|
Geology Of The Bryce Canyon Area
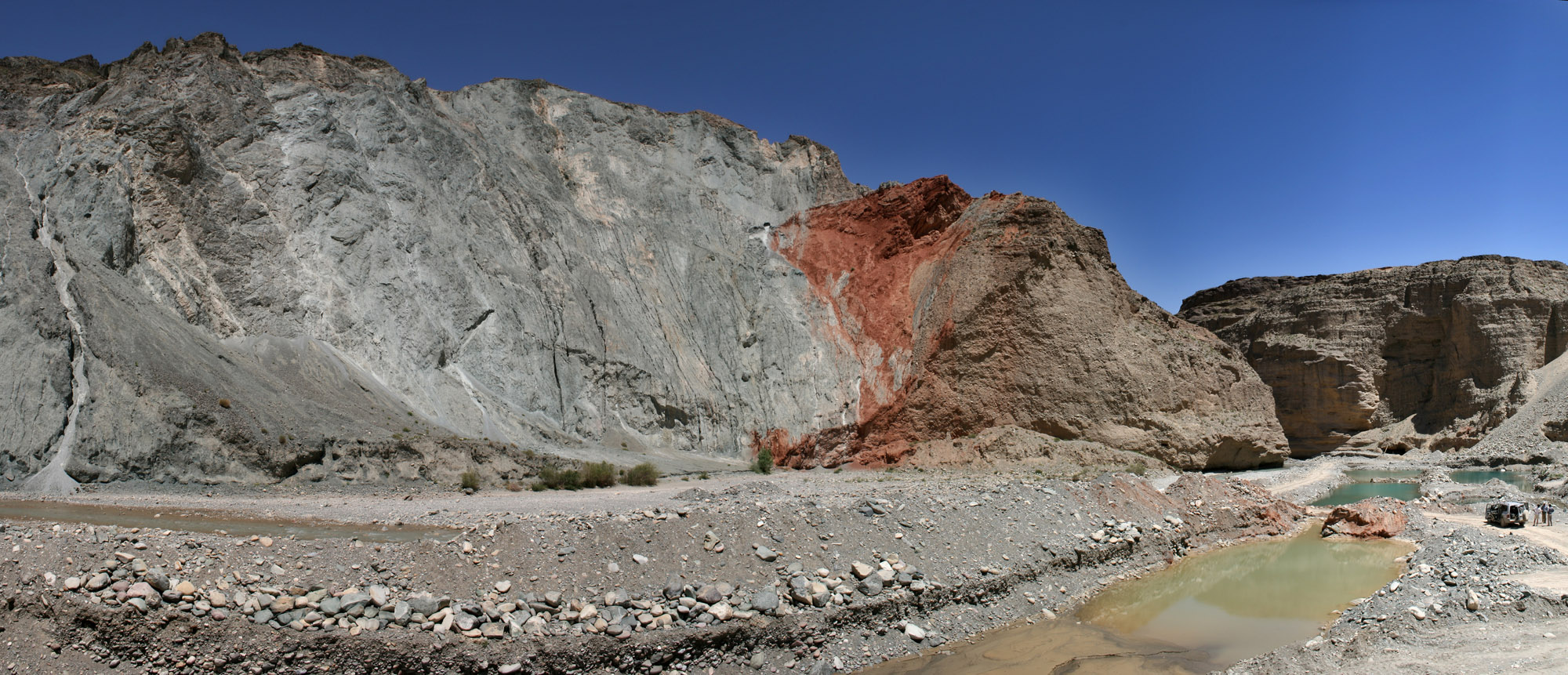
The exposed geology of the Bryce Canyon area in Utah shows a record of deposition that covers the last part of the Cretaceous Period and the first half of the Cenozoic era in that part of North America. The ancient depositional environment of the region around what is now Bryce Canyon National Park varied from the warm shallow sea (called the Cretaceous Seaway) in which the Dakota Sandstone and the Tropic Shale were deposited to the cool streams and lakes that contributed sediment to the colorful Claron Formation that dominates the park's amphitheaters. Other formations were also formed but were mostly eroded following uplift from the Laramide orogeny which started around 70 million years ago ( Mya). This event raised the Rocky Mountains far to the east and caused the retreat of the sea that covered the Bryce Canyon area. After Laramide mountain building came to an end, about 15 mya, a large part of western North America began to be stretched into the nearby Basin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paria View At Bryce Canyon NP
Paria may refer to the following : Places and jurisdictions Old World * Paria, Gujarat, village in Vapi, Valsad, Gujarat, India * Paria in Proconsulari, an Ancient city and former bishopric, now a Latin titular see in Tunisia * Paria, of, from, or related to Paros, a Greek island in the central Aegean Sea Americas * Paria (Peru), a mountain in the Andes * Paria, Bolivia, founded in 1535, the first Spanish settlement in Bolivia. * Paria, Utah, or ''Pahreah'', a ghost town on the Paria River in Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument in Utah, United States * Paria, a Spanish colonial province of Venezuela, constituting the eastern portion of the country * Paria Point, a mountain in Zion National Park, Utah * Paria River, tributary of the Colorado River, United States * Paria Peninsula, peninsula in Sucre, Venezuela * Gulf of Paria, gulf on the South of Paria Peninsula, the Orinoco River delta in Venezuela and on west coast of Trinidad * The name given to North Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
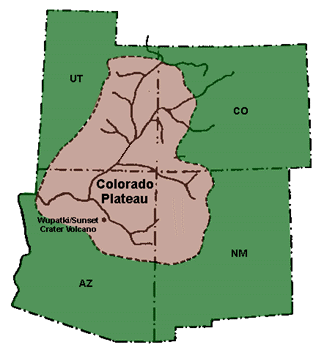
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. This plateau covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau, nicknamed High Country, lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored rock left bare to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular '' klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is called a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thrust fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain. The general definition used is one followed by the United States Geological Survey and the Geological Survey of Canada to describe the respective countries' Physiographic region, physiographic regions. The U.S. uses the term Appalachian Highlands and Canada uses the term Appalachian Uplands; the Appalachian Mountains are not synonymous with the Appalachian Plateau, which is one of the provinces of the Appalachian Highlands. The Appalachian range runs from the Newfoundland (island), Island of Newfoundland in Canada, southwestward to Central Alabama in the United States; south of Newfoundland, it crosses the 96-square-mile (248.6 km2) archipelago of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, an overseas collectivity of France, meaning it is technica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing world ocean. The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and North America, and the borders follow topographic features: the Bering Strait on the Pacific side and the Greenland Scotland Ridge on the Atlantic side. It is mostly covered by sea ice throughout the year and almost completely in winter. The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature and salinity vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes; its salinity is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatán, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The coastal areas along the Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are occasionally referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific coasts), but more often as "the Gulf Coast". The Gulf of Mexico took shape about 300 million years ago (mya) as a result of plate tectonics. The Gulf of Mexico basin is roughly oval and is about wide. Its floor consists of sedimentary rocks and recent sediments. It is connected to part of the Atlantic Ocean through the Straits of Florida between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zion National Park
Zion National Park is a national park of the United States located in southwestern Utah near the town of Springdale. Located at the junction of the Colorado Plateau, Great Basin, and Mojave Desert regions, the park has a unique geography and a variety of life zones that allow for unusual plant and animal diversity. Numerous plant species as well as 289 species of birds, 75 mammals (including 19 species of bat), and 32 reptiles inhabit the park's four life zones: desert, riparian, woodland, and coniferous forest. Zion National Park includes mountains, canyons, buttes, mesas, monoliths, rivers, slot canyons, and natural arches. The lowest point in the park is at Coalpits Wash and the highest peak is at Horse Ranch Mountain. A prominent feature of the park is Zion Canyon, which is long and up to deep. The canyon walls are reddish and tan-colored Navajo Sandstone eroded by the North Fork of the Virgin River. The park attracted 5 million visitors in 2023. Human habitation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile (). The canyon and adjacent rim are contained within Grand Canyon National Park, the Kaibab National Forest, Grand Canyon–Parashant National Monument, the Hualapai, Hualapai Indian Reservation, the Havasupai Indian Reservation and the Navajo Nation. President Theodore Roosevelt was a major proponent of the preservation of the Grand Canyon area and visited it on numerous occasions to hunt and enjoy the scenery. Nearly two billion years of Earth's geological history have been exposed as the Colorado River and its tributaries cut their Stream channel, channels through layer after layer of rock while the Colorado Plateau was Tectonic uplift, uplifted. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Staircase
The Grand Staircase is an immense sequence of sedimentary rock layers that stretches south from Bryce Canyon National Park and Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, through Zion National Park, and into Grand Canyon National Park. Characterization In the 1870s, geologist Clarence Dutton first conceptualized this region as a huge stairway ascending out of the bottom of the Grand Canyon northward with the cliff edge of each layer forming giant steps. Dutton divided this layer cake of Earth history into five steps from the youngest (uppermost) rocks: * Pink Cliffs * Grey Cliffs * White Cliffs * Vermilion Cliffs * Chocolate Cliffs Since then, modern geologists have further divided Dutton's steps into individual rock formations. Formations in the Grand Staircase starting with the youngest (uppermost) rocks: * Claron Formation * Kaiparowits Formation * Wahweap Formation * Straight Cliffs Formation * Tropic Shale * Dakota Sandstone * Carmel Formation * Temple Cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolith
A monolith is a geological feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock, such as some mountains. Erosion usually exposes the geological formations, which are often made of very hard and solid igneous or metamorphic rock. Some monoliths are volcanic plugs, solidified lava filling the vent of an extinct volcano. In architecture, the term has considerable overlap with megalith, which is normally used for prehistory, and may be used in the contexts of rock-cut architecture that remains attached to solid rock, as in monolithic church, or for exceptionally large stones such as obelisks, statues, monolithic columns or large architraves, that may have been moved a considerable distance after quarrying. It may also be used of large glacial erratics moved by natural forces. The word derives, via the Latin , from the Ancient Greek word (), from () meaning "one" or "single" and () meaning "stone". Geological monoliths Large, well-known monoliths include: Africa * Aso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badland
Badlands are a type of dry terrain where softer sedimentary rocks and clay-rich soils have been extensively eroded."Badlands" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 47. They are characterized by steep slopes, minimal vegetation, lack of a substantial regolith, and high drainage density.A.J. Parsons and A.D. Abrahams, Editors (2009) ''Geomorphology of Desert Environments'' (2nd ed.) Springer Science & Business Media Ravines, gullies, buttes, hoodoos and other such geologic forms are common in badlands. Badlands are found on every continent except Antarctica, being most common where there are unconsolidated sediments. They are often difficult to navigate by foot, and are unsuitable for agriculture. Most are a result of natural processes, but destruction of vegetation by overgrazing or pollution can produce anthropogenic badlands. Badlands topography Badlands are characterized by a distinctive badlands topography. This is terrain in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoodoo (geology)
A hoodoo (also called a tent rock, fairy chimney, or earth pyramid) is a tall, thin spire of rock (geology), rock formed by erosion. Hoodoos typically consist of relatively soft rock topped by harder, less easily eroded stone that protects each column from the elements. They generally form within sedimentary rock and volcanic rock formations. Hoodoos range in size from the height of an average human to heights exceeding a 10-story building. Hoodoo shapes are affected by the erosional patterns of alternating hard and softer rock layers. Minerals deposited within different rock types can cause hoodoos to have different colors throughout their height. Etymology In certain regions of western North America these rocky structures are called hoodoos. Hoodoo comes from a Southern Paiute people, Southern Paiute word, oo’doo, which refers to a thing that is scary or inspires fear. Hoodoos form part of some legends of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans in the American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |