|
Heat
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, atomic, or molecular particles, or small surface irregularities, as distinct from the macroscopic modes of energy transfer, which are thermodynamic work and transfer of matter. For a closed system (transfer of matter excluded), the heat involved in a process is the difference in internal energy between the final and initial states of a system, after subtracting the work done in the process. For a closed system, this is the formulation of the first law of thermodynamics. Calorimetry is measurement of quantity of energy transferred as heat by its effect on the states of interacting bodies, for example, by the amount of ice melted or by change in temperature of a body. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement for heat, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conduction
Thermal conduction is the diffusion of thermal energy (heat) within one material or between materials in contact. The higher temperature object has molecules with more kinetic energy; collisions between molecules distributes this kinetic energy until an object has the same kinetic energy throughout. Thermal conductivity, frequently represented by , is a property that relates the rate of heat loss per unit area of a material to its rate of change of temperature. Essentially, it is a value that accounts for any property of the material that could change the way it conducts heat. Heat spontaneously flows along a temperature gradient (i.e. from a hotter body to a colder body). For example, heat is conducted from the hotplate of an electric stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an opposing external driving energy source, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work (thermodynamics)
Thermodynamic work is one of the principal kinds of process by which a thermodynamic system can interact with and transfer energy to its surroundings. This results in externally measurable macroscopic forces on the system's surroundings, which can cause mechanical work, to lift a weight, for example,Kittel, C. Kroemer, H. (1980). ''Thermal Physics'', second edition, W.H. Freeman, San Francisco, or cause changes in electromagnetic,Guggenheim, E.A. (1985). ''Thermodynamics. An Advanced Treatment for Chemists and Physicists'', seventh edition, North Holland, Amsterdam, .Jackson, J.D. (1975). ''Classical Electrodynamics'', second edition, John Wiley and Sons, New York, .Konopinski, E.J. (1981). ''Electromagnetic Fields and Relativistic Particles'', McGraw-Hill, New York, . or gravitationalNorth, G.R., Erukhimova, T.L. (2009). ''Atmospheric Thermodynamics. Elementary Physics and Chemistry'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (UK), . variables. Also, the surroundings can perform t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incandescence
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electronic, molecular, and lattice oscillations in a material. Kinetic energy is converted to electromagnetism due to Larmor formula, charge-acceleration or dipole oscillation. At room temperature, most of the emission is in the infrared (IR) spectrum, though above around 525 °C (977 °F) enough of it becomes Visible spectrum, visible for the matter to visibly glow. This visible glow is called incandescence. Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer, along with Thermal conduction, conduction and Convection (heat transfer), convection. The primary method by which the Sun transfers heat to the Earth is thermal radiation. This energy is partially absorbed and scattered in the atmosphere, the latter process bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot
Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (; 1 June 1796 – 24 August 1832) was a French people, French military engineering, military engineer and physicist. A graduate of the École polytechnique, Carnot served as an officer in the Engineering Arm (''le génie'') of the French Army. He also pursued scientific studies and in June 1824 published an essay titled ''Reflections on the Motive Power of Fire''. In that book, which would be his only publication, Carnot developed the first successful theory of the Thermal efficiency, maximum efficiency of heat engines. Carnot's scientific work attracted little attention during his lifetime, but in 1834 it became the object of a detailed commentary and explanation by another French engineer, Émile Clapeyron. Clapeyron's commentary in turn attracted the attention of William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) and Rudolf Clausius. Thomson used Carnot's analysis to develop an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoception
In physiology, thermoception or thermoreception is the sensation and perception of temperature, or more accurately, temperature differences inferred from heat flux. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a temperature stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal in order to trigger an appropriate response. Thermal stimuli may be noxious (posing a threat to the subject) or innocuous (no threat). The temperature sensitive proteins in thermoreceptors may also be activated by menthol or capsaicin, hence why these molecules evoke cooling and burning sensations, respectively. A thermoreceptor may absorb heat via conduction, convection or radiation. However, the type of heat transfer is usually irrelevant to the functioning of a thermoceptor. Transient receptor potential channels (TRP channels) are believed to play a role in many species in sensation of hot, cold, and pain. Vertebrates have at le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Energy
The term "thermal energy" is often used ambiguously in physics and engineering. It can denote several different physical concepts, including: * Internal energy: The energy contained within a body of matter or radiation, excluding the potential energy of the whole system. * Heat: Energy in transfer between a system and its surroundings by mechanisms other than Work (thermodynamics), thermodynamic work and transfer of matter. * The characteristic energy kT (energy), associated with a single microscopic degree of freedom, where denotes temperature and denotes the Boltzmann constant. Mark Zemansky (1970) has argued that the term "thermal energy" is best avoided due to its ambiguity. He suggests using more precise terms such as "internal energy" and "heat" to avoid confusion. The term is, however, used in some textbooks.For example: Relation between heat and internal energy In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer to or from a thermodynamic system by mechanisms other than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
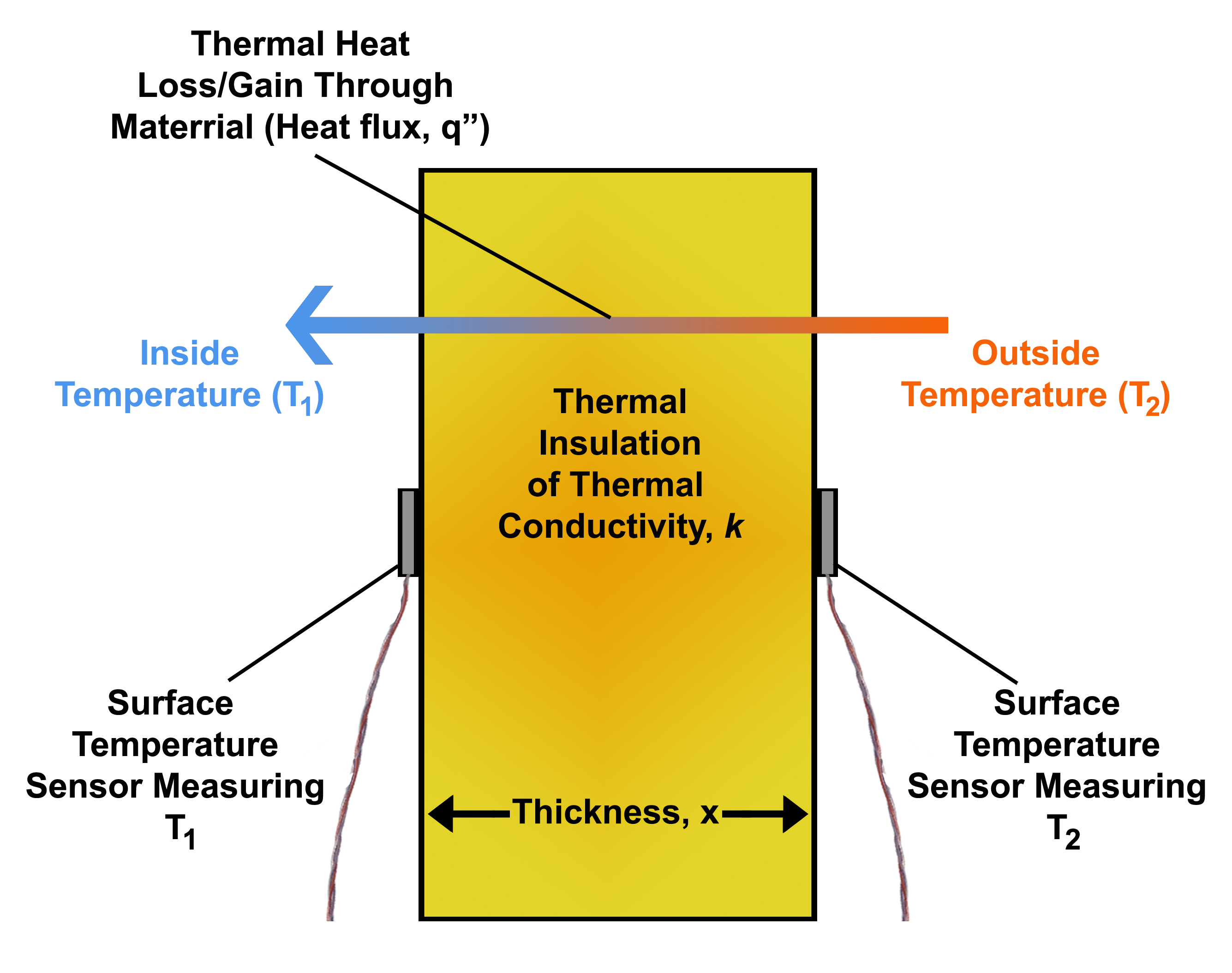
Heat Flux
In physics and engineering, heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as heat flux density, heat-flow density or heat-flow rate intensity, is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time (physics), time. Its SI units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a Vector (geometric), vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small. Heat flux is often denoted \vec_\mathrm, the subscript specifying ''heat'' flux, as opposed to ''Mass flux, mass'' or Transport phenomena, ''momentum'' flux. Heat conduction#Fourier's law, Fourier's law is an important application of these concepts. Fourier's law For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by thermal conduction, conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier's law. Fourier's law in one dimension \phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functions Of State
In the thermodynamics of equilibrium, a state function, function of state, or point function for a thermodynamic system is a mathematical function relating several state variables or state quantities (that describe equilibrium states of a system) that depend only on the current equilibrium thermodynamic state of the system (e.g. gas, liquid, solid, crystal, or emulsion), not the path which the system has taken to reach that state. A state function describes equilibrium states of a system, thus also describing the type of system. A state variable is typically a state function so the determination of other state variable values at an equilibrium state also determines the value of the state variable as the state function at that state. The ideal gas law is a good example. In this law, one state variable (e.g., pressure, volume, temperature, or the amount of substance in a gaseous equilibrium system) is a function of other state variables so is regarded as a state function. A state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macquorn Rankine
William John Macquorn Rankine (; 5 July 1820 – 24 December 1872) was a Scottish mathematician and physicist. He was a founding contributor, with Rudolf Clausius and William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, William Thomson (Lord Kelvin), to the science of thermodynamics, particularly focusing on its First Law. He developed the Rankine scale, a Fahrenheit-based equivalent to the Celsius-based Kelvin scale of temperature. Rankine developed a complete theory of the steam engine and indeed of all heat engines. His manuals of engineering science and practice were used for many decades after their publication in the 1850s and 1860s. He published several hundred papers and notes on science and engineering topics, from 1840 onwards, and his interests were extremely varied, including, in his youth, botany, music theory and number theory, and, in his mature years, most major branches of science, mathematics and engineering. He was also a singer, pianist and cellist as well as a rifleman. Life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |