|
Generalized Vector Space Model
The Generalized vector space model is a generalization of the vector space model used in information retrieval. Wong ''et al.'' presented an analysis of the problems that the pairwise orthogonality assumption of the vector space model (VSM) creates. From here they extended the VSM to the generalized vector space model (GVSM). Definitions GVSM introduces term to term correlations, which deprecate the pairwise orthogonality assumption. More specifically, the factor considered a new space, where each term vector ''ti'' was expressed as a linear combination of ''2n'' vectors ''mr'' where ''r = 1...2n''. For a document ''dk'' and a query ''q'' the similarity function now becomes: :sim(d_k,q) = \frac where ''ti'' and ''tj'' are now vectors of a ''2n'' dimensional space. Term correlation t_i \cdot t_j can be implemented in several ways. For an example, Wong et al. uses the term occurrence frequency matrix obtained from automatic indexing as input to their algorithm. The term occurren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Vector Space Model
Vector space model or term vector model is an algebraic model for representing text documents (or more generally, items) as vector space, vectors such that the distance between vectors represents the relevance between the documents. It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, index (search engine), indexing and relevancy rankings. Its first use was in the SMART Information Retrieval System. Definitions In this section we consider a particular vector space model based on the Bag-of-words model, bag-of-words representation. Documents and queries are represented as vectors. :d_j = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) :q = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) Each Dimension (vector space), dimension corresponds to a separate term. If a term occurs in the document, its value in the vector is non-zero. Several different ways of computing these values, also known as (term) weights, have been developed. One of the best known schemes is tf-idf weighting (see the example below). The definition of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the task of identifying and retrieving information system resources that are relevant to an Information needs, information need. The information need can be specified in the form of a search query. In the case of document retrieval, queries can be based on full-text search, full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; it also stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user enters a query into the sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Association For Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, reporting nearly 110,000 student and professional members . Its headquarters are in New York City. The ACM is an umbrella organization for academic and scholarly interests in computer science (informatics). Its motto is "Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession". History In 1947, a notice was sent to various people: On January 10, 1947, at the Symposium on Large-Scale Digital Calculating Machinery at the Harvard computation Laboratory, Professor Samuel H. Caldwell of Massachusetts Institute of Technology spoke of the need for an association of those interested in computing machinery, and of the need for communication between them. ..After making some inquiries during May and June, we believe there is ample interest to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
WordNet
WordNet is a lexical database of semantic relations between words that links words into semantic relations including synonyms, hyponyms, and meronyms. The synonyms are grouped into ''synsets'' with short definitions and usage examples. It can thus be seen as a combination and extension of a dictionary and thesaurus. Its primary use is in automatic natural language processing, text analysis and artificial intelligence applications. It was first created in the English language and the English WordNet database and software tools have been released under a BSD License, BSD style license and are freely available for download. The latest official release from Princeton was released in 2011. Princeton currently has no plans to release any new versions due to staffing and funding issues. New versions are still being released annually through the Open English WordNet website. Until about 2024 an online version was previously available through wordnet.princeton.edu. That version of WordNet h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Linked Data
In computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database. Tim Berners-Lee, director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), coined the term in a 2006 design note about the Semantic Web project. Linked data may also be open data, in which case it is usually described as Linked Open Data. Principles In his 2006 "Linked Data" note, Tim Berners-Lee outlined four principles of linked data, paraphrased along the following lines: #Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) should be used to name and identify individual things. #HTTP URIs should be used to allow these things to be looked up, interpreted, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
DBpedia
DBpedia (from "DB" for "database") is a project aiming to extract structured content from the information created in the Wikipedia project. This structured information is made available on the World Wide Web using OpenLink Virtuoso. DBpedia allows users to semantically query relationships and properties of Wikipedia resources, including links to other related datasets. The project was heralded as "one of the more famous pieces" of the decentralized Linked Data effort by Tim Berners-Lee, one of the Web's pioneers. As of June 2021, DBPedia contained over 850 million triples. Background The project was started by people at the Free University of Berlin and Leipzig University''DBpedia: A Nucleus for a Web of Open Data'', available a in collaboration with OpenLink Software, and is now maintained by people at the University of Mannheim and Leipzig University. The first publicly available dataset was published in 2007. The data is made available under free licenses (CC BY- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
YAGO (database)
YAGO (Yet Another Great Ontology) is an open source knowledge base developed at the Max Planck Institute for Informatics in Saarbrücken. It is automatically extracted from Wikidata and Schema.org. YAGO4, which was released in 2020, combines data that was extracted from Wikidata with relationship designators from Schema.org. The previous version of YAGO, YAGO3, had knowledge of more than 10 million entities and contained more than 120 million facts about these entities. The information in YAGO3 was extracted from Wikipedia (e.g., categories, redirects, infoboxes), WordNet (e.g., synsets, hyponymy), and GeoNames. The accuracy of YAGO was manually evaluated to be above 95% on a sample of facts. To integrate it to the linked data cloud, YAGO has been linked to the DBpedia ontology and to the SUMO ontology. YAGO3 is provided in Turtle and tsv formats. Dumps of the whole database are available, as well as thematic and specialized dumps. It can also be queried through various online ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
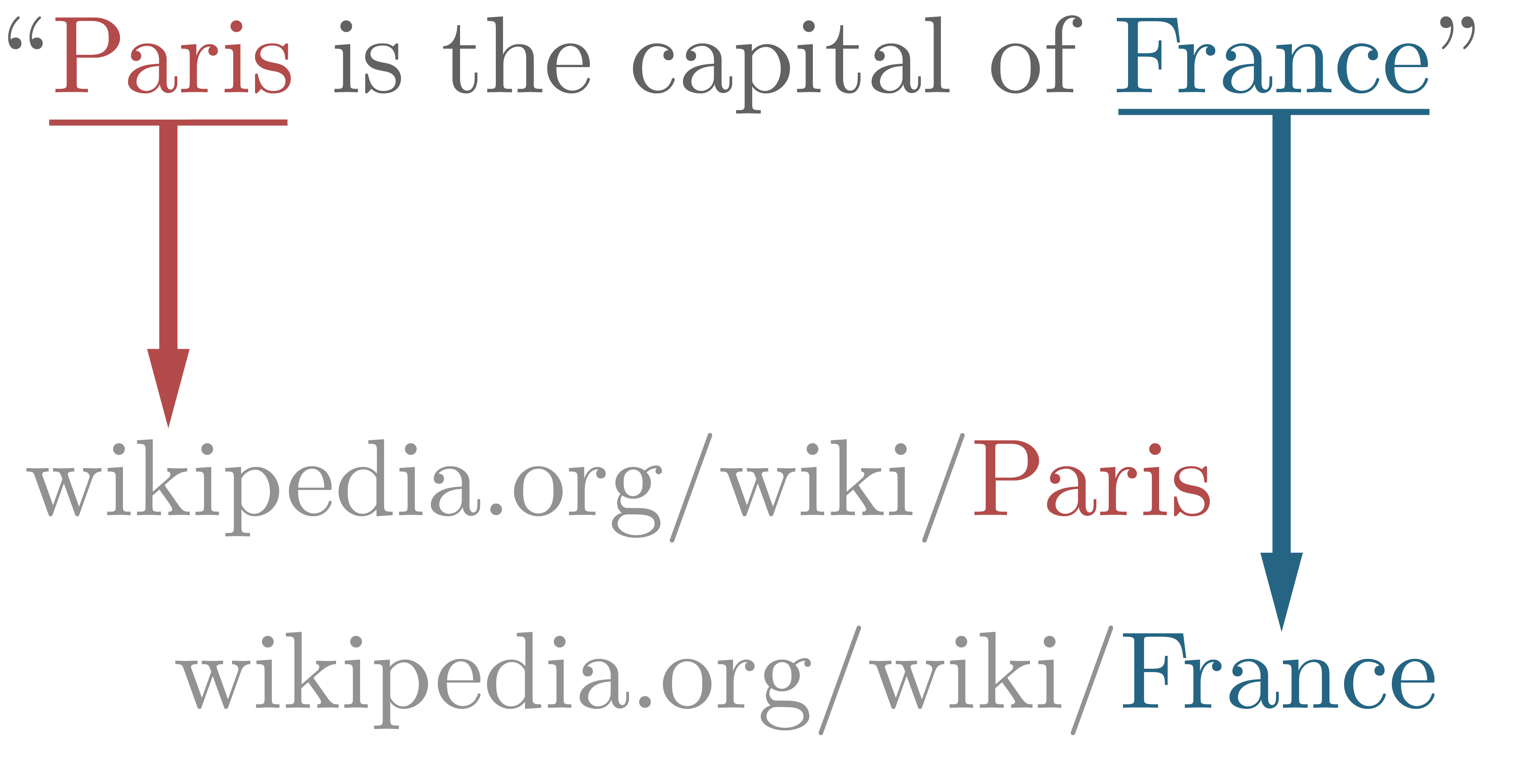 |
Entity Linking
In natural language processing, Entity Linking, also referred to as named-entity disambiguation (NED), named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD), named-entity normalization (NEN), or Concept Recognition, is the task of assigning a unique identity to entities (such as famous individuals, locations, or companies) mentioned in text. For example, given the sentence ''"Paris is the capital of France"'', the main idea is to first identify ''"Paris"'' and ''"France"'' as named entities, and then to determine that ''"Paris"'' refers to the city of Paris and not to Paris Hilton or any other entity that could be referred to as ''"Paris"'' and ''"France"'' to the french country. The Entity Linking task is composed of 3 subtasks. # Named Entity Recognition: Extraction of named entities from a text. # Candidate Generation: For each named entity, select possible candidates from a Knowledge Base (e.g. Wikipedia, Wikidata, DBPedia, ...). # Disambiguation: Choose the correct entit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |