|
Geodimeter
__NOTOC__ The Geodimeter (acronym of geodetic distance meter) was the first optical electronic distance meter surveying instrument. It was originally developed for measuring the speed of light. It was invented in 1947 by and commercialized in 1953 by the AGA (''Aktiebolaget Gasaccumulator'') company of Sweden. It was used in the Transcontinental Traverse. The Geodimeter business was acquired by SpectraPrecision which was acquired by Trimble Inc. Electronic mechanism The mechanism uses a Kerr cell in an optical train that chops a collimated beam of light under the control of a precision electronic oscillator in the megahertz range. It is similar in principle to earlier mechanical choppers in Fizeau–Foucault apparatus that used a toothed wheel or a rotating mirror. See also * Laser rangefinder * Lidar * Tellurometer References Sources * * * * * * Further reading * * * * External links AGA Geodimeter Model 6(''Going the Distance: A Photo Collection Illustrating the Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodimeter 8 Control Panel
__NOTOC__ The Geodimeter (acronym of geodetic distance meter) was the first optical electronic distance meter surveying instrument. It was originally developed for measuring the speed of light. It was invented in 1947 by and commercialized in 1953 by the AGA (''Aktiebolaget Gasaccumulator'') company of Sweden. It was used in the Transcontinental Traverse. The Geodimeter business was acquired by SpectraPrecision which was acquired by Trimble Inc. Electronic mechanism The mechanism uses a Kerr cell in an optical train that chops a collimated beam of light under the control of a precision electronic oscillator in the megahertz range. It is similar in principle to earlier mechanical choppers in Fizeau–Foucault apparatus that used a toothed wheel or a rotating mirror. See also * Laser rangefinder * Lidar * Tellurometer References Sources * * * * * * Further reading * * * * External links AGA Geodimeter Model 6(''Going the Distance: A Photo Collection Illustrating the Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcontinental Traverse
The Transcontinental Traverse (TCT) was a geodetic survey traverse conducted in the Continental United States by the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey between 1961 and 1976. It was the most accurate large-area survey ever done prior to Global Positioning System surveys. TCT included over 2,700 survey stations, covered over 13,600 miles, and passed through 44 states. This nationwide survey increased the accuracy of the existing U.S. survey network. It was also fundamental to the sophisticated mathematical readjustment of the nation's survey network known as the North American Datum of 1983. It was the "end of an era" as the last conventional, purely terrestrial large scale survey. Forerunner surveys The first major transcontinental survey was the Transcontinental Arc of Triangulation, completed in 1896 along the 39th parallel north with coastal endpoints at Cape May, New Jersey, and Point Arena, California lighthouses. It established the Meades Ranch survey marker, also called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
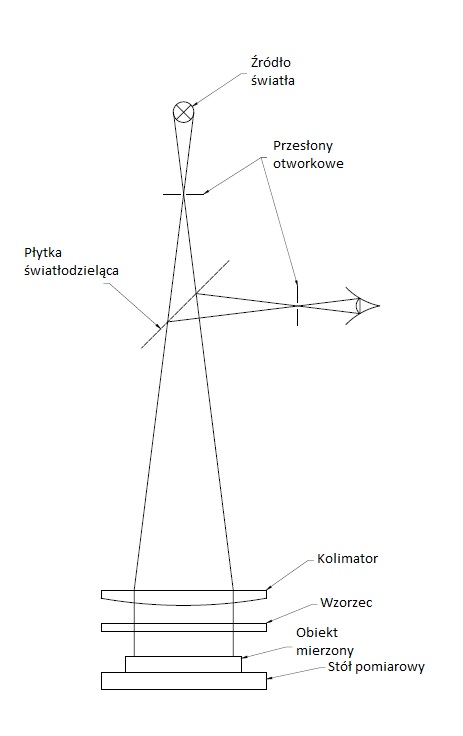
Fizeau–Foucault Apparatus
The Fizeau–Foucault apparatus is either of two types of instrument historically used to measure the speed of light. The conflation of the two instrument types arises in part because Hippolyte Fizeau and Léon Foucault had originally been friends and collaborators. They worked together on such projects as using the Daguerreotype process to take images of the Sun between 1843 and 1845 and characterizing absorption bands in the infrared spectrum of sunlight in 1847. In 1834, Charles Wheatstone developed a method of using a rapidly rotating mirror to study transient phenomena, and applied this method to measure the velocity of electricity in a wire and the duration of an electric spark. He communicated to François Arago the idea that his method could be adapted to a study of the speed of light. Arago expanded upon Wheatstone's concept in an 1838 publication, emphasizing the possibility that a test of the relative speed of light in air ''versus'' water could be used to distinguish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geodetic Survey
The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a United States federal agency that defines and manages a national coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication; mapping and charting; and a large number of applications of science and engineering. Since its foundation in its present form in 1970, it has been part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), of the United States Department of Commerce. History The National Geodetic Surveys history and heritage are intertwined with those of other NOAA offices. It traces its history to the Survey of the Coast, which was formed in 1807 as the first scientific agency of the United States Government. It became the United States Coast Survey in 1836 and the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1878, the latter name change reflecting the increasing role of geodesy in its work. Upon the creation of NOAA in 1970, the Coast and Geodetic Survey was abolished and its responsibilities were sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartography (journal)
The ''Journal of Spatial Science'' is an academic journal about spatial sciences published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the Mapping Sciences Institute (Australia) and the Surveying and Spatial Sciences Institute. It covers cartography, geodesy, geographic information science, hydrography, digital image analysis and photogrammetry, remote sensing, surveying and related areas. Its editor-in-chief is Graeme Wright; its 2018 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... is 1.711. It started in 2004 as a continuation of both ''Cartography'' (1954-2003) and ''Australian Surveyor'' (1928-2003). It also absorbed ''Geomatics Research Australasia'' (1995-2004), a continuation of the ''Australian Journal of Geodesy, Photogrammetry, and Surveying'' (1979-1994). Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HathiTrust
HathiTrust Digital Library is a large-scale collaborative repository of digital content from research libraries including content digitized via Google Books and the Internet Archive digitization initiatives, as well as content digitized locally by libraries. History HathiTrust was founded in October 2008 by the twelve universities of the Committee on Institutional Cooperation and the eleven libraries of the University of California. The partnership includes over 60 research libraries across the United States, Canada, and Europe, and is based on a shared governance structure. Costs are shared by the participating libraries and library consortia. The repository is administered by the University of Michigan. The executive director of HathiTrust is Mike Furlough. The HathiTrust Shared Print Program is a distributed collective collection whose participating libraries have committed to retaining almost 18 million monograph volumes for 25 years, representing three-quarters of HathiT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellurometer
The tellurometer was the first successful microwave electronic distance measurement equipment. The name derives from the Latin ''tellus'', meaning Earth. History The original tellurometer, known as the Micro-Distancer MRA 1, was introduced in 1957. It was invented by Trevor Wadley of the Telecommunications Research Laboratory of the South African Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). He was also responsible for the Wadley Loop receiver, which allowed precision tuning over wide bands, a task that had previously required switching out multiple crystal oscillators. Principle The tellurometer emits a microwave-frequency radio wave. The remote station carries a transponder that reradiates the incoming wave in a similar wave of more complex modulation. The resulting phase shift is a measure of the two-way distance travelled. The results appear on a cathode ray tube with circular sweep. Application The tellurometer design yields high accuracy distance measureme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, or LiDAR; sometimes LADAR) is a method for determining ranges (variable distance) by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. It can also be used to make digital 3-D representations of areas on the Earth's surface and ocean bottom of the intertidal and near coastal zone by varying the wavelength of light. It has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications. ''Lidar'' is an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging". It is sometimes called 3-D laser scanning, a special combination of 3-D scanning and laser scanning. Lidar is commonly used to make high-resolution maps, with applications in surveying, geodesy, geomatics, archaeology, geography, geology, geomorphology, seismology, forestry, atmospheric physics, laser guidance, airborne laser swath mapping (ALSM), and laser altimetry. It is also used in control and navigation for som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in a narrow beam towards the object and measuring the time taken by the pulse to be reflected off the target and returned to the sender. Due to the high speed of light, this technique is not appropriate for high precision sub-millimeter measurements, where triangulation and other techniques are often used. Pulse The pulse may be coded to reduce the chance that the rangefinder can be jammed. It is possible to use Doppler effect techniques to judge whether the object is moving towards or away from the rangefinder, and if so, how fast. Precision The precision of the instrument is determined by the rise or fall time of the laser pulse and the speed of the receiver. One that uses very sharp laser pulses and has a very fast detector can ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megahertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |