|
Graph Edit Distance
In mathematics and computer science, graph edit distance (GED) is a measure of similarity (or dissimilarity) between two graphs. The concept of graph edit distance was first formalized mathematically by Alberto Sanfeliu and King-Sun Fu in 1983. A major application of graph edit distance is in inexact graph matching, such as error-tolerant pattern recognition in machine learning. The graph edit distance between two graphs is related to the string edit distance between strings. With the interpretation of strings as connected, directed acyclic graphs of maximum degree one, classical definitions of edit distance such as Levenshtein distance, Hamming distance and Jaro–Winkler distance may be interpreted as graph edit distances between suitably constrained graphs. Likewise, graph edit distance is also a generalization of tree edit distance between rooted trees. Formal definitions and properties The mathematical definition of graph edit distance is dependent upon the defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bell System Technical Journal
The ''Bell Labs Technical Journal'' was the in-house scientific journal for scientists of Bell Labs, published yearly by the IEEE society. The journal was originally established as ''The Bell System Technical Journal'' (BSTJ) in New York by the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1922. It was published under this name until 1983, when the breakup of the Bell System placed various parts of the companies in the system into independent corporate entities. The journal was devoted to the scientific fields and engineering disciplines practiced in the Bell System for improvements in the wide field of electrical communication. After the restructuring of Bell Labs in 1984, the journal was renamed to ''AT&T Bell Laboratories Technical Journal''. In 1985, it was published as the ''AT&T Technical Journal'' until 1996, when it was renamed to ''Bell Labs Technical Journal''. The journal was discontinued in 2020. The last managing editor was Charles Bahr. History The Bell System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lecture Notes In Computer Science
''Lecture Notes in Computer Science'' is a series of computer science books published by Springer Science+Business Media since 1973. Overview The series contains proceedings, post-proceedings, monographs, and Festschrifts. In addition, tutorials, state-of-the-art surveys, and "hot topics" are increasingly being included. The series is indexed by DBLP. See also *'' Monographiae Biologicae'', another monograph series published by Springer Science+Business Media *'' Lecture Notes in Physics'' *'' Lecture Notes in Mathematics'' *'' Electronic Workshops in Computing'', published by the British Computer Society image:Maurice Vincent Wilkes 1980 (3).jpg, Sir Maurice Wilkes served as the first President of BCS in 1957. The British Computer Society (BCS), branded BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, since 2009, is a professional body and a learned ... References External links * Academic journals established in 1973 Computer science books Series of non-fiction books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
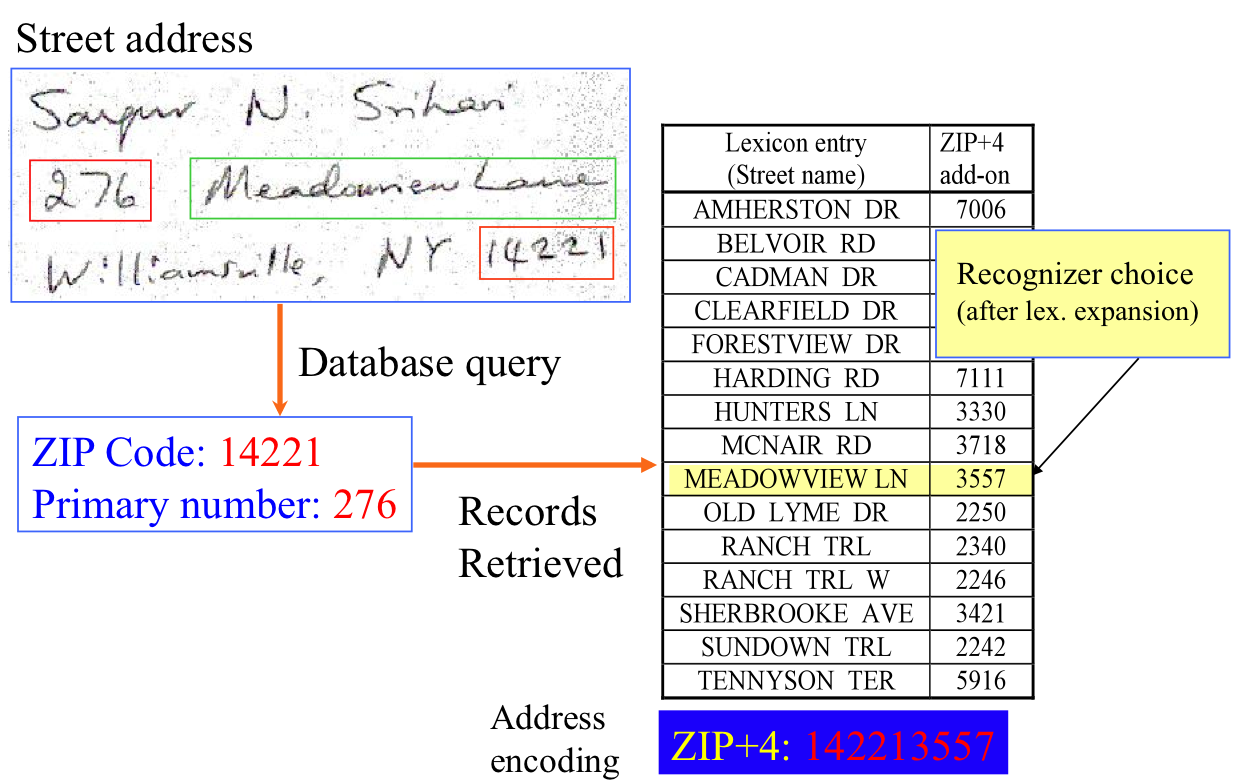
Handwriting Recognition
Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwriting, handwritten input from sources such as paper documents, photographs, touch-screens and other devices. The image of the written text may be sensed "off line" from a piece of paper by optical scanning (optical character recognition) or intelligent word recognition. Alternatively, the movements of the pen tip may be sensed "on line", for example by a pen-based computer screen surface, a generally easier task as there are more clues available. A handwriting recognition system handles formatting, performs correct Segment (handwriting), segmentation into characters, and finds the most possible words. Offline recognition Offline handwriting recognition involves the automatic conversion of text in an image into letter codes that are usable within computer and text-processing applications. The data obtained by this form is reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edge Contraction
In graph theory, an edge contraction is an operation that removes an edge from a graph while simultaneously merging the two vertices that it previously joined. Edge contraction is a fundamental operation in the theory of graph minors. Vertex identification is a less restrictive form of this operation. Definition The edge contraction operation occurs relative to a particular edge, e. The edge e is removed and its two incident vertices, u and v, are merged into a new vertex w, where the edges incident to w each correspond to an edge incident to either u or v. More generally, the operation may be performed on a set of edges by contracting each edge (in any order). The resulting graph is sometimes written as G/e. (Contrast this with G \setminus e, which means simply removing the edge e without merging its incident vertices.) As defined below, an edge contraction operation may result in a graph with multiple edges even if the original graph was a simple graph. However, some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Graph Isomorphism
In graph theory, an isomorphism of graphs ''G'' and ''H'' is a bijection between the vertex sets of ''G'' and ''H'' : f \colon V(G) \to V(H) such that any two vertices ''u'' and ''v'' of ''G'' are adjacent in ''G'' if and only if f(u) and f(v) are adjacent in ''H''. This kind of bijection is commonly described as "edge-preserving bijection", in accordance with the general notion of isomorphism being a structure-preserving bijection. If an isomorphism exists between two graphs, then the graphs are called isomorphic, often denoted by G\simeq H. In the case when the isomorphism is a mapping of a graph onto itself, i.e., when ''G'' and ''H'' are one and the same graph, the isomorphism is called an automorphism of ''G''. Graph isomorphism is an equivalence relation on graphs and as such it partitions the class of all graphs into equivalence classes. A set of graphs isomorphic to each other is called an isomorphism class of graphs. The question of whether graph isomorphism can be dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Graph Operations
In the mathematical field of graph theory, graph operations are operations which produce new graphs from initial ones. They include both unary (one input) and binary (two input) operations. Unary operations Unary operations create a new graph from a single initial graph. Elementary operations Elementary operations or editing operations, which are also known as graph edit operations, create a new graph from one initial one by a simple local change, such as addition or deletion of a vertex or of an edge, merging and splitting of vertices, edge contraction, etc. The graph edit distance between a pair of graphs is the minimum number of elementary operations required to transform one graph into the other. Advanced operations Advanced operations create a new graph from an initial one by a complex change, such as: * transpose graph; * complement graph; * line graph; * graph minor; * graph rewriting; * power of graph; * dual graph; * medial graph; * quotient graph; * Y- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Graph Labeling
In the mathematical discipline of graph theory, a graph labeling is the assignment of labels, traditionally represented by integers, to edges and/or vertices of a graph. Formally, given a graph , a vertex labeling is a function of to a set of labels; a graph with such a function defined is called a vertex-labeled graph. Likewise, an edge labeling is a function of to a set of labels. In this case, the graph is called an edge-labeled graph. When the edge labels are members of an ordered set (e.g., the real numbers), it may be called a weighted graph. When used without qualification, the term labeled graph generally refers to a vertex-labeled graph with all labels distinct. Such a graph may equivalently be labeled by the consecutive integers , where is the number of vertices in the graph. For many applications, the edges or vertices are given labels that are meaningful in the associated domain. For example, the edges may be assigned weights representing the "cost" of trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ACM Transactions On Algorithms
''ACM Transactions on Algorithms'' (''TALG'') is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of algorithms. It was established in 2005 and is published by the Association for Computing Machinery. The editor-in-chief is Edith Cohen. The journal was created when the editorial board of the ''Journal of Algorithms'' resigned out of protest to the pricing policies of the publisher, Elsevier. Apart from regular submissions, the journal also invites selected papers from the ''ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA)''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Science Citation Index Expanded, Current Contents/Engineering, Computing & Technology, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algorithmica
''Algorithmica'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal focusing on research and the application of computer science algorithms. The journal was established in 1986 and is published by Springer Science+Business Media. The editor in chief is Mohammad Hajiaghayi. Subject coverage includes sorting, searching, data structures, computational geometry, and linear programming, VLSI, distributed computing, parallel processing, computer aided design, robotics, graphics, data base design, and software tool A programming tool or software development tool is a computer program that is used to software development, develop another computer program, usually by helping the developer manage computer files. For example, a programmer may use a tool called ...s. Springer Science+Business Media. 2013 Abstract ...
|