|
Hard Money (policy)
Hard money policies support a specie standard, usually gold or silver, typically implemented with representative money. In 1836, when President Andrew Jackson's veto of the recharter of the Second Bank of the United States took effect, he issued the Specie Circular, an executive order that all public lands had to be purchased with hard money. Bentonian currency In the US, hard money is sometimes referred to as Bentonian, after Senator Thomas Hart Benton, who was an advocate for the hard money policies of Andrew Jackson. In Benton's view, fiat currency favored rich urban Easterners at the expense of the small farmers and tradespeople of the West. He proposed a law requiring payment for federal land in hard currency only, which was defeated in Congress but later enshrined in an executive order, the Specie Circular. See also * Gold standard * Silver standard * Bimetallic standard * Bullion coin * Digital gold currency * Fractional reserve banking * Free banking * Hard money ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1875 CC Double Eagle
Events January * January 1 – The Midland Railway of England abolishes the Second Class passenger category, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies follow Midland's lead during the rest of the year (Third Class is renamed Second Class in 1956). * January 5 – The Palais Garnier, one of the most famous opera houses in the world, is inaugurated as the home of the Paris Opera. * January 12 – Guangxu Emperor, Guangxu becomes the 11th Qing dynasty Emperor of China at the age of 3. He succeeds his cousin, the Tongzhi Emperor, who had no sons of his own. * January 14 – The newly proclaimed King Alfonso XII of Spain (Queen Isabella II's son) arrives in Spain to restore the monarchy during the Third Carlist War. * January 24 – Camille Saint-Saëns' orchestral ''Danse macabre (Saint-Saëns), Danse macabre'' receives its première. February * February 3 – Third Carlist War: Battle of Lácar – Carlist commander Torcuat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
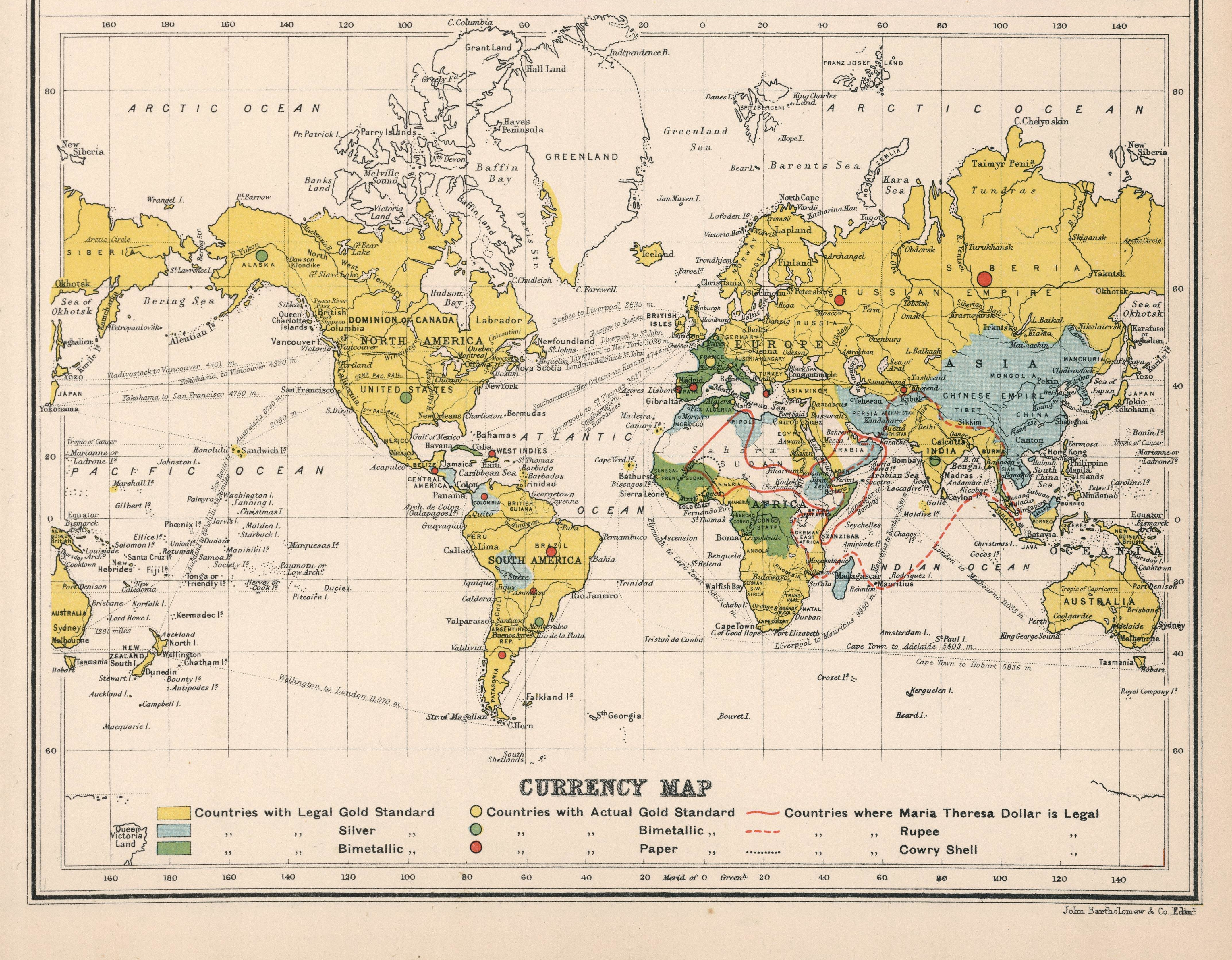
Silver Standard
The silver standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed weight of silver. Silver was far more widespread than gold as the monetary standard worldwide, from the Sumerians 3000 BC until 1873. Following the discovery in the 16th century of large deposits of silver at the Cerro Rico in Potosí, Bolivia, an international silver standard came into existence in conjunction with the Spanish pieces of eight. These silver dollar coins were an international trading currency for nearly four hundred years. The move away from the silver to the gold standard began in the 18th century when Great Britain set the gold guinea’s price in silver higher than international prices, on the recommendation of Sir Isaac Newton, thus attracting gold and putting Great Britain on a de facto gold standard. Great Britain formalised the gold standard in 1821 and introduced it to its colonies afterwards. Imperial Germany’s move to the gold standard in 1873 trigger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitcoin
Bitcoin (abbreviation: BTC; Currency symbol, sign: ₿) is the first Decentralized application, decentralized cryptocurrency. Based on a free-market ideology, bitcoin was invented in 2008 when an unknown entity published a white paper under the pseudonym of Satoshi Nakamoto. Use of bitcoin as a currency began in 2009, with the release of its open-source software, open-source implementation. In 2021, Bitcoin in El Salvador, El Salvador adopted it as legal tender. It is mostly seen as an investment and has been described by some scholars as an economic bubble. As bitcoin is pseudonymous, Cryptocurrency and crime, its use by criminals has attracted the attention of regulators, leading to Legality of cryptocurrency by country or territory, its ban by several countries . Bitcoin works through the collaboration of computers, each of which acts as a Node (networking), node in the peer-to-peer bitcoin network. Each node maintains an independent copy of a public distributed ledger of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according to which each individual has the right to live as they choose, as long as they do not violate the rights of others by initiating force or fraud against them. Libertarians advocate the expansion of individual autonomy and political self-determination, emphasizing the principles of equality before the law and the protection of civil rights, including the rights to freedom of association, freedom of speech, freedom of thought and freedom of choice. They generally support individual liberty and oppose Political authority, authority, State (polity), state power, warfare, militarism and nationalism, but some libertarians diverge on the scope and nature of their opposition to existing Economic system, economic and political systems. Schools of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Money (other)
Hard money may refer to: * Hard currency, globally traded currency that can serve as a reliable and stable store of value * Hard money (policy), currency backed by precious metal * "Hard money" donations to candidates for political office (tightly regulated, as opposed to unregulated "soft money") * "Hard money" funding for academic research (consistently flowing, as opposed to "soft money" provided by competitive grants) * Hard money loan A hard money loan is a specific type of asset-based loan: a financing instrument through which a borrower receives funds secured by real property. Interest rates are typically higher than conventional commercial or residential property loans bec ...s, an asset-based loan financing secured by the value of a parcel of real estate * Hardmoney, Kentucky, a community in the United States {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Banking
Free banking is a monetary arrangement where banks are free to issue their own paper currency ( banknotes) while also being subject to no special regulations beyond those applicable to most enterprises. In a free banking system, market forces control the total quantity of banknotes and deposits that can be supported by any given stock of cash reserves, where such reserves consist either of a scarce commodity (such as gold) or of an artificially limited stock of fiat money issued by a central bank. In the strictest versions of free banking, however, there is either no role at all for a central bank, or the supply of central bank money is supposed to be permanently "frozen". There is, therefore, no government agency acting as a monopoly "lender of last resort", leaving that to the private sector as happened in the US in the panic of 1907. Nor is there any government insurance for banknotes or bank deposit accounts. Notable supporters include Milton Friedman, Fred Foldvary, Davi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Reserve Banking
Fractional-reserve banking is the system of banking in all countries worldwide, under which banks that take deposits from the public keep only part of their deposit liabilities in liquid assets as a reserve, typically lending the remainder to borrowers. Bank reserves are held as cash in the bank or as balances in the bank's account at the central bank. Fractional-reserve banking differs from the hypothetical alternative model, full-reserve banking, in which banks would keep all depositor funds on hand as reserves. The country's central bank may determine a minimum amount that banks must hold in reserves, called the " reserve requirement" or "reserve ratio". Most commercial banks hold more than this minimum amount as excess reserves. Some countries, e.g. the core Anglosphere countries of the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand, and the three Scandinavian countries, do not impose reserve requirements at all. Bank deposits are usually of a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Gold Currency
Digital gold currency (or DGC) is a form of electronic money (or digital currency) based on mass units of gold. It is a kind of representative money, like a gold certificate (United States), US paper gold certificate at the time (from 1873 to 1933) that these were exchangeable for gold on demand. The typical unit of account for such currency is linked to grams or troy ounces of gold, although other units such as the gold dinar are sometimes used. DGCs are backed by gold through unallocated or allocated gold storage. Digital gold currencies are issued by a number of companies, each of which provides a system that enables users to pay each other in units that hold the same value as gold bullion. These competing providers issue a type of independent currency. The Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe is also issuing the ZiG, a digital token backed by gold, which has also been granted legal tender status. Features Universal currency Proponents claim that DGC offers a truly global and bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullion Coin
A bullion coin (also known as a specie) is a coin struck from highly refined precious metal (bullion) and kept as a store of value or an investment rather than used in day-to-day commerce, or collectable, with numismatic value beyond that of its metal content. A bullion coin is distinguished by its weight (or mass) and fineness on the coin. Unlike rounds, bullion coins are minted by government mints and have a legal tender face value. Bullion coins can have fineness ranging from 91.9% (22 karat) to 99.99% purity (24 karat). In the United Kingdom coins deemed to be investment coins are exempt from value-added tax (VAT) on transactions. A coin is considered to be an investment coin if it was minted after 1800, and at least 900 thousandths fine, and has been legal tender in its country of origin, and not normally sold at more than 180% of the value of its precious metal content; or if it is on a long list of coins deemed to be investment coins. This Web page links to the current list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimetallic Standard
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed Exchange rate, rate of exchange between them. For scholarly purposes, "proper" bimetallism is sometimes distinguished as permitting that both gold and silver money are legal tender in unlimited amounts and that gold and silver may be taken to be coined by the Mint (facility), government mints in unlimited quantities. This distinguishes it from "limping standard" bimetallism, where both gold and silver are legal tender but only one is freely coined (e.g. the monies of France, Germany, and the United States after 1873), and from "trade" bimetallism, where both metals are freely coined but only one is legal tender and the other is used as "trade money" (e.g. most monies in western Europe from the 13th to 18th centuries). Economists also distinguish ''legal'' bimeta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the late 1920s to 1932 as well as from 1944 until 1971 when the United States unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system. Many states nonetheless hold substantial gold reserves. Historically, the silver standard and bimetallism have been more common than the gold standard. The shift to an international monetary system based on a gold standard reflected accident, network externalities, and path dependence. Great Britain accidentally adopted a ''de facto'' gold standard in 1717 when Isaac Newton, then-master of the Royal Mint, set the exchange rate of silver to gold too low, thus causing silver coins to go out of circulation. As Great Britain became the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USA-1924-Coin-20
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic nuclear missiles. The program was announced in 1983, by President Ronald Reagan. Reagan called for a system that would render nuclear weapons obsolete, and to end the doctrine of mutual assured destruction (MAD), which he described as a "suicide pact". Elements of the program reemerged in 2019 under the Space Development Agency (SDA). The Strategic Defense Initiative Organization (SDIO) was set up in 1984 within the US Department of Defense to oversee development. Advanced weapon concepts, including lasers, particle-beam weapons, and ground and space-based missile systems were studied, along with sensor, command and control, and computer systems needed to control a system consisting of hundreds of combat centers and satellites spanning the globe. The US held a significant advantage in advanced missile defense systems through decades of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |