|
Greater Sciatic Foramen
The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (:wikt:foramen, foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament, sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies most of its volume. The greater sciatic foramen is wider in women than in men. Structure It is bounded as follows: * anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the Ilium (bone), ilium. * posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament. * inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine. * superiorly by the anterior sacroiliac ligament. Function The piriformis, which exits the pelvis through the foramen, occupies most of its volume. The following structures also exit the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen: See also *Lesser sciatic foramen References External links * * (, ) {{Authority control Anatomy Bones of the pelvis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
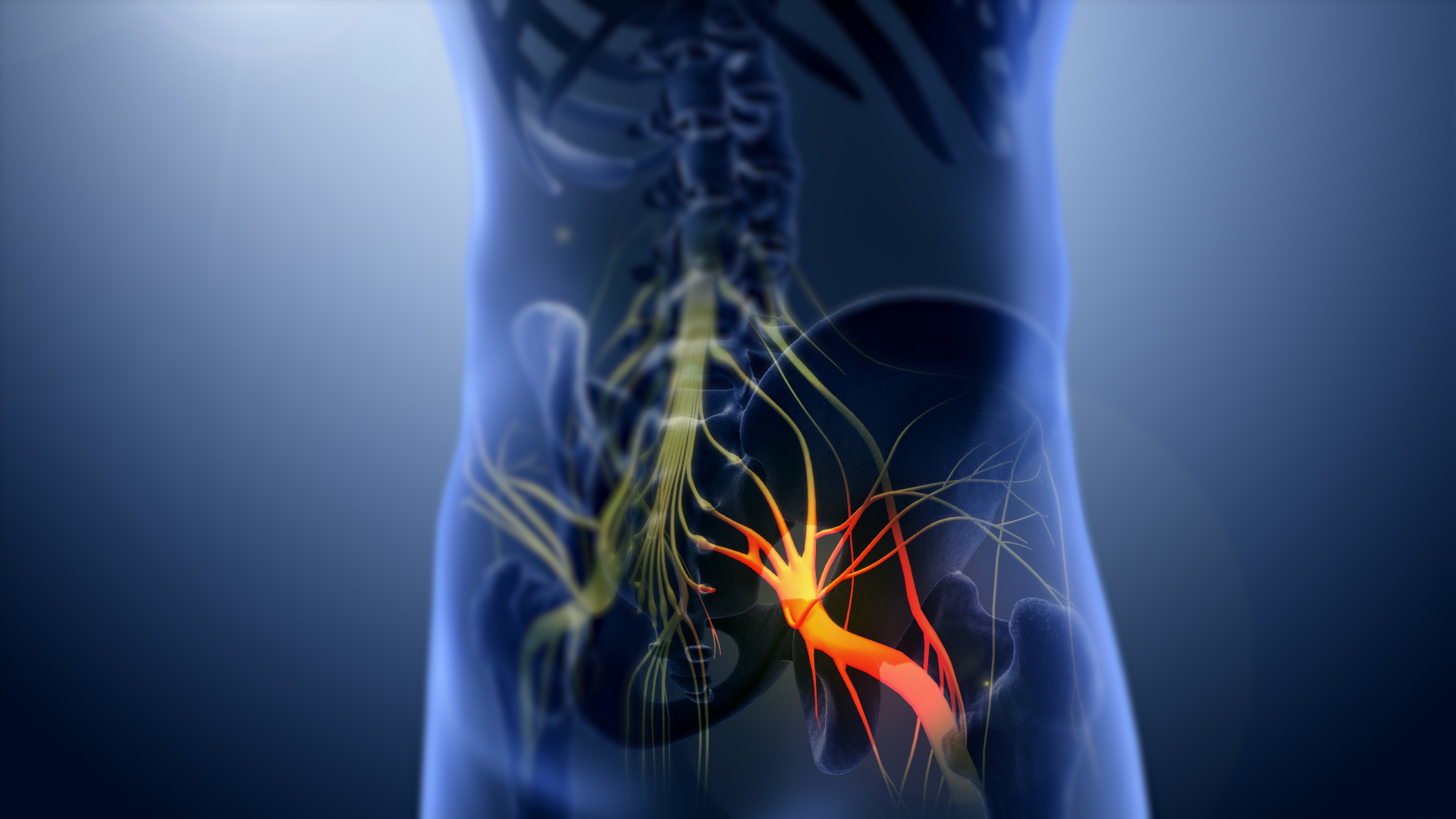
Inferior Gluteal Vessels
The inferior gluteal artery (sciatic artery) is a terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It is distributed chiefly to the buttock and the back of the thigh. Anatomy Origin It is the smaller of the two terminal branches of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. Course It passes posterior-ward within parietal pelvic fascia. It travels in between the S1 nerve and S2 (or S2-S3) nerve(s). It descends upon the nerves of the sacral plexus and the piriformis muscle, posterior to the internal pudendal artery. It passes through the inferior part of the greater sciatic foramen. It exits the pelvis inferior to the piriformis muscle, between piriformis muscle and coccygeus muscle. It then descends in the interval between the greater trochanter of the femur and tuberosity of the ischium. It is accompanied by the sciatic nerve and the posterior femoral cutaneous nerves, and covered by the glut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Sciatic Foramen
The lesser sciatic foramen is an opening (foramen) between the pelvis and the back of the thigh. The foramen is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial tuberosity and the sacrospinous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial spine. Structure The lesser sciatic foramen has the following boundaries: * Anterior: the tuberosity of the ischium * Superior: the spine of the ischium and sacrospinous ligament * Posterior: the sacrotuberous ligament Alternatively, the foramen can be defined by the boundaries of the lesser sciatic notch and the two ligaments. Function The following pass through the foramen: * the tendon of the obturator internus * internal pudendal vessels * pudendal nerve * nerve to the obturator internus See also *Greater sciatic foramen The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (:wikt:foramen, foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament, sacrotuberous and sacrospino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve To Quadratus Femoris
The nerve to quadratus femoris is a nerve of the sacral plexus that provides motor innervation to the quadratus femoris muscle and gemellus inferior muscle, and an articular branch to the hip joint. The nerve leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. Structure Origin The nerve to quadratus femoris is a branch of the sacral plexus. It arises from the anterior divisions of the spinal nerves L4- S1. Course It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle. It passes inferior-ward upon the ischium deep to the sciatic nerve, the superior and inferior gemellus muscles, and the tendon of the obturator internus. It traverses the posterior aspect of the hip joint, here issuing an articular (sensory) branch to the joint. It proceeds inferior-ward deep to the superior and inferior gemelli muscles and the obturator internus muscle. It enters the anterior surfaces of quadratus femoris muscle and gemellus inferior muscle. Varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve To Obturator Internus
The nerve to obturator internus (also known as the obturator internus nerve) is a mixed (sensory and motor) nerve providing motor innervation to the obturator internus muscle and gemellus superior muscle, and sensory innervation to the hip joint. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It is one of the group of deep gluteal nerves. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen to innervate the gemellus superior muscle, then re-enters the pelvis to innervate the obturator internus muscle. Structure Origin The nerve to obturator internus is a branch of the lumbosacral plexus. It arises from the anterior divisions of (the anterior rami of) L5- S2. Course and relations It emerges inferior to the piriformis muscle and exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It travels round the base of the ischial spine lateral to the internal pudendal artery and nerve, and - while doing so - issues a branch to the gemellus superior, which enters the upper part of the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (also called the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve) is a sensory nerve of the thigh. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum. Unlike most nerves termed "cutaneous" which are subcutaneous, only the terminal branches of this nerve pass into subcutaneous tissue before being distributed to the skin, with most of the nerve itself situated deep to the deep fascia. Structure Origin The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a branch of the sacral plexus. It arises from the posterior divisions of the S1- S2, and the anterior divisions of S2- S3 sacral spinal nerves. Course It leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle. It then descends deep to the gluteus maximus muscle, medial or posterior to the sciatic nerve, and alongside the inferior gluteal artery. It descends within the posterior thigh deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciatic Nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from Spinal nerve, spinal nerves Lumbar spinal nerve 4, L4 to Sacral spinal nerve 3, S3. It contains Axon, fibres from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus. Structure In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the Sacrum, sacral part of the spinal cord. The lumbosacral trunk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a Mixed nerve, mixed (motor and sensory) nerve and also conveys Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic Autonomic nervous system, autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the Human anus, anus and perineum, as well as the Motor neuron, motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the external sphincter muscle of male urethra, male or external sphincter muscle of female urethra, female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, loss of sensation or fecal incontinence may result. The nerve may be temporarily anesthetized, called pudendal anesthesia or pudendal block. The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Structure Origin The pudendal nerve is paired, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Gluteal Nerve
The inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this nerve is rare but often occurs as a complication of posterior approach to the hip during hip replacement. When damaged, one would develop gluteus maximus lurch, which is a gait abnormality which causes the individual to 'lurch' backwards to compensate lack in hip extension. Anatomy The largest muscle of the posterior hip, gluteus maximus, is innervated by the inferior gluteal nerve.Skalak, A. F., et al. "Relationship of Inferior Gluteal Nerves and Vessels: Target for Application of Stimulation Devices for the Prevention of Pressure Ulcers in Spinal Cord Injury." Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy 30.1 (2008): 41-45. Print. It branches out and then enters the deep surface of the gluteus maximus, the principal extensor of the thigh, and suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Pudendal Vessels
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia. Structure The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It is smaller in the female than in the male. Path It arises from the anterior division of internal iliac artery. It runs on the lateral pelvic wall. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the gluteal region. It then curves around the sacrospinous ligament to enter the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen. It travels through the pudendal canal with the internal pudendal veins and the pudendal nerve. Branches The internal pudendal artery gives off the following branches: The deep artery of clitoris is a branch of the internal pudendal artery and supplies the clitoral crura. Another branch of the internal pudendal artery is the do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Gluteal Nerve
The superior gluteal nerve is a mixed (motor and sensory) nerve of the sacral plexus that originates in the pelvis. It provides motor innervation to the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fasciae latae; it also has a cutaneous branch. Structure Origin The superior gluteal nerve originates in the sacral plexus. It arises from the posterior divisions of L4, L5 and S1. Course It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen superior to the piriformis muscle. It is accompanied by the superior gluteal artery and the superior gluteal vein.''Thieme Atlas of Anatomy'' (2006), p 476 It passes lateral-ward in between the gluteus medius muscle and the gluteus minimus muscle, accompanied by the deep branch of the superior gluteal artery. It divides into a superior branch and an inferior branch. The inferior branch continues to pass between the two muscles to end in the tensor fasciae latae muscle. Distribution Motor * tensor fasciae latae musclePlatzer (2004) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |