|
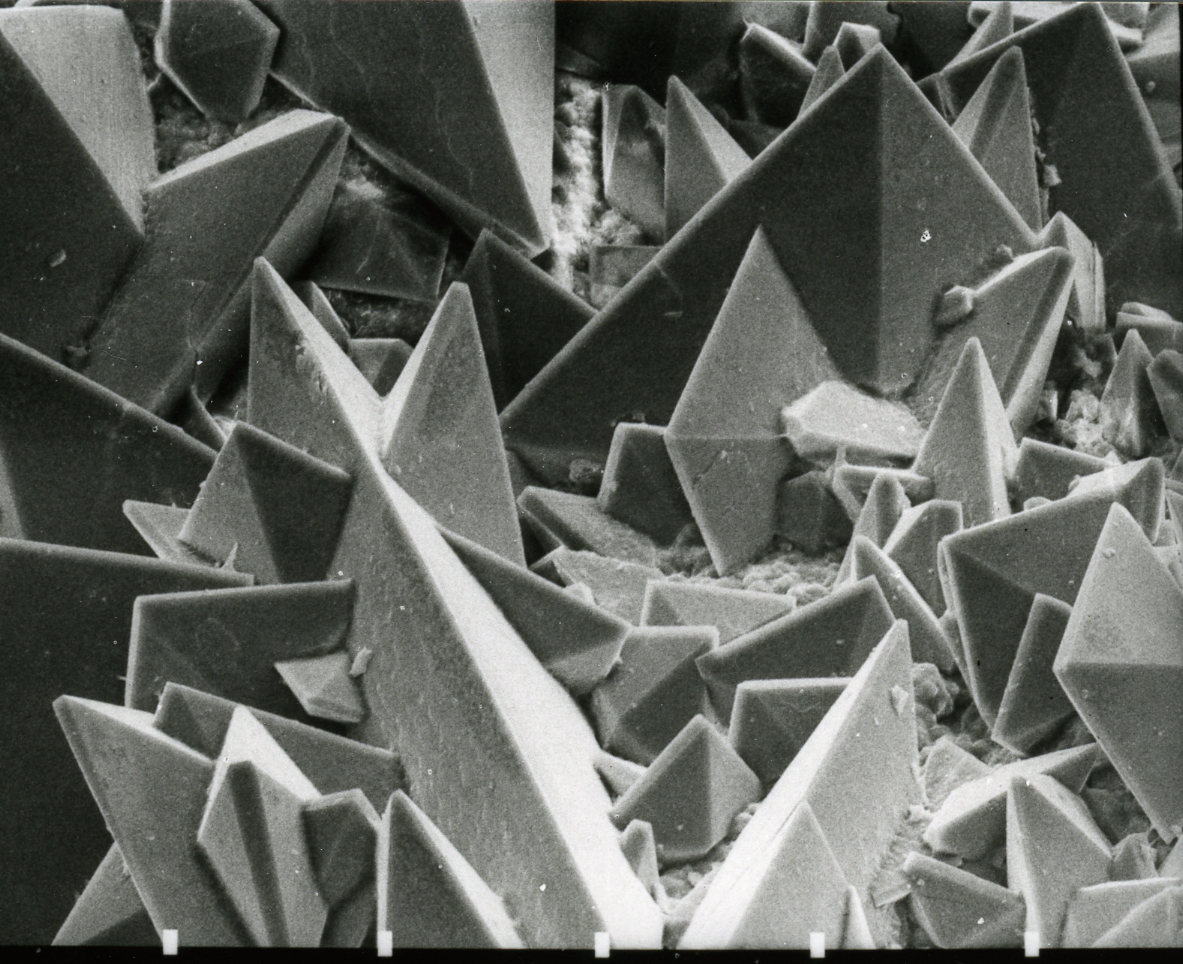
Gadolinium(III) Oxide
Gadolinium(III) oxide (archaically gadolinia) is an inorganic compound with the formula Gd2O3. It is one of the most commonly available forms of the rare-earth element gadolinium, derivatives of which are potential contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Structure Gadolinium oxide adopts two structures. The cubic ( cI80, Ia), No. 206) structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide and heavy trivalent lanthanide sesquioxides. The cubic structure features two types of gadolinium sites, each with a coordination number of 6 but with different coordination geometries. The second polymorph is monoclinic (Pearson symbol mS30, space group C2/m, No. 12). At room temperature, the cubic structure is more stable. The phase change to the monoclinic structure takes place at 1200 °C. Above 2100 °C to the melting point at 2420 °C, a hexagonal phase dominates. Preparation and chemistry Gadolinium oxide can be formed by thermal decomposition of the hydroxide, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gd2O3structure
GD, Gd, or gd may refer to: Arts and entertainment * G-Dragon (born 1988), leader of the South Korean musical group Big Bang * Grateful Dead, an American rock band * Green Day, an American rock band * '' Geometry Dash'', a rhythm-based video game for smartphones and PC *Good Drawing, in text this means that the drawing of a person is good Business and economics * Gardner Denver, a US-based manufacturer of industrial equipment * General Dynamics, a US-based defense conglomerate * Good Delivery, a specification for gold and silver bars * Great Depression, a sudden collapse of the global economy in the 1920s * Composite Index on the Athens Stock Exchange (stock symbol GD) Math, science and technology Biology and medicine * Gaucher's disease, a lipid storage diseases * Gender dysphoria, distress caused by a difference between the sex and gender a person was assigned at birth * Generalized dystonia, a neurological movement disorder * Gestational diabetes, a form of diabetes ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dextran
Dextran is a complex branched glucan ( polysaccharide derived from the condensation of glucose), originally derived from wine. IUPAC defines dextrans as "Branched poly-α-d-glucosides of microbial origin having glycosidic bonds predominantly C-1 → C-6". Dextran chains are of varying lengths (from 3 to 2000 kilodaltons). The polymer main chain consists of α-1,6 glycosidic linkages between glucose monomers, with branches from α-1,3 linkages. This characteristic branching distinguishes a dextran from a dextrin, which is a straight chain glucose polymer tethered by α-1,4 or α-1,6 linkages. Occurrence Dextran was discovered by Louis Pasteur as a microbial product in wine, but mass production was only possible after the development by Allene Jeanes of a process using bacteria. Dental plaque is rich in dextrans. Dextran is a complicating contaminant in the refining of sugar because it elevates the viscosity of sucrose solutions and fouls plumbing. Dextran is now produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are usually distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 µm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nanop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate (C2O4(CH3)2). It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate. Relationship to oxalic acid The dissociation of protons from oxalic acid proceeds in a stepwise manner; as for other polyprotic acids, loss of a single proton results in the monovalent hydrogenoxalate anion . A salt with this anion is sometimes called an acid oxalate, monobasic oxalate, or hydrogen oxalate. The equilibrium constant ( ''K''a) for loss of the first proton is (p''K''a = 1.27). The loss of the second proton, which yields the oxalate ion, has an equilibrium constant of (p''K''a = 4.28). These values imply, in solutions with neutral pH, no oxalic acid and only trace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of an object in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of an object that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list was complete was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese(III) Oxide
Manganese(III) oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Mn2O3. It occurs in nature as the mineral bixbyite (recently changed to bixbyite-(Mn)IMA 21-H: Redefinition of bixbyite and definition of bixbyite-(Fe) and bixbyite-(Mn). CNMNC Newsletter, 64, 2021; Mineralogical Magazine, 85, 2021).) and is used in the production of ferrites and thermistors. Preparation and chemistry Heating MnO2 in air at below 800 °C produces α-Mn2O3 (higher temperatures produce Mn3O4). γ-Mn2O3 can be produced by oxidation followed by dehydration of manganese(II) hydroxide. Many preparations of nano-crystalline Mn2O3 have been reported, for example syntheses involving oxidation of MnII salts or reduction of MnO2. Manganese(III) oxide is formed by the redox reaction in an alkaline cell: : 2 MnO2 + Zn → Mn2O3 + ZnO Manganese(III) oxide Mn2O3 must not be confused with MnOOH manganese(III) oxyhydroxide. Contrary to Mn2O3, MnOOH is a compound that decomposes at about 300 °C to form MnO2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Space Groups
There are 230 space groups in three dimensions, given by a number index, and a full name in Hermann–Mauguin notation, and a short name (international short symbol). The long names are given with spaces for readability. The groups each have a point group of the unit cell. Symbols In Hermann–Mauguin notation, space groups are named by a symbol combining the point group identifier with the uppercase letters describing the lattice type. Translations within the lattice in the form of screw axes and glide planes are also noted, giving a complete crystallographic space group. These are the Bravais lattices in three dimensions: *P primitive *I body centered (from the German ''Innenzentriert'') *F face centered (from the German ''Flächenzentriert'') *A centered on A faces only *B centered on B faces only *C centered on C faces only *R rhombohedral A reflection plane m within the point groups can be replaced by a glide plane, labeled as a, b, or c depending on which axis the gli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Symbol
The Pearson symbol, or Pearson notation, is used in crystallography as a means of describing a crystal structure, and was originated by W. B. Pearson. The symbol is made up of two letters followed by a number. For example: * Diamond structure, ''cF''8 * Rutile structure, ''tP''6 The two (italicised) letters specify the Bravais lattice. The lower-case letter specifies the crystal family, and the upper-case letter the centering type. The number at the end of the Pearson symbol gives the number of the atoms in the conventional unit cell.Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations 2005 IR-3.4.4, pp. 49–51; IR-11.5, pp. 241–242. |
Tl2O3structure
TL or Tl may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Teens' love, Japanese erotic fiction marketed towards women * Télé Liban, a Lebanese television network * ''Turn Left'' (newspaper), Cornell University student publication Language * Tl (digraph), a digraph representing a voiceless alveolar lateral affricate in some languages * Tagalog language (ISO 639 alpha-2 code: tl) Organisations * Airnorth (IATA airline code TL), an airline * Public transport in the Lausanne Region, a transport company * ''Teknisk Landsforbund'', the Danish Union of Professional Technicians * Team Liquid, a professional gaming and eSports team and community website Science and technology * Liquidus temperature, the maximum temperature at which crystals can co-exist with the melt * Teralitre (Tl or TL), a metric unit of volume or capacity * Thallium, symbol Tl, a chemical element * Thermoluminescence dating, in geochronology * Total length in fish measurement * Transmission loss (TL), in acoustics, elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |