|
Hemicrania Continua
Hemicrania continua (HC) is a persistent unilateral headache that responds to indomethacin. It is usually unremitting, but rare cases of remission have been documented. Hemicrania continua is considered a primary headache disorder, meaning that another condition does not cause it. Symptoms In hemicrania continua, basal pain is a dull aching pressure similar to that of TTHs (Tension-Type Headaches) that occurs nearly always on the same side of the head and face. Pain ranges from mild to severe and is characterized by fluctuations that increase in intensity up to three to five times per 24-hour cycle. The range of duration of exacerbations has no boundaries and varies from a few seconds to up to two weeks. While attacks tend to be more frequent at night, no circadian periodicity such as in cluster headache can be observed. The nature of pain changes during the exacerbation phase, becoming more piercing, throbbing, and intense, generally paired with other highly debilitating symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Headache And Pain
''The Journal of Headache and Pain'' is a peer-reviewed open access medical journal covering research on headache and related types of pain. It was established in 2000 and is published by BioMed Central. It is the official journal of the European Headache Federation and Lifting The Burden anAsian Regional Consortium for Headache The Founding Editor-in-Chief is Paolo Martelletti ( Unitelma Sapienza University of Rome). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 7.3. References External links * Anesthesiology and palliative medicine journals BioMed Central academic journals Academic journals established in 2000 English-language journals Creative Commons Attribution-licensed journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Occipital Nerve
The greater occipital nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a spinal nerve, specifically the medial branch of the dorsal primary ramus of cervical spinal nerve 2. It arises from between the first and second cervical vertebrae, ascends, and then passes through the semispinalis muscle. It ascends further to supply the skin along the posterior part of the scalp to the vertex. It supplies sensation to the scalp at the top of the head, over the ear and over the parotid glands. Structure The greater occipital nerve is the medial branch of the dorsal primary ramus of cervical spinal nerve 2. It may also involve fibres from cervical spinal nerve 3. It arises from between the first and second cervical vertebrae, along with the lesser occipital nerve. It ascends after emerging from below the suboccipital triangle beneath the obliquus capitis inferior muscle. Just below the superior nuchal ridge, it pierces the fascia. It ascends further to supply the skin along the posterior part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topiramate
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used for alcohol dependence and essential tremor. For epilepsy, this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken orally (by mouth). Common side effects include tingling, feeling tired, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, weight loss, and decreased cognitive function such as trouble concentrating. Serious side effects may include suicide, increased ammonia levels resulting in encephalopathy, and kidney stones. Topiramate can cause birth defects, including cleft lip and palate. Risks/benefits should be carefully discussed with the full treatment team. Topiramate is considered "probably compatible" with lactation and is not contraindicated for breastfeeding, though monitoring of the infant for diarrhea or poor weight gain may be considered. The mechanism of action is unclear. Topiramate was approved for medical us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
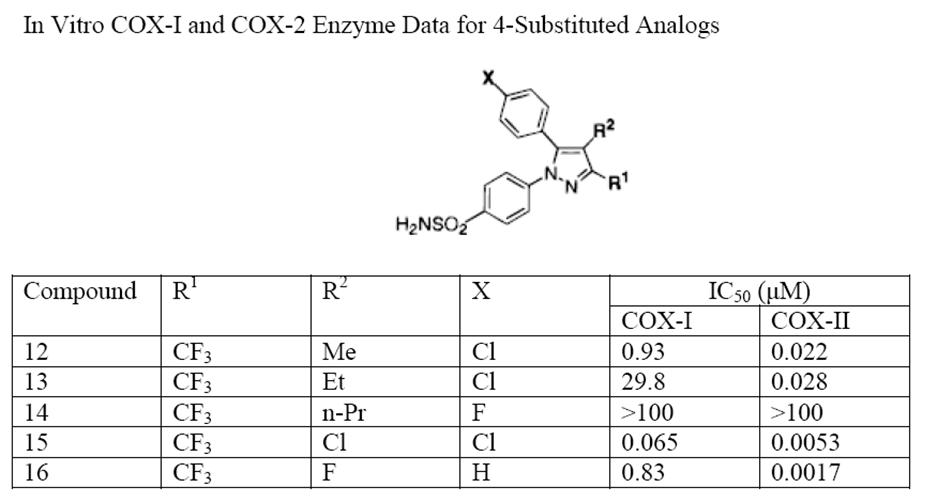
Rofecoxib
Rofecoxib is a COX-2-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It was marketed by Merck & Co. to treat osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, acute pain conditions, migraine, and dysmenorrhea. Rofecoxib was approved in the US by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 1999, and was marketed under the brand names Vioxx, Ceoxx, and Ceeoxx. Rofecoxib was available by prescription in both tablets and as an oral suspension. Rofecoxib gained widespread use among physicians treating patients with arthritis and other conditions causing chronic or acute pain. Worldwide, over 80 million people were prescribed rofecoxib at some time. In September 2004, Merck voluntarily withdrew rofecoxib from the market because of concerns about increased risk of heart attack and stroke associated with long-term, high-dosage use. Merck withdrew the drug after disclosures that it withheld information about rofecoxib's risks from doctors and patients for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celecoxib
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat the pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, painful menstruation, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to decrease the risk of colorectal adenomas in people with familial adenomatous polyposis. It is taken by mouth. Benefits are typically seen within an hour. Common side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea. Serious side effects may include heart attacks, strokes, gastrointestinal perforation, gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney failure, and anaphylaxis. Use is not recommended in people at high risk for heart disease. The risks are similar to other NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Use in the later part of pregnancy or during breastfeeding is not recommended. Celecoxib has demonstrated adjunctive bene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Headache Society
The International Headache Society (IHS) is a London-based charity membership organisation that was founded in 1981 for those with a professional commitment to helping people affected by headache disorders and facial pains. In 1994, the IHS was incorporated in England and Wales as a Company Limited by Guarantee and then registered as a charity in 1995. The current President is Professor Cristina Tassorelli, who is a full professor and Chair of Neurology, Director of the Neurology Residency Program and Director of the Department of Brain and Behavioral Sciences at the University of Pavia The University of Pavia (, UNIPV or ''Università di Pavia''; ) is a university located in Pavia, Lombardy, Italy. There was evidence of teaching as early as 1361, making it one of the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest un .... The IHS currently has about 1,000 ordinary members and 1,000 associated members. The official journal of the IHS is Cephalalgia, which is a pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triptans
Triptans are a family of tryptamine-based drugs used as abortive medication in the treatment of migraines and cluster headaches. This drug class was first commercially introduced in the 1990s. While effective at treating individual headaches, they do not provide preventive treatment and are not considered a cure. They are not effective for the treatment of tension–type headache, except in persons who also experience migraines. Triptans do not relieve other kinds of pain. The drugs of this class act as agonists for serotonin 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors at blood vessels and nerve endings in the brain. The first clinically available triptan was sumatriptan, which has been marketed since 1991. Triptans have largely replaced ergotamines, an older class of medications used to relieve migraine and cluster headaches. Medical uses Migraine Triptans are used for the treatment of severe migraine attacks or those that do not respond to NSAIDs or other over-the-counter drugs. Triptan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Headache
Cluster headache is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent severe headaches on one side of the head, typically around the eye, eye(s). There is often accompanying eye watering, nasal congestion, or swelling around the eye on the affected side. These symptoms typically last 15 minutes to 3 hours. Attacks often occur in clusters which typically last for weeks or months and occasionally more than a year. The disease is considered among the most painful conditions known to medical science. The cause is unknown, but is most likely related to dysfunction of the posterior hypothalamus. Risk factors include a history of exposure to tobacco smoke and a Family history (medicine), family history of the condition. Exposures which may trigger attacks include ethanol, alcohol, nitroglycerin (medication), nitroglycerin, and histamine. They are a primary headache disorder of the trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TAC) type. Diagnosis is based on symptoms. Recommended management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may include vomiting, cognitive dysfunction, allodynia, and dizziness. Exacerbation or worsening of headache symptoms during physical activity is another distinguishing feature. Up to one-third of people with migraine experience aura, a premonitory period of sensory disturbance widely accepted to be caused by cortical spreading depression at the onset of a migraine attack. Although primarily considered to be a headache disorder, migraine is highly heterogenous in its clinical presentation and is better thought of as a spectrum disease rather than a distinct clinical entity. Disease burden can range from episodic discrete attacks to chronic disease. Migraine is believed to be caused by a mixture of environmental and genetic factors that influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miosis
Miosis, or myosis (), is excessive constriction of the pupil. citing: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th ed. The opposite condition, mydriasis, is the dilation of the pupil. Anisocoria is the condition of one pupil being more dilated than the other. Causes Age * Senile miosis (a reduction in the size of a person's pupil in old age)Diseases *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe headaches. Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society, which classifies it into more than 150 types of Primary headache disorder, primary and secondary headaches. Causes of headaches may include dehydration; fatigue; sleep deprivation; Stress (biology), stress; the effects of medications (overuse) and recreational drugs, including withdrawal; viral infections; loud noises; head injury; rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage; and dental or sinus issues (such as sinusitis). Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves analgesic, pain medication (esp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |