|
Genoeconomics
Genoeconomics is an interdisciplinary field of protoscience that aims to combine molecular genetics and economics. Genoeconomics is based on the idea that economic indicators have a genetic basis — that a person's financial behaviour can be traced to their DNA and that genes are related to economic behaviour. As of 2023, the results have been inconclusive. Some minor correlations may have been identified between genetics and economic preferences. History The word ''genoeconomics'' was coined in 2007. The field of economics and the economic indicators used by economists predate the Empiricist Age. Genoeconomics adds biological foundations to these traditional economic indicators. Quantitative genetic data was not available to researchers until the year 2000, when the human genome was sequenced as part of the Human Genome Project. Genetic milestones of the late 20th and early 21st century, such as the sequencing of the human genome, has spurred interest in research combinin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoscience
In the philosophy of science, protoscience is a research field that has the characteristics of an undeveloped science that may ultimately develop into an established science. Philosophers use protoscience to understand the history of science and distinguish protoscience from science and pseudoscience. The word "protoscience" is a hybrid Greek-Latin compound of the roots '' proto-'' + '' scientia'', meaning a first or primeval rational knowledge. Examples of protoscience include alchemy, Wegener's original theory of continental drift and political economy (the predecessor to the modern economic sciences). History Protoscience as a research field with the characteristics of an undeveloped science appeared in the early 20th century. In 1910, Jones described the field of political economy as it began the transition to the modern field of economics: : I confess to a personal predilection for some term such as proto-science, pre-science, or nas-science, to give expression to what I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cigarette Taxes In The United States
In the United States, cigarettes are taxed at both the federal and state levels, in addition to any state and local sales taxes and local cigarette-specific taxes. Cigarette taxation has appeared throughout American history and is still a contested issue today. History Although cigarettes were not popular in the United States until the mid-19th century, the federal government still attempted to implement a tax on tobacco products such as snuff early on in its history. In 1794, secretary of the treasury Alexander Hamilton introduced the first ever federal excise tax on tobacco products. Hamilton's original proposal passed after major modifications, only to be repealed shortly thereafter with an insignificant effect on the federal budget. Even though Hamilton's tax on tobacco failed, tobacco taxation continued to play an important role in American history. On July 1, 1862, the United States Congress passed excise taxes on many items including tobacco. This occurred as a result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdisciplinary Subfields Of Economics
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economics, etc. It is related to an '' interdiscipline'' or an ''interdisciplinary field,'' which is an organizational unit that crosses traditional boundaries between academic disciplines or schools of thought, as new needs and professions emerge. Large engineering teams are usually interdisciplinary, as a power station or mobile phone or other project requires the melding of several specialties. However, the term "interdisciplinary" is sometimes confined to academic settings. The term ''interdisciplinary'' is applied within education and training pedagogies to describe studies that use methods and insights of several established disciplines or traditional fields of study. Interdisciplinarity involves researchers, students, and teachers in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity (statistics)
In statistics, homogeneity and its opposite, heterogeneity, arise in describing the properties of a dataset, or several datasets. They relate to the validity of the often convenient assumption that the statistical properties of any one part of an overall dataset are the same as any other part. In meta-analysis, which combines the data from several studies, homogeneity measures the differences or similarities between the several studies (see also Study heterogeneity). Homogeneity can be studied to several degrees of complexity. For example, considerations of homoscedasticity examine how much the variability of data-values changes throughout a dataset. However, questions of homogeneity apply to all aspects of the statistical distributions, including the location parameter. Thus, a more detailed study would examine changes to the whole of the marginal distribution. An intermediate-level study might move from looking at the variability to studying changes in the skewness. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproducibility
Reproducibility, closely related to replicability and repeatability, is a major principle underpinning the scientific method. For the findings of a study to be reproducible means that results obtained by an experiment or an observational study or in a statistical analysis of a data set should be achieved again with a high degree of reliability when the study is replicated. There are different kinds of replication but typically replication studies involve different researchers using the same methodology. Only after one or several such successful replications should a result be recognized as scientific knowledge. History The first to stress the importance of reproducibility in science was the Anglo-Irish chemist Robert Boyle, in England in the 17th century. Boyle's air pump was designed to generate and study vacuum, which at the time was a very controversial concept. Indeed, distinguished philosophers such as René Descartes and Thomas Hobbes denied the very possibility of vacuum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
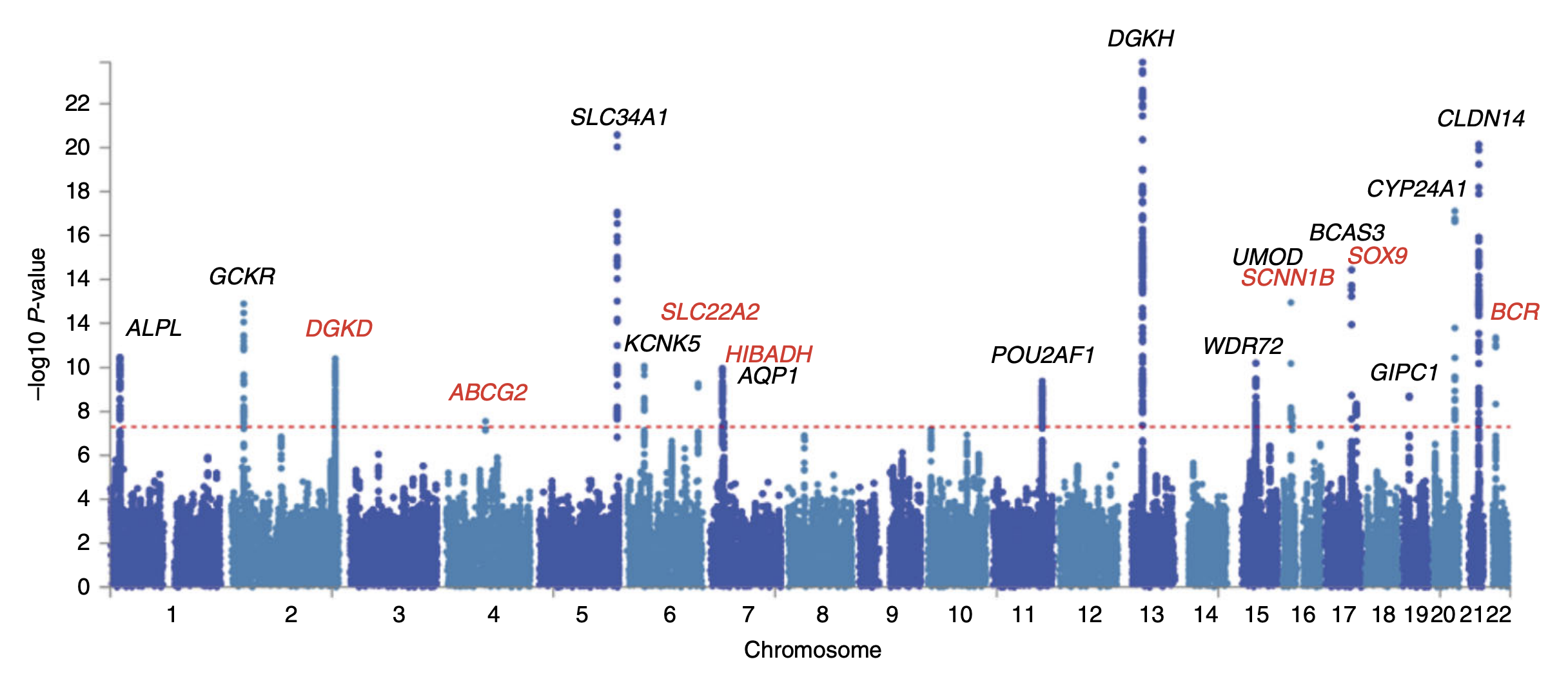
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to Genotype-first approach, genotype-first. Each person gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Economic Review
The ''American Economic Review'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal first published by the American Economic Association in 1911. The current editor-in-chief is Erzo FP Luttmer, a professor of economics at Dartmouth College. The journal is based in Pittsburgh. It is one of the " top five" journals in economics. In 2004, the ''American Economic Review'' began requiring "data and code sufficient to permit replication" of a paper's results, which is then posted on the journal's website. Exceptions are made for proprietary data. Until 2017, the May issue of the ''American Economic Review'', titled the ''Papers and Proceedings'' issue, featured the papers presented at the American Economic Association's annual meeting that January. After being selected for presentation, the papers in the ''Papers and Proceedings'' issue did not undergo a formal process of peer review. Starting in 2018, papers presented at the annual meetings have been published in a separate journal, '' AEA Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causality
Causality is an influence by which one Event (philosophy), event, process, state, or Object (philosophy), object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is at least partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is at least partly dependent on the cause. The cause of something may also be described as the reason for the event or process. In general, a process can have multiple causes,Compare: which are also said to be ''causal factors'' for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysics , metaphysically prior to notions of time and space. Causality is an abstraction that indicates how the world progresses. As such it is a basic concept; it is more apt to be an explanation of other concepts of progression than something to be explained by other more fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Versus Nurture
Nature versus nurture is a long-standing debate in biology and society about the relative influence on human beings of their genetics, genetic inheritance (nature) and the environmental conditions of their development (nurture). The alliterative expression "nature and nurture" in English has been in use since at least the Elizabethan era, Elizabethan period and goes back to medieval French. The complementary combination of the two concepts is an ancient concept (). Nature is what people think of as pre-wiring and is influenced by genetic inheritance and other biological factors. Nurture is generally taken as the influence of external factors after conception e.g. the product of exposure, experience and learning on an individual. The phrase in its modern sense was popularized by the Victorian era, Victorian polymath Francis Galton, the modern founder of eugenics and behavioral genetics when he was discussing the influence of heredity and Social environment, environment on social adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enrico Spolaore
Enrico is both an Italian masculine given name and a surname, Enrico means homeowner, or king, derived from '' Heinrich'' of Germanic origin. It is also a given name in Ladino. Equivalents in other languages are Henry ( English), Henri (French), Enrique (Spanish), Henrique ( Portuguese) and Hendrik (Dutch). Notable people with the name include: Given name * Enrico Albertosi (born 1939), Italian former football goalkeeper * Enrico Alfonso (born 1988), Italian football player * Enrico Alvino (1808–1872), Italian architect and urban designer * Enrico Annoni (born 1966), retired Italian professional footballer * Enrico Arrigoni (1894–1986), Italian individualist anarchist * Enrico Baj (1924–2003), Italian artist and art writer * Enrico Banducci (1922–2007), American impresario * Enrico Barone (1859–1924), Italian economist * Enrico Berlinguer (1923–1984), Italian politician * Enrico Bertaggia (born 1964), Italian former racing driver * Enrico Betti (1823–1892), Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is distinguished from '' genetic variability'', which describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to vary. Genetic diversity serves as a way for populations to adapt to changing environments. With more variation, it is more likely that some individuals in a population will possess variations of alleles that are suited for the environment. Those individuals are more likely to survive to produce offspring bearing that allele. The population will continue for more generations because of the success of these individuals. The academic field of population genetics includes several hypotheses and theories regarding genetic diversity. The neutral theory of evolution proposes that diversity is the result of the accumulation of neutral substitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |