|
Grey-hooded Parakeet
The grey-hooded parakeet (''Psilopsiagon aymara''), also known as the Aymara parakeet or Sierra parakeet, is a species of parrot in the family Psittacidae. It is found in northwestern Argentina and Bolivia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical high-altitude shrubland. Description The grey-hooded parakeet is a small, slender parakeet growing to a length of about . The upper parts are green and the flanks and underwing coverts are greenish-yellow. The forehead and crown are brownish-grey, and the chin, throat and breast are whitish-grey, sometimes with a bluish tinge at the side of the breast. The belly is green with a bluish tinge. The upper side of the long, narrow, pointed tail is green and the underside is grey. The beak is flesh-coloured, the iris is brown and the legs and feet are brownish-grey. The sexes are similar in appearance, but the male often has a more vivid grey breast, and immature birds have shorter tails. Distribution and habitat The grey-hooded parakee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capilla Del Monte
Capilla del Monte is a small city in the northeastern part of the provinces of Argentina, province of Córdoba Province (Argentina), Córdoba, Argentina, located by the Sierras Chicas mountain chain, in the northern end of the Punilla Valley. It has about 11,281 inhabitants as per the . Tourism is the main source of income in Capilla del Monte. The most popular tourist attraction in the area is the Uritorco, Cerro Uritorco, a small mountain only 3 km away from the city, famed around Argentina as a center of alleged paranormal phenomena and unidentified flying objects, UFO sightings. There are many other locations in Capilla del Monte that attract tourists from all over the country. The city also features the tall El Cajón Dam (Argentina), El Cajón Dam and its large reservoir (water), reservoir. Capilla del Monte was founded on October 30, 1585. Its name means "Chapel on the Hill" in Spanish. The area has been used as a special stage for Rally Argentina. Origin 1585 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
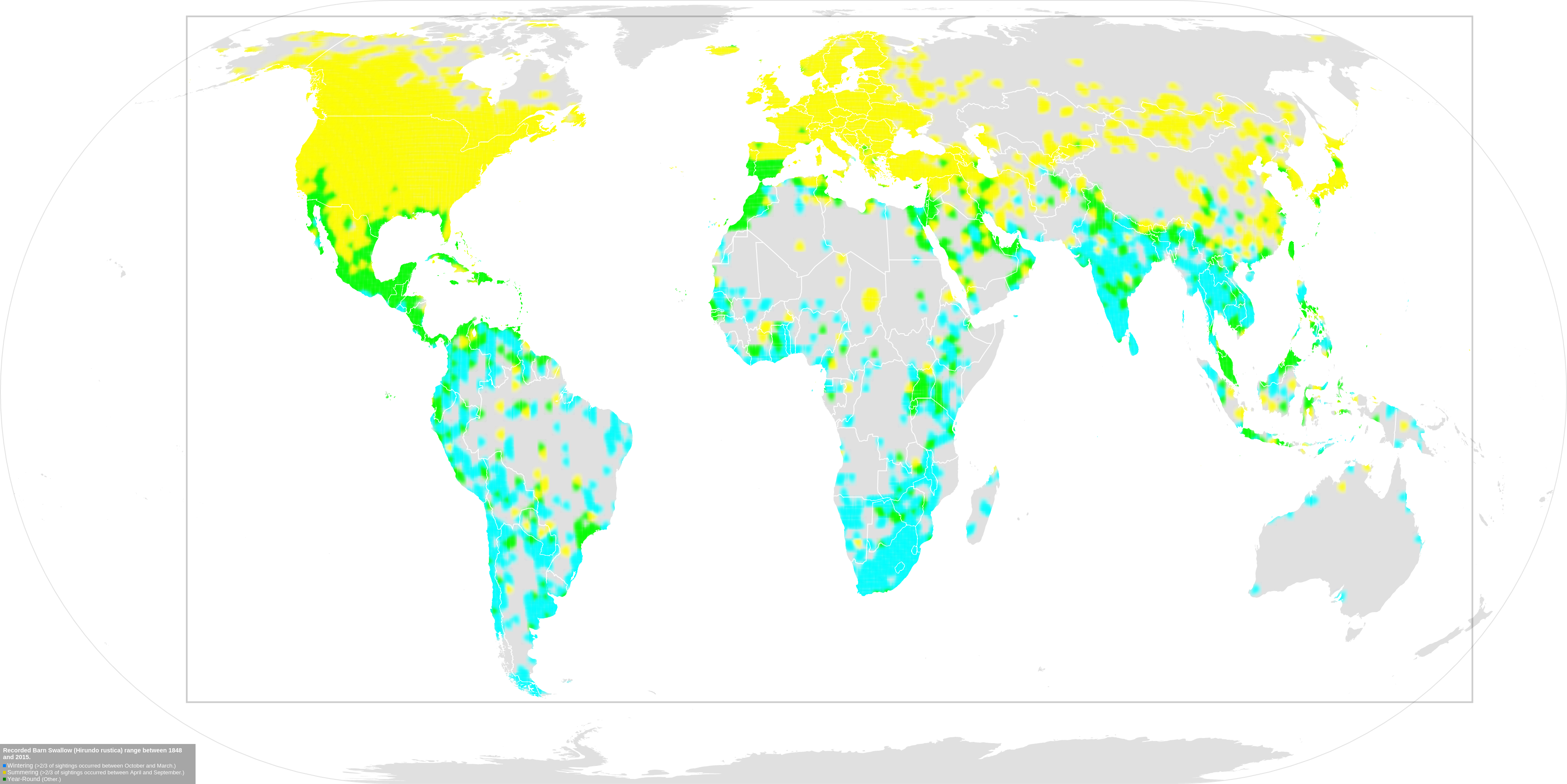
Barn Swallow
The barn swallow (''Hirundo rustica'') is the most widespread species of swallow in the world, occurring on all continents, with vagrants reported even in Antarctica. It is a distinctive passerine bird with blue upperparts and a long, deeply forked tail. In English-speaking world, Anglophone Europe, it is just called the swallow; in northern Europe, it is the only member of family Hirundinidae called a "swallow" rather than a "Martin (bird), martin". There are six subspecies of barn swallow, which breed across the Northern Hemisphere. Two subspecies, (''H. r. savignii and H. r. transitiva'') have fairly restricted ranges in the Nile valley and eastern Mediterranean, respectively. The other four are more widespread, with winter ranges covering much of the Southern Hemisphere. The barn swallow is a bird of open country that normally nests in man-made structures and consequently has spread with human expansion. It builds a cup bird nest, nest from mud pellets in barns or similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of The Southern Andean Yungas
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parakeets
A parakeet is any one of many small- to medium-sized species of parrot, in multiple genera, that generally has long tail feathers. Etymology and naming The name ''parakeet'' is derived from the French word ''perroquet'', which is reflected in some older spellings that are still sometimes encountered, including paroquet or paraquet. However, in modern French, ''perruche'' is used to refer to parakeets and similar-sized parrots. In American English, the word ''parakeet'' usually refers to the budgerigar, which is one species of parakeet. Summary Parakeets comprise about 115 species of birds that are seed-eating parrots of small size, slender build, and long, tapering tails. The Australian budgerigar, also known as "budgie", ''Melopsittacus undulatus'', is probably the most common parakeet. It was first described by zoologists in 1891. It is the most popular species of parakeet kept as a pet in North America and Europe. The term "grass parakeet" (or ''grasskeet'') ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilopsiagon
''Psilopsiagon'' is a genus of parrot in the family Psittacidae The Family (biology), family Psittacidae or holotropical parrots is one of three families of true parrots. It comprises the 12 species of subfamily Psittacinae (the Afrotropics, Afrotropical parrots) and 167 of subfamily Arinae (the New World or .... It contains the following species: References Psittacidae Bird genera Taxa named by Robert Ridgway Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{parrot-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least-concern Species
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. They do not qualify as threatened, near threatened, or (before 2001) conservation dependent. Species cannot be assigned the "Least Concern" category unless they have had their population status evaluated. That is, adequate information is needed to make a direct, or indirect, assessment of its risk of extinction based on its distribution or population status. Evaluation Since 2001 the category has had the abbreviation "LC", following the IUCN 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1). Before 2001 "least concern" was a subcategory of the " Lower Risk" category and assigned the code "LR/lc" or lc. Around 20% of least concern taxa (3261 of 15,636) in the IUCN database still use the code "LR/lc", which indicates they have not been re- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Conservation Of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through building partners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteraceae
Asteraceae () is a large family (biology), family of flowering plants that consists of over 32,000 known species in over 1,900 genera within the Order (biology), order Asterales. The number of species in Asteraceae is rivaled only by the Orchidaceae, and which is the larger family is unclear as the quantity of Extant taxon, extant species in each family is unknown. The Asteraceae were first described in the year 1740 and given the original name Composita, Compositae. The family is commonly known as the aster, Daisy (flower), daisy, composite, or sunflower family. Most species of Asteraceae are herbaceous plants, and may be Annual plant, annual, Biennial plant, biennial, or Perennial plant, perennial, but there are also shrubs, vines, and trees. The family has a widespread distribution, from subpolar to tropical regions, in a wide variety of habitats. Most occur in Hot desert climate, hot desert and cold or hot Semi-arid climate, semi-desert climates, and they are found on ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
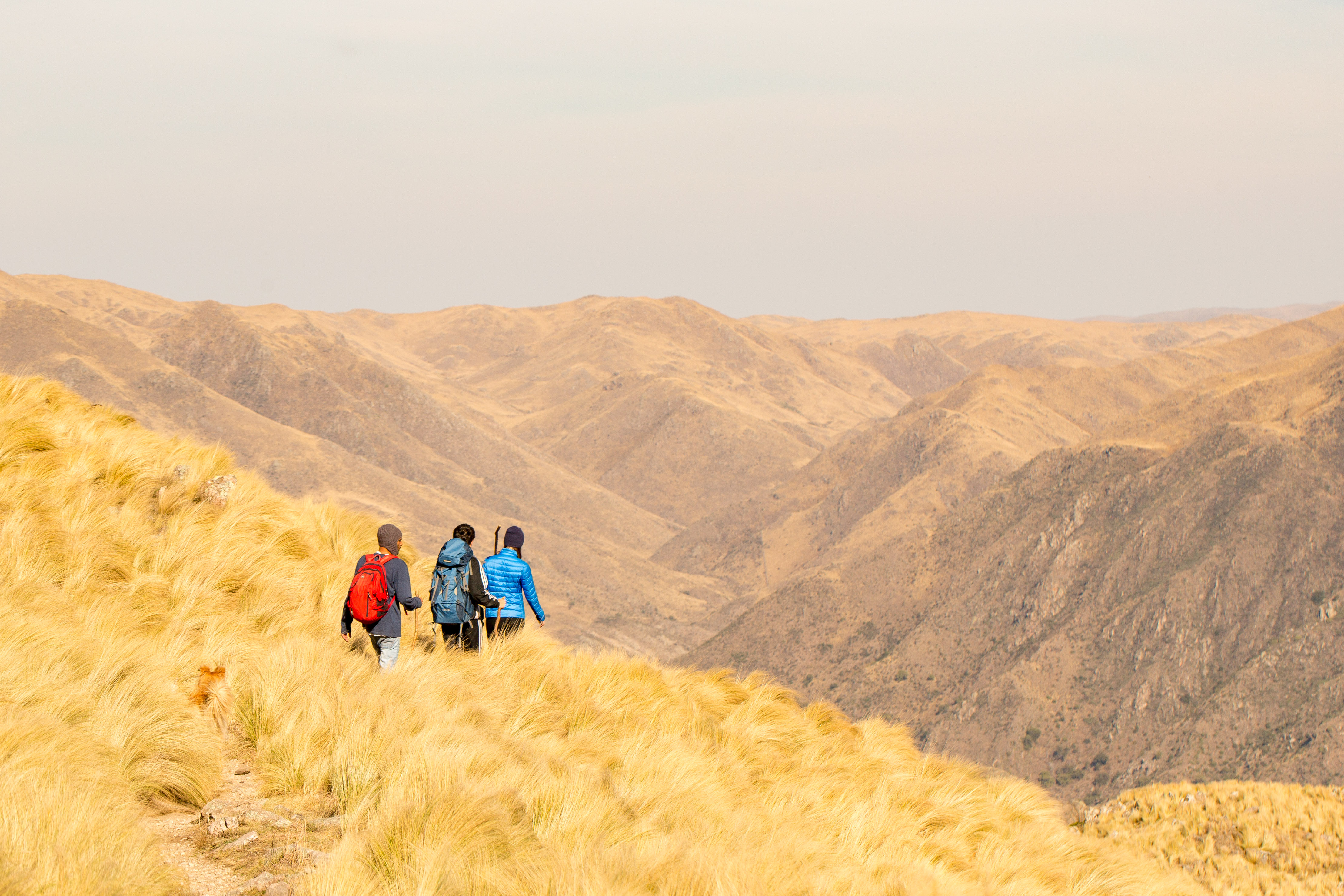
Southern Andean Yungas
The Southern Andean Yungas is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Yungas of southwestern Bolivia and northwestern Argentina. Geography The ecoregion occurs along the eastern slope of the Andes from southern Bolivia into northern Argentina, at elevations ranging from . In the lowlands to the east the Yungas transition to the semi-arid Gran Chaco, Dry Chaco. To the northwest they are bounded by the Bolivian montane dry forests, and by the high-elevation Central Andean puna and High Monte grasslands to the west. Climate This ecoregion has a subtropical highland climate. The climate is influenced by trade winds from the east that bring up to of rain per year. There is a dry season from April to October, and occasional snowfall at higher elevations during the winter months.Malizia, L.; Pacheco, S.; Blundo, C.; Brown, A.D. "Caracterización altitudinal, uso y conservación de las Yungas Subtropicales de Argentina". ''Ecosistemas'', vol. 21, núm. 1-2, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcide D'Orbigny
Alcide Charles Victor Marie Dessalines d'Orbigny (6 September 1802 – 30 June 1857) was a French naturalist who made major contributions in many areas, including zoology (including malacology), palaeontology, geology, archaeology and anthropology. D'Orbigny was born in Couëron (Loire-Atlantique), the son of a ship's physician and amateur naturalist. The family moved to La Rochelle in 1820, where his interest in natural history was developed while studying the marine fauna and especially the microscopic creatures that he named "foraminiferans". In Paris he became a disciple of the geologist Louis Cordier, Pierre Louis Antoine Cordier (1777–1861) and Georges Cuvier. All his life, he would follow the theory of Cuvier and stay opposed to Lamarckism. South American era D'Orbigny travelled on a mission for the Paris Museum, in South America between 1826 and 1833. He visited Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Argentina, Paraguay, and Brazil, and returned to Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominance (ecology), dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbaceous plant, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It may be the mature vegetation type in a particular region and remain stable over time, or it may be a transitional community that occurs temporarily as the result of a disturbance, such as fire. A stable state may be maintained by regular natural disturbance such as fire or browsing (predation), browsing. Shrubland may be unsuitable for human habitation because of the danger of fire. The term was coined in 1903. Shrubland species generally show a wide range of adaptations to fire, such as heavy seed production, lignotubers, and fire-induced germination. Botanical structural form In botany and ecology a shrub is defined as a much-branched woody plant less than 8 m high, usually with many plant stem, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as Biophysical environment, environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and Luminous intensity, light intensity. Biotic index, Biotic factors include the availability of food and the presence or absence of Predation, predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, habitat generalist species are able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species require a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |