|
Greater Spear-nosed Bat
The greater spear-nosed bat (''Phyllostomus hastatus'') is a bat species of the family Phyllostomidae from South and Central America. It is one of the larger bats of this region and is omnivorous. Habitat ''Phyllostomus hastatus'' lives in tropical regions of the Americas. The species ranges from Guatemala and Belize south to Peru, Bolivia, Paraguay, northern Argentina and Brazil. It also occurs in Trinidad and Tobago and on Margarita Island (Venezuela). Although most commonly found around streams and other bodies of water, these bats are also present in drier areas. They inhabit both open and forested regions. Appearance The greater spear-nosed bat has a body length of around , with a wing span of . Despite the large size, it is very light, weighing on average . Its long, thick hair is dark brown, with a slight orange tinge on the ventral side. It has a well-developed nose shaped like a spear-head, which gives it its more common name. The ears are spread far apart and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussia, Prussian zoologist, botanist, Ethnography, ethnographer, Exploration, explorer, Geography, geographer, Geology, geologist, Natural history, natural historian, and Taxonomy, taxonomist. He studied natural sciences at various universities in Germany in the early modern period, early modern Germany and worked primarily in the Russian Empire between 1767 and 1810. Life and work Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, Kingdom of Prussia, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University of Göttingen. In 1760, he moved to the University of Leiden and passed his doctor's degree at the age of 19. Pallas travelled throughout the Dutch Republic and to London, improving his medical and surgical knowledge. He then settled at The Hague, and his new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
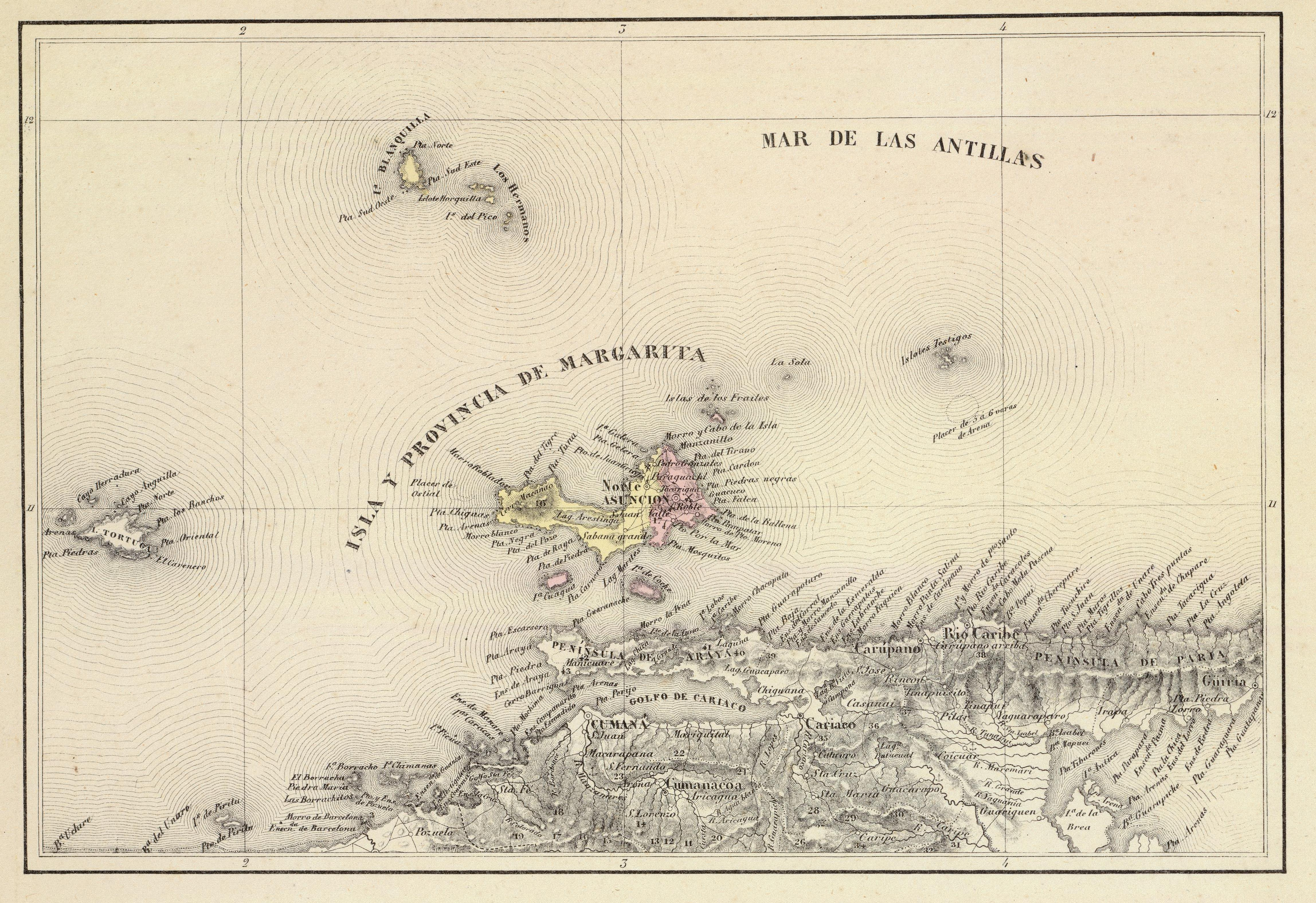
Isla Margarita
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the north west coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island. History Age of Exploration Christopher Columbus was the first European to arrive on Margarita Island in 1498. The local natives were the Guaiqueries people. The coast of the island was abundant in pearls, which represented almost a third of all New World tribute to the Spanish Crown. Margarita Island was fortified against the increasing threat of pirate attacks, and some fortifications remain today. It was the center of Spanish colonial Margarita Province, established in 1525. In 1561, the island was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador who killed the governor Juan Villadrando. Around 1675, the island was captured again, this time by Red Legs Greaves, a pirate known for his humanity and morality. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Colombia
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of Brazil
Bats are flying mammals of the order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox (''Acerodon jubatus'') reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiroptera, with megabats as members of the former a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of South America
Bats are flying mammals of the Order (biology), order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as Bat wing development, wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained Bat flight, flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the Smallest organisms, smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox (''Acerodon jubatus'') reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the Animal echolocation, echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of Central America
Bats are flying mammals of the order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox (''Acerodon jubatus'') reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiroptera, with megabats as members of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrous Cycle
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is a set of recurring physiological changes induced by reproductive hormones in females of mammalian subclass Theria. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phases, otherwise known as "rest" phases, or by pregnancies. Typically, estrous cycles repeat until death. These cycles are widely variable in duration and frequency depending on the species.Bronson, F. H., 1989. Mammalian Reproductive Biology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, USA. Some animals may display bloody vaginal discharge, often mistaken for menstruation. Many mammals used in commercial agriculture, such as cattle and sheep, may have their estrous cycles artificially controlled with hormonal medications for optimum productivity. The male equivalent, seen primarily in ruminants, is called rut. Differences from the menstrual cycle Mammals share the same reproductive system, including the regulatory hypothalamic system that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all female creatures is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called ''breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although in humans and goats, it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has teats; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only a handful of species of mammals, certain bat species, is milk production a normal Male lactation, male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs following sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a Live birth (human), live birth, a miscarriage, an Abortion#Induced, induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the Menstruation#Onset and frequency, last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the Gestational age (obstetrics), ''gestational age''; this is just over nine months. Counting by Human fertilization#Fertilization age, ''fertilization age'', the length is about 38 weeks. Implantation (embryology), Implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after Human fertilization, fertilization. An ''embryo'' is the term for the deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vismia
''Vismia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Hypericaceae. Members of the genus are small trees and shrubs found in tropical and subtropical areas of Central America and South America. Including the countries of Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panamá, Peru, Suriname, Trinidad-Tobago and Venezuela. Like many members of the Hypericaceae, these plants contain xanthonoids. The genus name of ''Vismia'' is in honour of Gérard de Visme (c. 1725 – c. 1797), a French and English merchant in Lisbon, Portugal. It was first described and published in Fl. Lusit. Bras. Spec. on page 51 in 1788. Known species Plants of the World Online Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online taxonomic database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. History Following the Convention on Biological Diversity, the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew launched Plants of the World Online ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solanum
''Solanum'' is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, which include three food crops of high economic importance: the potato, the tomato and the eggplant (aubergine, brinjal). It is the largest genus in the nightshade family Solanaceae, comprising around 1,500 species. It also contains the so-called horse nettles (unrelated to the genus of true nettles, ''Urtica''), as well as numerous plants cultivated for their ornamental flowers and fruit. ''Solanum'' species show a wide range of growth habits, such as annuals and perennials, vines, subshrubs, shrubs, and small trees. Many formerly independent genera like '' Lycopersicon'' (the tomatoes) and '' Cyphomandra'' are now included in ''Solanum'' as subgenera or sections. Thus, the genus today contains roughly 1,500–2,000 species. Name The generic name was first used by Pliny the Elder (AD 23–79) for a plant also known as , most likely ''S. nigrum''. Its derivation is uncertain, possibly stemming from the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piper (plant)
''Piper'', the pepper plants or pepper vines, is an economically and ecologically important genus in the family Piperaceae. It contains about 1,000–2,000 species of shrubs, herbs, and lianas, many of which are dominant species in their native habitat. The diversification of this taxon is of interest to understanding the evolution of plants. Pepper plants belong to the magnoliids, which are angiosperms but neither monocots nor eudicots. Their family, Piperaceae, is most closely related to the lizardtail family ( Saururaceae), which in fact generally look like smaller, more delicate and amphibious pepper plants. Both families have characteristic tail-shaped inflorescences covered in tiny flowers. A somewhat less close relative is the pipevine family ( Aristolochiaceae). A well-known and very close relative – being also part of the Piperaceae – are the radiator plants of the genus '' Peperomia''. The scientific name ''Piper'' and the common name "pepper" are derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |