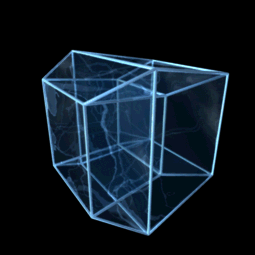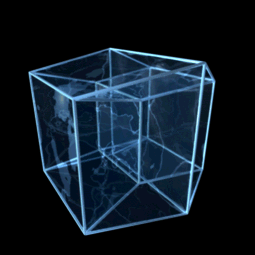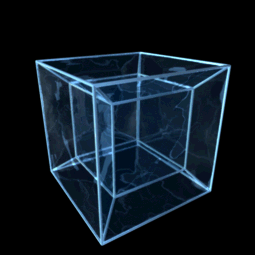
Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square ( ) and a cube ( ); the special case for is known as a ''tesseract''. It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1- skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length. A unit hypercube's longest diagonal in ''n'' dimensions is equal to \sqrt. An ''n''-dimensional hypercube is more commonly referred to as an ''n''-cube or sometimes as an ''n''-dimensional cube. The term measure polytope (originally from Elte, 1912) is also used, notably in the work of H. S. M. Coxeter who also labels the hypercubes the γn polytopes. The hypercube is the special case of a hyperrectangle (also called an ''n-orthotope''). A ''unit hypercube'' is a hypercube whose side has length one unit. Often, the hypercube whose corners (or ''vertices'') are the 2''n'' points in R''n'' with each coordinate equal to 0 or 1 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-sphere
In mathematics, an -sphere or hypersphere is an - dimensional generalization of the -dimensional circle and -dimensional sphere to any non-negative integer . The circle is considered 1-dimensional and the sphere 2-dimensional because a point within them has one and two degrees of freedom respectively. However, the typical embedding of the 1-dimensional circle is in 2-dimensional space, the 2-dimensional sphere is usually depicted embedded in 3-dimensional space, and a general -sphere is embedded in an -dimensional space. The term ''hyper''sphere is commonly used to distinguish spheres of dimension which are thus embedded in a space of dimension , which means that they cannot be easily visualized. The -sphere is the setting for -dimensional spherical geometry. Considered extrinsically, as a hypersurface embedded in -dimensional Euclidean space, an -sphere is the locus of points at equal distance (the ''radius'') from a given '' center'' point. Its interior, consisting of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Cover
In topology, a covering or covering projection is a map between topological spaces that, intuitively, locally acts like a projection of multiple copies of a space onto itself. In particular, coverings are special types of local homeomorphisms. If p : \tilde X \to X is a covering, (\tilde X, p) is said to be a covering space or cover of X, and X is said to be the base of the covering, or simply the base. By abuse of terminology, \tilde X and p may sometimes be called covering spaces as well. Since coverings are local homeomorphisms, a covering space is a special kind of étalé space. Covering spaces first arose in the context of complex analysis (specifically, the technique of analytic continuation), where they were introduced by Riemann as domains on which naturally multivalued complex functions become single-valued. These spaces are now called Riemann surfaces. Covering spaces are an important tool in several areas of mathematics. In modern geometry, covering spaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the center (geometry), ''center'' of the sphere, and the distance is the sphere's ''radius''. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental surface in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is spherical Earth, often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus
In geometry, a torus (: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanarity, coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses include ring toruses, horn toruses, and spindle toruses. A ring torus is sometimes colloquially referred to as a donut or doughnut. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution, also known as a ring torus. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a Lemon (geometry), spindle torus (or ''self-crossing torus'' or ''self-intersecting torus''). If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a ''toroid'', as in a square toroid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformations, such as Stretch factor, stretching, Torsion (mechanics), twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a Set (mathematics), set endowed with a structure, called a ''Topology (structure), topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of List of continuity-related mathematical topics, continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of topological spaces, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and Homotopy, homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |