|
Grammatico-historical
The historical-grammatical method is a modern Christian hermeneutical method that strives to discover the biblical authors' original intended meaning in the text. According to the historical-grammatical method, if based on an analysis of the grammatical style of a passage (with consideration to its cultural, historical, and literary context), it appears that the author intended to convey an account of events that actually happened, then the text should be taken as representing history; passages should only be interpreted symbolically, poetically, or allegorically if to the best of our understanding, that is what the writer intended to convey to the original audience. It is the primary method of interpretation for many conservative Protestant exegetes who reject the historical-critical method to various degrees (from complete rejection by some fundamentalist Protestants, to moderated acceptance by the Roman Catholic tradition since the '' Divino afflante Spiritu'' encyclical lett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann August Ernesti
Johann August Ernesti (; ; 4 August 1707 – 11 September 1781) was a German Rationalist Lutheran theologian and philology, philologist. Ernesti was the first who formally separated the hermeneutics of the Old Testament from those of the New Testament, New. Biography Ernesti was born in Bad Tennstedt, Tennstedt, Electorate of Saxony, Saxony (in present-day Thuringia), where his father, Johann Christoph Ernesti, was pastor, besides being superintendent of the electoral dioceses of Thuringia, Salz and Sangerhausen. At the age of sixteen, Ernesti was sent to the celebrated Saxon cloister school of Pforta (''Schulpforta''). At twenty he entered the University of Wittenberg, and studied afterwards at the University of Leipzig. In 1730 he was made master in the faculty of philosophy. In the following year he accepted the office of conrector in the Thomasschule zu Leipzig, Thomas school of Leipzig, of which Johann Matthias Gesner was then rector, an office to which Ernesti succeeded in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Hermeneutics
Biblical hermeneutics is the study of the principles of interpretation concerning the books of the Bible. It is part of the broader field of hermeneutics, which involves the study of principles of interpretation, both theory and methodology, for all nonverbal and verbal communication forms. While Jewish and Christian biblical hermeneutics have some overlap and dialogue, they have distinctly separate interpretative traditions. Jewish Traditional Talmudical hermeneutics (Hebrew: approximately, מידות שהתורה נדרשת בהן) refers to Jewish methods for the investigation and determination of the meaning of the Hebrew Bible, as well as rules by which Jewish law could be established. One well-known summary of these principles appears in the Baraita of Rabbi Ishmael. Methods by which the Talmud explores the meaning of scripture: :* grammar and exegesis :* the interpretation of certain words and letters and apparently superfluous or missing words or letters, and pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Delitzsch
Franz Delitzsch (23 February 1813, in Leipzig – 4 March 1890, in Leipzig) was a German Lutheran theologian and Hebraist. Delitzsch wrote many commentaries on books of the Bible, Jewish antiquities, Biblical psychology, as well as a history of Jewish poetry, and works of Christian apologetics. Today, Delitzsch is best known for his translation of the New Testament into Hebrew (1877), and his series of commentaries on the Old Testament published with Johann Friedrich Karl Keil, Carl Friedrich Keil. Delitzsch's son, Friedrich Delitzsch (1850–1922), was an influential Assyriology, Assyriologist and author of works on Assyrian language, literature, and history. Biography Although Delitzsch was Christian, he was often supposed to be of Jewish ancestry, due to the unusual breadth of his rabbinical learning, as well as his strong sympathy with the Jewish people, whom he defended against attacks. His family circumstances were also unusual, in that he had a Jewish benefactor who lived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confessional Hermeneutics
A confessional is a box, cabinet, booth, or stall where the priest from some Christian denominations sits to hear the confessions of a penitent's sins. It is the traditional venue for the sacrament in the Roman Catholic Church and the Lutheran Churches, but similar structures are also used in Anglican churches of an Anglo-Catholic orientation. In the Catholic Church, confessions should occur only in a confessional or oratory, except under special circumstances or just reason. The confessional is usually a wooden structure, with a centre compartment—entered through a door or curtain—where the priest sits, and on each side there is a latticed opening for the penitents to speak through and a step on which they kneel. By this arrangement the priest is hidden, but the penitent is visible to the public. Confessionals sometimes form part of the architectural scheme of the church; many finely decorated specimens, dating from the late 16th and the 17th centuries, are found in churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canonical Criticism
Canonical criticism, sometimes called canon criticism or the canonical approach, is a way of interpreting the Bible that focuses on the text of the biblical canon itself as a finished product. Brevard Childs (1923–2007) popularised this approach, though he personally rejected the term. Whereas other types of biblical criticism focus on the origins, structure and history of texts, canonical criticism looks at the meaning which the overall text, in its final form, has for the community which uses it. Description Canonical criticism involves "paying attention to the present form of the text in determining its meaning for the believing community." According to opponent James Barr, it involves concentrating authority "in the canonical text, and not in the people or events out of which that text came." Childs says that the canon "not only serves to establish the outer boundaries of authoritative Scripture," but "forms a prism through which light from the different aspects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aesthetics Of Reception
Aesthetics (also spelled esthetics) is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of beauty and taste, which in a broad sense incorporates the philosophy of art.Slater, B. H.Aesthetics ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy,'' , accessed on 15 September 2024. Aesthetics examines values about, and critical judgments of, artistic taste and preference. It thus studies how artists imagine, create, and perform works of art, as well as how people use, enjoy, and criticize art. Aesthetics considers why people consider certain things beautiful and not others, as well as how objects of beauty and art can affect our moods and our beliefs. Aesthetics tries to find answers to what exactly is art and what makes good art. It considers what happens in our minds when we view visual art, listen to music, read poetry, enjoy delicious food, and engage in large artistic projects like creating and experiencing plays, fashion shows, films, and television programs. It can also focus on how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reader-response
Reader-response criticism is a school of literary theory that focuses on the reader (or "audience") and their experience of a literary work, in contrast to other schools and theories that focus attention primarily on the author, content, or form of the work. Development Although literary theory has long paid some attention to the reader's role in creating the meaning and experience of a literary work, modern reader-response criticism began in the 1960s and '70s, particularly in the US and Germany. This movement shifted the focus from the text to the reader and argues that affective response is a legitimate point for departure in criticism. Its conceptualization of critical practice is distinguished from theories that favor textual autonomy (for example, Formalism and New Criticism) as well as recent critical movements (for example, structuralism, semiotics, and deconstruction) due to its focus on the reader's interpretive activities. Classic reader-response critics include Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karaite Judaism
Karaite Judaism or Karaism is a Rabbinic Judaism, non-Rabbinical Jewish religious movements, Jewish sect characterized by the recognition of the written Tanakh alone as its supreme religious text, authority in ''halakha'' (religious law) and theology. Karaites believe that all of the Mitzvah, divine commandments which were handed down to Moses by God were recorded in the written Torah without any additional Oral Torah, Oral Law or explanation. Unlike mainstream Rabbinic Judaism, which regards the Oral Torah, codified in the Talmud and subsequent works, as authoritative interpretations of the Torah, Karaite Jews do not treat the written collections of the oral tradition in the Midrash or the Talmud as binding. Karaite interpretation of the Torah strives to adhere to the plain or most obvious meaning (''peshat'') of the text; this is not necessarily the literal meaning of the text—instead, it is the meaning of the text that would have been naturally understood by the ancient He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exegesis
Exegesis ( ; from the Ancient Greek, Greek , from , "to lead out") is a critical explanation or interpretation (philosophy), interpretation of a text. The term is traditionally applied to the interpretation of Bible, Biblical works. In modern usage, exegesis can involve critical interpretations of virtually any text, including not just religious texts but also philosophy, literature, or virtually any other genre of writing. The phrase ''Biblical exegesis'' can be used to distinguish studies of the Bible from other critical textual explanations. Textual criticism investigates the history and origins of the text, but exegesis may include the study of the historical and cultural backgrounds of the author, text, and original audience. Other analyses include classification of the type of literary genres presented in the text and analysis of grammar, grammatical and syntax, syntactical features in the text itself. Usage One who practices exegesis is called an ''exegete'' (; from Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermeneutics
Hermeneutics () is the theory and methodology of interpretation, especially the interpretation of biblical texts, wisdom literature, and philosophical texts. As necessary, hermeneutics may include the art of understanding and communication. Modern hermeneutics includes both verbal and non-verbal communication,''The Routledge Companion to Philosophy in Organization Studies'', Routledge, 2015p. 113Joann McNamara, ''From Dance to Text and Back to Dance: A Hermeneutics of Dance Interpretive Discourse'', PhD thesis, Texas Woman's University, 1994. as well as semiotics, presuppositions, and pre-understandings. Hermeneutics has been broadly applied in the humanities, especially in law, history and theology. Hermeneutics was initially applied to the interpretation, or exegesis, of scripture, and has been later broadened to questions of general interpretation. p. 2 The terms ''hermeneutics'' and ''exegesis'' are sometimes used interchangeably. Hermeneutics is a wider discipline wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milton S
Milton may refer to: Names * Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname) ** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet * Milton (given name) Places Australia * Milton, New South Wales * Milton, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane ** Milton Courts, a tennis centre ** Milton House, Milton, a heritage-listed house ** Milton railway station, Brisbane ** Milton Reach, a reach of the Brisbane River ** Milton Road, an arterial road in Brisbane Canada * Milton, Newfoundland and Labrador * Milton, Nova Scotia in the Region of Queens Municipality * Milton, Ontario ** Milton line, a commuter train line ** Milton GO Station * Milton (federal electoral district), Ontario ** Milton (provincial electoral district), Ontario * Beaverton, Ontario a community in Durham Region and renamed as Beaverton in 1835 * Rural Municipality of Milton No. 292, Saskatchewan New Zealand * Milton, New Zealand United Kingdom England * Milton, Cambridgeshire, a village north of Cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
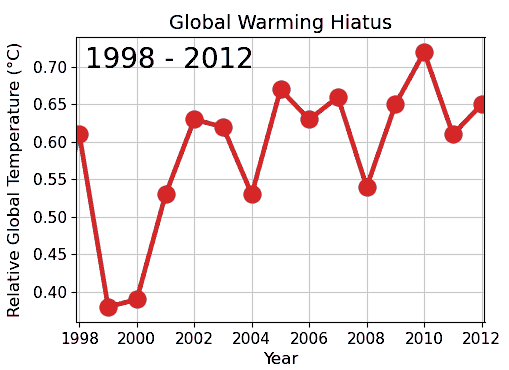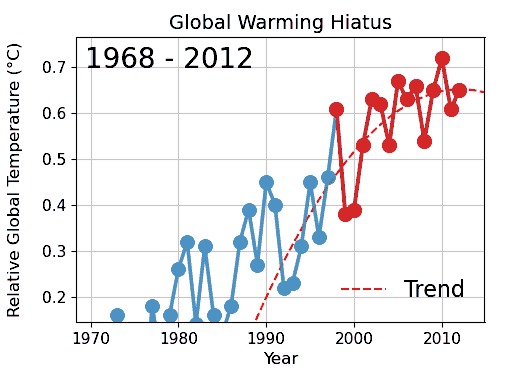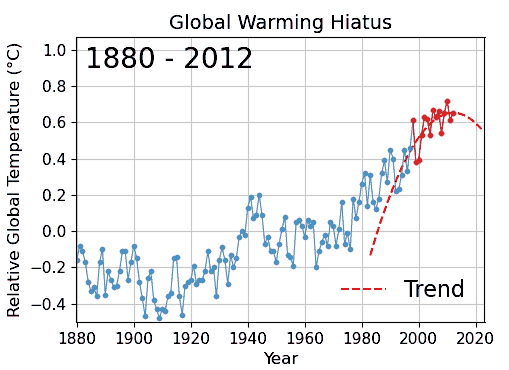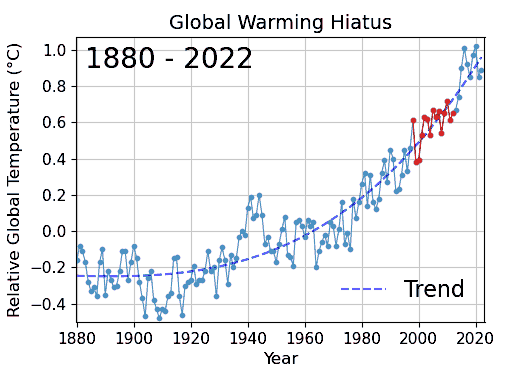
Cherry Picking
Cherry picking, suppressing evidence, or the fallacy of incomplete evidence is the act of pointing to individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position while ignoring a significant portion of related and similar cases or data that may contradict that position. Cherry picking may be committed intentionally or unintentionally. The term is based on the perceived process of harvesting fruit, such as cherries. The picker would be expected to select only the ripest and healthiest fruits. An observer who sees only the selected fruit may thus wrongly conclude that most, or even all, of the tree's fruit is in a likewise good condition. This can also give a false impression of the quality of the fruit (since it is only a sample and is not a representative sample). A concept sometimes confused with cherry picking is the idea of gathering only the fruit that is easy to harvest, while ignoring other fruit that is higher up on the tree and thus more difficult to obtain (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |