|
Gun Port
A gunport is an opening in the side of the hull (watercraft), hull of a ship, above the waterline, which allows the muzzle of artillery pieces mounted on the gun deck to fire outside. The origin of this technology is not precisely known, but can be traced back to the late 15th century, with the appearance of artillery in naval warfare. Ships featuring gunports were said to be pierced, since the ports were cut through the hull after the construction. History Origin The origin of the gunport is difficult to specify. In France, it has often been attributed to François Descharges (or Deschenges), a master carpenter in Brest in 1501;. this is now known to be incorrect, since the ships of this era had long since adopted guns as their main armament.Dominique Brissou, dans . Examples of earlier occurrence are a 1498 terra cotta tile featuring a Portuguese caravel pierced with gunports; a relation of the Siege of Rhodes (1480), Siege of Rhodes, printed in Ulm in 1496, that mentions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunport
A gunport is an opening in the side of the hull of a ship, above the waterline, which allows the muzzle of artillery pieces mounted on the gun deck to fire outside. The origin of this technology is not precisely known, but can be traced back to the late 15th century, with the appearance of artillery in naval warfare. Ships featuring gunports were said to be pierced, since the ports were cut through the hull after the construction. History Origin The origin of the gunport is difficult to specify. In France, it has often been attributed to François Descharges (or Deschenges), a master carpenter in Brest in 1501;. this is now known to be incorrect, since the ships of this era had long since adopted guns as their main armament.Dominique Brissou, dans . Examples of earlier occurrence are a 1498 terra cotta tile featuring a Portuguese caravel pierced with gunports; a relation of the Siege of Rhodes, printed in Ulm in 1496, that mentions a ship with 10 gunports; and a text that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrack
A carrack (; ; ) is a three- or four- masted ocean-going sailing ship that was developed in the 14th to 15th centuries in Europe, most notably in Portugal and Spain. Evolving from the single-masted cog, the carrack was first used for European trade from the Mediterranean to the Baltic and quickly found use with the newly found wealth of the trade between Europe and Africa and then the trans-Atlantic trade with the Americas. In their most advanced forms, they were used by the Portuguese and Spaniards for trade between Europe, Africa and Asia starting in the late 15th century, before being gradually superseded in the late 16th and early 17th centuries by the galleon. In its most developed form, the carrack was a carvel-built ocean-going ship: large enough to be stable in heavy seas, and capacious enough to carry a large cargo and the provisions needed for very long voyages. The later carracks were square-rigged on the foremast and mainmast and lateen- rigged on the mizzenma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinker (boat Building)
Clinker-built, also known as lapstrake-built, is a method of boat building in which the edges of longitudinal (lengthwise-running) hull planks overlap each other. The technique originated in Northern Europe, with the first known examples using metal fastenings that join overlapped planks in . It was employed by the Anglo-Saxons, Frisians, and Scandinavians in the early middle ages, and later in the Basque shipbuilding region where the Newport medieval ship was built. It was also used in cogs, the other major ship construction type found in Northern Europe in the latter part of the medieval period. UNESCO named the Nordic clinker boat tradition to its List of Intangible Cultural Heritage on December 14, 2021, in the first approval of a joint Nordic application. Description Clinker construction is a boat and ship-building method in which the hull planks overlap and are joined by nails that are driven through the overlap (often called the "lap"). These fastenings typically go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Fournier (priest)
Georges Fournier (31 August 1595 – 13 April 1652) was a French Jesuit priest, geographer and mathematician. Biography Fournier served as a naval military chaplain on a ship of the line, and acquired a strong knowledge of technical and naval matters. In 1642, he published the treaty ''Hydrographie'', where he attempted to provide a scientific foundation to the design of ships. Bertrand Gille, ''Histoire des techniques''. At the time, results like ''Couronne'' or ''Sovereign of the Seas'' were obtained by empirical trials and errors. He also authored a ''Treaty of fortifications or military architecture, drawn from the most estimated places of our times, for fortifications'',Voir bibliographie et traité en ligne sur le site ''Architectura'' du Centre d'études ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quincunx
A quincunx ( ) is a geometry, geometric pattern consisting of five points arranged in a cross, with four of them forming a Square (geometry), square or rectangle and a fifth at its center. The same pattern has other names, including "in saltire" or "in cross" in heraldry (depending on the orientation of the outer square), the five-point stencil in numerical analysis, and the five dots tattoo. It forms the arrangement of five units in the pattern corresponding to the five-spot on six-sided dice, playing cards, and dominoes. It is represented in Unicode as or (for the die pattern) . Historical origins of the name The Quincunx (coin), quincunx was originally a coin issued by the Roman Republic , whose value was five twelfths (''quinque'' and ''uncia'') of an as (coin), as, the Roman standard aes grave, bronze coin. On the Roman quincunx coins, the value was sometimes indicated by a pattern of five dots or pellets. However, these dots were not always arranged in a quincunx pattern. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36-pounder Long Gun
The 36-pounder long gun was the largest piece of naval artillery in the Age of Sail, artillery mounted on French warships of the Age of Sail. They were also used for Coastal defense and fortification. They largely exceeded the heaviest guns fielded by the Army, which were 24-pounder long guns. The nominal weight of shot was 36 French units of measurement, French ''livres'', . Usage Installed on the lower deck of the larger warships, the 36-pounder long gun was the largest caliber used in the Navy of the Age of the Sail. Attempts to use 48-pounders were made, for instance on French ship Royal Louis (1692), ''Royal Louis'', but these proved impractical to use on ships, partly because their weight allowed for only a few pieces, and because the heavy balls were unwieldy to load by hand. However, some coastal batteries fielded 48-pounders and even 64-pounders. In the Royal Navy, a similar role was fulfilled by 32-pounder long guns. History French warships began to carry 36-pounders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chase Gun
A chase gun (or chaser), usually distinguished as bow chaser and stern chaser, was a cannon mounted in the bow (aiming forward) or stern (aiming backward) of a sailing ship. They were used to attempt to slow down an enemy ship either chasing (pursuing) or being chased, when the ship's broadside could not be brought to bear. Typically, the chasers were used to attempt to damage the rigging and thereby cause the target to lose performance. Bow chasers could be regular guns brought up from the gundeck and aimed through specially cut-out ports on either side of the bowsprit, or dedicated weapons made with an unusually long bore and a relatively light ball, and mounted in the bow. Stern chasers could also be improvised, or left permanently in the cabins at the stern, covered up and used as part of the furniture. Development In the Age of Sail, shiphandling had been brought to a high art, and chases frequently lasted for hours or sometimes days, as each crew fine-tuned their sails t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Morel-Fatio Pl10
Antoine is a French given name (from the Latin ''Antonius'' meaning 'highly praise-worthy') that is a variant of Danton, Titouan, D'Anton and Antonin. The name is most common in France, Switzerland, Belgium, Canada, West Greenland, Haiti, French Guiana, Madagascar, Benin, Niger, Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast, Guinea, Senegal, Mauritania, Western Sahara, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Chad, Central African Republic, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, and Rwanda. It is a cognate of the masculine given name Anthony. Similar names include Antaine, Anthoine, Antoan, Antoin, Antton, Antuan, Antwain, Antwan, Antwaun, Antwoine, Antwone, Antwon and Antwuan. Feminine forms include Antonia, Antoinette, and (more rarely) Antionette. As a first name *Antoine Alexandre Barbier (1765–1825), a French librarian and bibliographer *Antoine Arbogast (1759–1803), a French mathematician *Antoine Arnauld (1612–1694), a Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
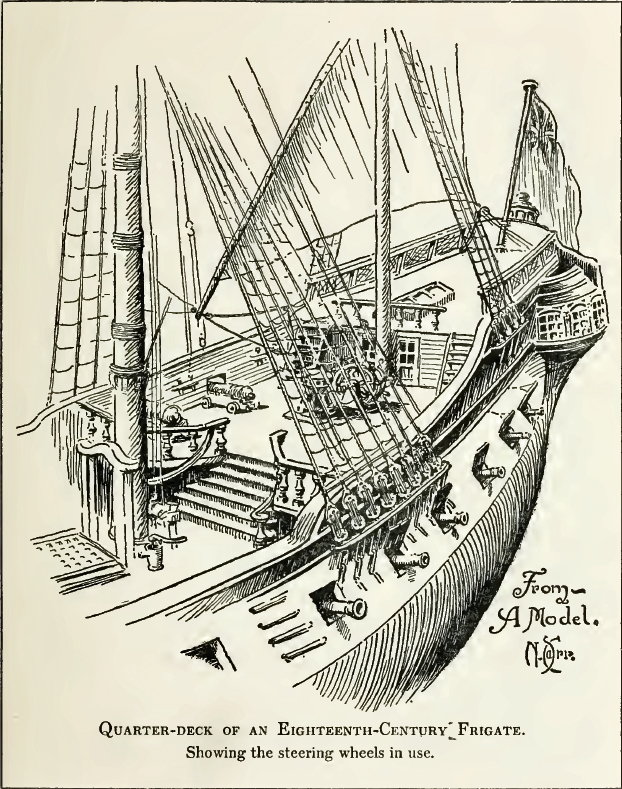
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all carried shrines which were given special respect. This continued into Christian times, and in medieval British warships, the religious shrine was set up on the quarterdeck. All hands were required to salute it by taking off their hats or caps. This le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
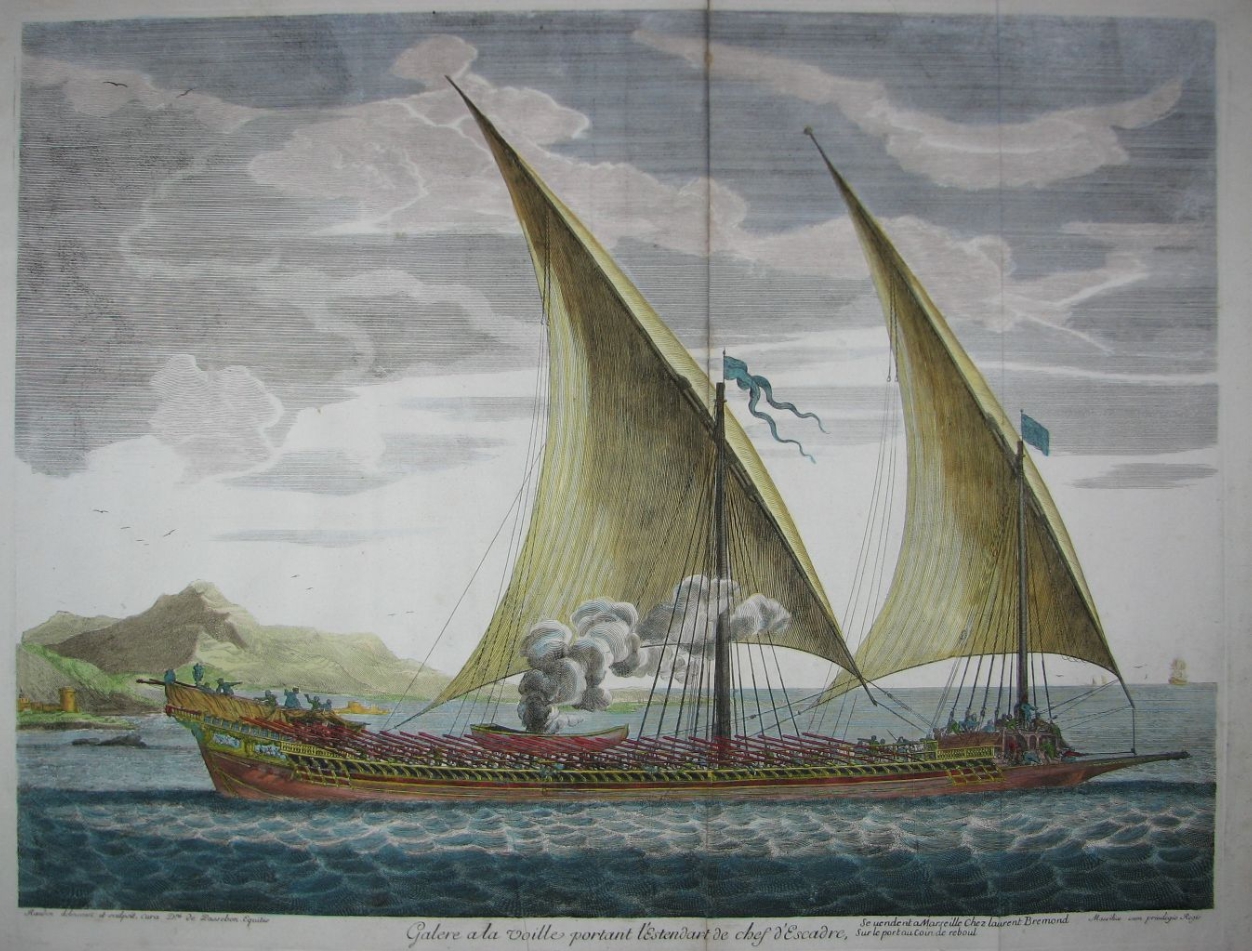
Galley
A galley is a type of ship optimised for propulsion by oars. Galleys were historically used for naval warfare, warfare, Maritime transport, trade, and piracy mostly in the seas surrounding Europe. It developed in the Mediterranean world during Classical antiquity, antiquity and continued to exist in various forms until the early 19th century. It typically had a long, slender hull, shallow draft (hull), draft, and often a low freeboard (nautical), freeboard. Most types of galleys also had sails that could be used in favourable winds, but they relied primarily on oars to move independently of winds and currents or in battle. The term "galley" originated from a Greek term for a small type of galley and came in use in English from about 1300. It has occasionally been used for unrelated vessels with similar military functions as galley but which were not Mediterranean in origin, such as medieval Scandinavian longships, 16th-century Ghali (ship), Acehnese ghalis and 18th-century North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battle, which involved the two columns of opposing warships manoeuvering to volley fire with the naval cannon, cannons along their Broadside (naval), broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the faction with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam engine, steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of propeller, screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mechanism. However, the rise of the ironclad warship, ironclad frigate, starting in 1859, made steam-assisted ships of the line obsolete. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |